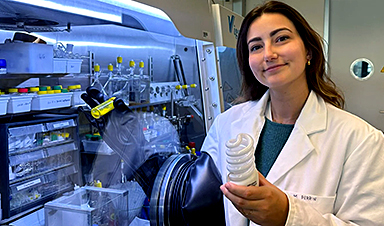
Scientists are developing a process inspired by nature that efficiently recovers europium from old fluorescent lamps. The approach could lead to the long-awaited recycling of rare earth metals.
- A small molecule that naturally serves as a binding site for metals in enzymes also proves useful for separating certain rare earth metals from each other.
- In a proof of concept, the process extracts europium directly from fluorescent powder in used energy-saving lamps in much higher quantities than existing methods.
- The researchers are now working on expanding their approach to other rare earth metals. They are in the process of founding a start-up to put the recycling of these raw materials into practice.
Rare earth metals are not as rare as their name suggests. However, they are indispensable for the modern economy. After all, these 17 metals are essential raw materials for digitalization and the energy transition. They are found in smartphones, computers, screens, and batteries – without them, no electric motor would run and no wind turbine would turn. Because Europe is almost entirely dependent on imports from China, these raw materials are considered to be critical.
However, rare earth metals are also critical because of their extraction. They always occur in compound form in natural ores – but as these elements are chemically very similar, they are difficult to separate. Traditional separation processes are therefore very chemical- and energy-intensive and require several extraction steps. This makes the extraction and purification of these metals expensive, resource- and time-consuming and extremely harmful to the environment.
Innovative Recycling Techniques
“Rare earth metals are hardly ever recycled in Europe,” says Victor Mougel, Professor at the Laboratory of Inorganic Chemistry at ETH Zurich. A team of researchers led by Mougel wants to change this. “There is an urgent need for sustainable and uncomplicated methods for separating and recovering these strategic raw materials from various sources,” says the chemist.
In a study recently published in the journal Nature Communications, the team presents a surprisingly simple method for efficiently separating and recovering the rare earth metal europium from complex mixtures including other rare earth metals.
Inspired by Nature
Marie Perrin, a doctoral student in Mougel’s group and first author of the study, explains: “Existing separation methods are based on hundreds of liquid-liquid extraction steps and are inefficient – the recycling of europium has so far been impractical.” In their study, they show how a simple inorganic reagent can significantly improve separation. “This allows us to obtain europium in a few simple steps – and in quantities that are at least 50 times higher than with previous separation methods,” says Perrin.
The key to this technique can be found in small inorganic molecules featuring four sulfur atoms around tungsten or molybdenum: tetrathiometallates. The researchers were inspired by the world of proteins. Tetrathiometallates are found as a binding site for metals in natural enzymes and are used as active substances against cancer and copper metabolism disorders.
For the first time, tetrathiometallates are now also being used as ligands for the separation of rare earth metals. Their unique redox properties come into play here, reducing europium to its unusual divalent state and thus simplifying separation from the other trivalent rare earth metals.
Rapid recycling of europium from fluorescent lamps. Credit: Marie Perrin / ETH Zurich
Practical Applications and Environmental Impact
“The principle is so efficient and robust that we can apply it directly to used fluorescent lamps without the usual pre-treatment steps,” says Mougel.
Electronic waste is an important but as yet underutilized source of rare earth metals. “If this source were tapped into, the lamp waste that Switzerland currently sends abroad to be disposed of in a landfill could be recycled here in Switzerland instead,” says Mougels. In this way, lamp waste could serve as an urban mine for europium and make Switzerland less dependent on imports.
“Our recycling approach is significantly more environmentally friendly than all conventional methods of extracting rare earth metals from mineral ores.”
— Victor Mougel
In the past, europium was mainly used as phosphor in fluorescent lamps and flat screens, which led to high market prices. As fluorescent lamps are now gradually being phased out, demand has fallen, so that the previous recycling methods for europium are no longer economically viable. More efficient separation strategies are nevertheless desirable and could help to utilize the vast quantities of cheap fluorescent lamp waste whose rare earth metal content is around 17 times higher than in natural ores.
Strategic Recycling Efforts
This makes it all the more urgent to recover rare metals at the end of a product’s life and keep them in circulation – but the recovery rate of rare earth elements in the EU is still below one percent.
In principle, any separation process for rare earth metals can be used both for extraction from ore and for recovery from waste. With their method, however, the researchers are deliberately focussing on recycling the raw materials, as this makes much more ecological and economic sense. “Our recycling approach is significantly more environmentally friendly than all conventional methods for extracting rare earth metals from mineral ores,” says Mougel.
New Ventures and Commercialization
The researchers have patented their technology and are in the process of founding a start-up called REEcover to commercialize it in the future. They are currently working on adapting the separation process for other rare earth metals such as neodymium and dysprosium, which are found in magnets. If this is successful, Marie Perrin wants to build up the start-up after her doctorate and establish the recycling of rare earth metals in practice.
Reference: “Recovery of europium from E-waste using redox active tetrathiotungstate ligands” by Marie A. Perrin, Paul Dutheil, Michael Wörle and Victor Mougel, 3 June 2024, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-48733-z
News
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard it is for scientists to [...]
Are Pesticides Breeding the Next Pandemic? Experts Warn of Fungal Superbugs
Fungicides used in agriculture have been linked to an increase in resistance to antifungal drugs in both humans and animals. Fungal infections are on the rise, and two UC Davis infectious disease experts, Dr. George Thompson [...]