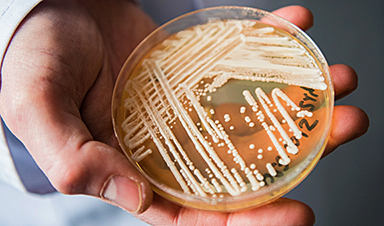
The fungus, a type of yeast called Candida auris, or C. auris, can cause severe illness in people with weakened immune systems.
A drug-resistant and potentially deadly fungus has been spreading rapidly through U.S. health care facilities, a new government study finds.
The fungus, a type of yeast called Candida auris, or C. auris, can cause severe illness in people with weakened immune systems. The number of people diagnosed with infections — as well as the number of those who were found through screening to be carrying C. auris — has been rising at an alarming rate since it was first reported in the U.S., researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported Monday.
The increases, “especially in the most recent years, are really concerning to us,” the study’s lead author, Dr. Meghan Lyman, chief medical officer in the CDC’s Mycotic Diseases Branch, said in an interview. “We’ve seen increases not just in areas of ongoing transmission, but also in new areas.”
The CDC’s new warning, published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, comes as the Mississippi Department of Health is fighting a growing outbreak of the fungus. Since November, at least 12 people have been infected with C. auris with four “potentially associated deaths,” the state’s epidemiologist Dr. Paul Byers, said in an email.
There has been ongoing transmission at two long-term care facilities, although cases have been identified at several other facilities in the state.
“Unfortunately, multi-drug resistant organisms such as C. auris have become more prevalent among our highest risk individuals, such as residents in long-term care facilities,” Byers said.
The fungus can be found on the skin and throughout the body, according to the CDC. It’s not a threat to healthy people, but about one-third of people who become sick with C. auris die.
In the CDC report, researchers analyzed state and local health department data on people sickened by the fungus from 2016 through Dec. 31, 2021, as well as those who were “colonized,” meaning they were not ill but were carrying it on their bodies with the potential of transmitting it to others who might be more vulnerable to it.
The number of infections increased by 59%, to 756, from 2019 to 2020 and then by an additional 95%, to 1,471, in 2021.
The researchers also found that the incidence of people not infected with the fungus but colonized by it increased by 21% in 2020, compared to 2019, and by 209% in 2021, with an increase to 4,041 in 2021 compared to 1,310 in 2020.
C. auris has now been detected in more than half of U.S. states, the new study found.
Most concerning was the increasing numbers of fungus samples resistant to the common treatments for it. Lyman hopes the paper will put C. auris on health care providers’ radar and spur facilities to practice “good infection control.”
The new findings are “worrisome,” said Dr. Waleed Javaid, an epidemiologist and an infectious disease expert and director of infection prevention and control at Mount Sinai Downtown in New York.
“But we don’t want people who watched ‘The Last of Us’ to think we’re all going to die,” Javaid said. “This is an infection that occurs in extremely ill individuals who are usually sick with a lot of other issues.”
Even if C. auris moves beyond health care facilities and into communities, it’s unlikely to become a problem for healthy people who do not have invasive medical devices, such as catheters, inserted into their blood vessels, Javaid said.
The main problem is preventing the fungus from spreading to patients in hospital intensive care units, Javaid said. Unfortunately C. auris can colonize not only people who come in contact with the fungus, but also patient rooms.
“By its nature it has an extreme ability to survive on surfaces,” he said. “It can colonize walls, cables, bedding, chairs. We clean everything with bleach and UV light.”
While the fungus was first identified in 2009 in Asia, scientists have determined that C. auris first appeared around the world about a decade earlier, after they re-examined older data and discovered instances where C. auris had been mistakenly identified as a different fungus, Dr. Graham Snyder, medical director of infection prevention at University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, said in an interview.
“It’s the pattern we’ve observed with these types of pathogens,” he said. “Often they start out extremely rare, then they emerge in more and more places and become widespread.”
It’s important to stop the pathogen so it doesn’t spread beyond hospitals and long-term facilities like the drug-resistant bacteria MRSA did, Snyder said.
“It’s not unusual to see MRSA in the community now,” Snyder said. “Will that happen with C. auris? I don’t know. That’s partly why the CDC is raising the alarm.”
News
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]