Peritoneal cancer is difficult to treat and has a poor survival prognosis. But a new and effective nanomedicine delivery system is offering some hope.
The work from which NaDeNo has evolved started in 2012. Initial research at SINTEF yielded promising results, and now both the technology and its patents are being spun off from the research institute and into a separate company.
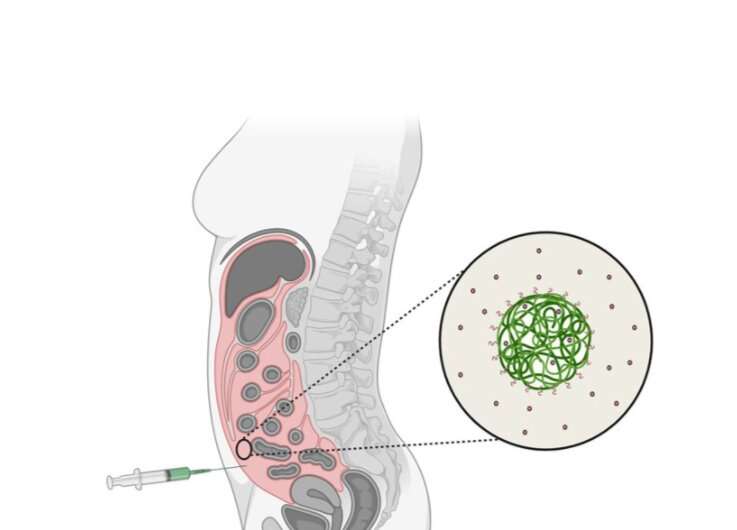
The technology makes it possible to embed large volumes of an active cancer drug in nanoparticle carriers. These carriers are then injected into the peritoneal cavity, enabling the drug to be evenly distributed and thus delivered to all the tumors developed in the peritoneum.
Delivering a large dose the tumors
Experiments using mice and rats demonstrate that the nanoparticles accumulate preferentially in the tumors, thus releasing a much greater proportion of the drug to cancer cells than they do to healthy cells.
“A solid foundation created by research carried out at SINTEF has enabled progress within the development of this technology,” says Ýrr Mørch, Chief Technology Officer (CTO) and co-founder at NaDeNo. “If we get the results we’re hoping for, the technology may represent a significant step forward, not only for the future treatment of peritoneal cancer, but also for other illnesses,” he says.
However, in order to make the technology accessible to cancer patients, it first has to be tested thoroughly and then manufactured at larger scales. It must be both safe and effective.
“We’re now getting ready to start pre-clinical trials,” says Mørch. “This phase will take some years, during which we will carry out a number of animal studies using standardized methods. We have to test the product thoroughly and also demonstrate that the drug is safe and can be manufactured with appropriate medical purity,” he says.
The company will then apply to carry out clinical trials on cancer patients.
“Nanoparticles are now being manufactured at laboratory scale at SINTEF, but we have to show that we can produce these at an industrial scale,” says Mørch. “This must be carried out by specialist manufacturers, but to do this we have to go overseas,” he says. “A lot of research remains to be completed before the technology can be applied on cancer patients. We are still at an early phase,” he says.
Difficult-to-treat peritoneal cancer
Peritoneal cancer is difficult to discover and to treat. It often arises as a result of the spread of cancer cells from other organs such as the ovaries or digestive tract. It gives few symptoms and is often discovered too late. Survival prognoses are usually poor.
Current treatment approaches are yet to be standardized, and they tend to be life-extending rather than curative.
Patients who gets this diagnosis are commonly treated by surgical removal of all visible cancer tissue followed by chemotherapy that is administered either locally, or to the entire body via the blood. The problem with this approach is that the drug either has too short residence time in the peritoneal cavity, or fails to reach the cavity and the cancer cells.
“This is due to a barrier that exists between the blood and the peritoneum,” says Annbjørg Falck, who is CEO and co-founder of NaDeNo.
In order for the drug to work effectively it has to be soluble in water. However, many chemotherapeutic treatments involve small-molecule drugs that are poorly soluble in water. Such treatments are thus difficult to deliver targeted at tumor sites.
Small particles with an enormous surface area
NaDeNo is aiming to address this by encapsulating the drug in tiny nanoparticle carriers. The nanoparticles are injected directly into the peritoneal cavity in a solution that ensures that they are distributed uniformly and reach all the tumors in the peritoneum. They then release the drug at the tumor sites.
“This drug is poorly soluble in water when it is ‘naked’ but becomes highly soluble when embedded in the nanocapsules developed by SINTEF,” says Mørch. “The capsules help the drug to reach the correct location. When the particles degrade in the body the drug is released,” she says.
In experiments with mice and rats, the researchers have observed that the nanoparticles accumulate in the tumors located in the peritoneum. This enables a greater proportion of the drug to reach the cancer cells and less is wasted on the healthy cells.
“The uniform distribution of the drug throughout the peritoneal cavity, combined with the longer residence time, demonstrates that the animals appear to tolerate the drug better when this delivery system is used,” says Mørch.
There are also other benefits.
“The size of the nanoparticles means that they have a large surface area in relation to their volume,” he says. “As many as 10¹² particles are contained in every milliliter of solution—literally billions of particles. This makes an enormous surface area available for interaction between the particles and their surroundings, and not least for attachment to the various cells and tissues in the human body,” says Mørch.
This enables the nanoparticles to deliver large amounts of the drug to the tumors.
The same material is used to close wounds, since it will gradually degrad in the body. Credit: SINTEF/NaDeNo
An effective anti-cancer cytotoxin
The product currently being developed by NaDeNo can thus be described as a nanotechnological platform for the encapsulation of non-water soluble (hydrophobic) drugs in nanoparticle carriers. There is currently great demand for the effective delivery of such drugs.
“If we succeed with our first product, it will enable us to offer a delivery technology that can benefit companies in both the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors,” says Mørch.
The cytotoxin that the company is using is called cabazitaxel. It is very effective, but current methods of delivery also cause major side effects.
“Cabazitaxel is currently used only for the treatment of prostate cancer,” says Annbjørg Falck. “The active component is highly toxic and is poorly soluble in water. For this reason, there are limits on how much of the drug can be administered without causing serious side effects,” she says.
The poor water solubility of cabazitaxel makes it difficult to develop nanoparticle delivery systems for the drug. NaDeNo thus has to demonstrate that embedding the drug in nanoparticles offers better efficacy compared to current treatments for patients suffering from cancer metastasis to the peritoneal cavity.
“Cabazitaxel is very powerful and exhibits less resistance development than other comparable cytotoxins,” says Falck. “A new and optimized delivery method will thus enable many more patients to benefit from this effective drug,” she says.
Multiple applications
Up until now, SINTEF’s development of its nanoparticle technology has been carried out in close collaboration with the Norwegian Radium Hospital in Oslo, with expertise in peritoneal cancer treatments.
This collaboration has provided NaDeNo’s first development candidate with a key clinical foundation and has enabled the company to obtain access to representative mouse models of human cancers, with very promising results.
“The Radium Hospital treats patients suffering from metastasis to the peritoneal cavity according to high international standards,” says Mørch. “The method is called hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC), where all visible tumor tissue is surgically removed from the cavity prior to local treatment with heated chemotherapy. In some cases, better efficacy is achieved by this methode. However, the treatment is very strenuous for the patients, who are very ill. The cytotoxin has a short residence time in the peritoneum and distributes rapidly to other parts of the body.
Kjersti Flatmark is a Professor and Senior Consultant in gastrosurgery at the Norwegian Radium Hospital and speaks very positively about the collaboration with NaDeNo and SINTEF.
“Metastasis to the peritoneum is difficult to treat and comes with a very poor prognosis. Unfortunately, our current treatment approaches very rarely cure our patients, so it is clearly a need for better treatment options. It has been exciting to be part of this collaborative effort, firstly with SINTEF and now with NaDeNo. Up to now we have focused on the development and testing of the technology in model systems, and are hoping that in the long term, the delivery of cytotoxins in nanoparticle carriers will contribute towards better treatment efficacy, enabling many more patients to enjoy a full recovery,” she says.
Initially, NaDeNo is focusing on a group comprising 37,000 patients annually in Europe and the U.S. The company also has ambitions to apply the technology to a greater number of patients.
“If the first drug delivery system works, this will be a good indication that we have a technology that can be used for the treatment of many types of cancer that are currently difficult to treat,” says Mørch.
In August 2022, NaDeNo’s first development candidate was accepted by the NCI as a promising nanomedicine. The NCI carries out a standardized preclinical test program free of charge, where the aim is to accelerate the development of nanomedicines that have the potential to treat patients with life-threatening diseases for which there is currently a pressing medical demand to find a cure.
“Inclusion in one of the NCI’s preclinical test programs is a key milestone for us, and offers valuable recognition of our development program,” says Annbjørg Falck. The criteria for inclusion are quite strict, so this demonstrates that the work carried out by SINTEF over many years is of a high international standard,” she says.
Heidi Johnsen is a research manager for the team at SINTEF that participated in the development of the NaDeNo technology platform, and is optimistic for the future of the spin-off company.
“At SINTEF we work towards developing technology for a better society and I am proud of what we have achieved so far. We will continue to do the best we can in terms of effective collaboration to ensure that NaDeNo is successful with its product development,” she says.
“Our current strategy is to secure sound future investment with the aim of bringing our first product to the market and to patients, while at the same time continuing to develop our technological platform,” says Falck. “In this connection, we also want to forge links with partners in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical sectors that are looking for new and better ways of delivering poorly water-soluble drugs,” she concludes.
News
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]





















