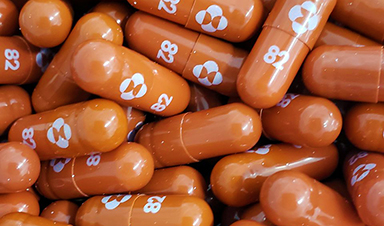
Nov 4 (Reuters) – Britain on Thursday became the first country in the world to approve a potentially game-changing COVID-19 antiviral pill jointly developed by U.S.-based Merck & Co Inc (MRK.N) and Ridgeback Biotherapeutics, in a boost to the fight against the pandemic.
Britain’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) recommended the drug, molnupiravir, for use in people with mild to moderate COVID-19 and at least one risk factor for developing severe illness, such as obesity, older age diabetes, and heart disease.
It will be administered as soon as possible following a positive COVID-19 test and within five days of the onset of symptoms, the regulator said, citing clinical data.
The green light is the first for an oral antiviral treatment for COVID-19 and the first for a COVID-19 drug that will be administered widely in the community. U.S. advisers will meet on Nov. 30 to review the drug’s safety and efficacy data and vote on whether molnupiravir should be authorized. Read more
The pill, which will be branded as Lagevrio in Britain, is designed to introduce errors into the genetic code of the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 and is taken twice a day for five days.
Drugs in the same class as molnupiravir have been linked to birth defects in animal studies. Merck, known as MSD outside of the United States and Canada, has said animal testing shows that molnupiravir is safe, but the data have not yet been made public.
Treatments to tackle the pandemic, which has killed more than 5.2 million people worldwide, have so far focused mainly on vaccines. Other options, including Gilead’s (GILD.O) infused antiviral remdesivir and generic steroid dexamethasone, are generally only given after a patient has been hospitalised.
Merck’s Molnupiravir has been closely watched since data last month showed it could halve the chances of dying or being hospitalised for those most at risk of developing severe COVID-19 when given early in the illness. read more
Professor Stephen Powis, national medical director for the National Health Service (NHS) in England, said the drug would be administered to patients at higher risk of complications as Britain heads into one of the most challenging winters ever.
A wider rollout will follow if it is clinically and cost effective in reducing hospitalisations and death, he added.
Many other big economies, including Germany, France and Israel, have either retained some basic COVID-19 measures like mask mandates or reintroduced them in response to rising cases.
The UK government has said its focus remains on administering vaccine boosters and inoculating 12- to 15-year-olds.
“With no compromises on quality, safety and effectiveness, the public can trust that the MHRA has conducted a robust and thorough assessment of the data (on molnupiravir),” MHRA chief June Raine said in a statement.
Last month, Britain agreed a deal with Merck to secure 480,000 courses of molnupiravir.
Professor Penny Ward, an independent pharmaceutical physician, welcomed the approval, but said the NHS needed to outline its plans for rollout and cautioned that supplies were likely to be tight given the strong global demand.
“Comments made by Mr Javid today suggest that it may be made available via a clinical trial, presumably to investigate its effectiveness in vaccinated patients with breakthrough infections, as the original study incorporated unvaccinated adults,” she said.
If given to everyone becoming unwell, the nearly half a million courses would not last very long given the more than 40,000 current daily case rate, she said.
“We are now working across government and the NHS to urgently get this treatment to patients initially through a national study so we can collect more data on how antivirals work in a mostly vaccinated population,” UK vaccines minister Maggie Throup told parliament.
Pressures
The speedy approval in Britain, which was also the first Western country to approve a COVID-19 vaccine, comes as it struggles to tame soaring infections.
Britain has about 40,000 daily cases of COVID-19, according to the latest seven-day average. That is second only to the roughly 74,000 a day in the United States, which has five times more people, and has fuelled criticism of the government’s decision to abandon most pandemic-related restrictions
Data released on Wednesday night showed COVID-19 prevalence in England hit its highest level on record last month, led by a high number of cases in children and a surge in the south-west of the country. read more
Pressure is growing on the government to implement its “Plan B” aimed at protecting the NHS from unsustainable demands, involving mask mandates, vaccine passes and work-from-home orders.
News
Scientists Discover Why Some COVID Survivors Still Can’t Taste Food Years Later
A new study provides the first direct biological evidence explaining why some people continue to experience taste loss long after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers have uncovered specific biological changes in taste buds that could help [...]
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]