A team of international researchers led by Prof Martin Hegner, Investigator in CRANN and Trinity’s School of Physics developed an automated diagnostic platform that indicates bleeding – and thrombotic risks in one drop of blood within seconds (Nanoscale, “Towards personalised rapid label free miRNA detection for cancer and liver injury diagnostics in cell lysates and blood based samples”).
They exploit micro-resonators for real-time measurements of the evolving blood plasma clot strength. Along with the clinically measured clotting time, other parameters, from specific factor deficiency to global coagulation parameters to assess fibrinolysis, can be extracted.
These technical developments now open up the possibility to introduce a miniaturized global haemostasis assay with capability to fine-tune anti-coagulation therapies.
In collaboration with the multinational Hoffman-la-Roche they report a novel strategy for quick, reliable and quantitative diagnostics of expression patterns of non-coding short RNA in blood plasma or cell cultures. They directly detect label-free specific miRNA biomarkers relevant to cancer and adverse drug effects in blood-based samples (right image).
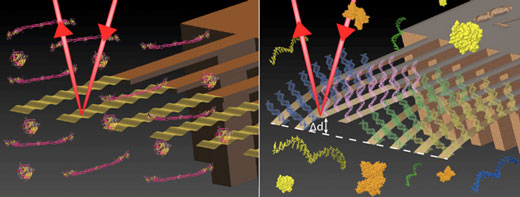
Image Credit: CRANN
News This Week
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]














Leave A Comment