Researchers have developed an artificial intelligence which can differentiate cancer cells from normal cells, as well as detect the very early stages of viral infection inside cells. The findings, published today in a study in the journal Nature Machine Intelligence, pave the way for improved diagnostic techniques and new monitoring strategies for disease. The researchers are from the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU), Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC) and the Fundación Biofisica Bizkaia (FBB, located in Biofisika Institute).
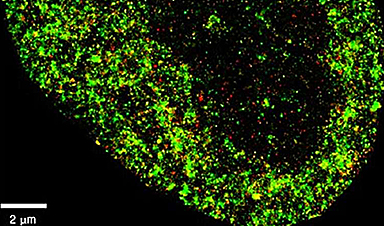
The tool, AINU (AI of the NUcleus), scans high-resolution images of cells. The images are obtained with a special microscopy technique called STORM, which creates a picture that captures many finer details than what regular microscopes can see. The high-definition snapshots reveal structures at nanoscale resolution.
A nanometer (nm) is one-billionth of a meter, and a strand of human hair is about 100,000nm wide. The AI can detect rearrangements inside cells as small as 20nm, or 5,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair. These alterations are too small and subtle for human observers to find with traditional methods alone.
“The resolution of these images is powerful enough for our AI to recognize specific patterns and differences with remarkable accuracy, including changes in how DNA is arranged inside cells, helping spot alterations very soon after they occur. We think that, one day, this type of information can buy doctors valuable time to monitor disease, personalize treatments and improve patient outcomes,” says ICREA Research Professor Pia Cosma, co-corresponding author of the study and researcher at the Centre for Genomic Regulation in Barcelona.
‘Facial recognition’ at the molecular level
AINU is a convolutional neural network, a type of AI specifically designed to analyze visual data like images. Examples of convolutional neural networks include AI tools which enable users to unlock smartphones with their face, or others used by self-driving cars to understand and navigate environments by recognizing objects on the road.
In medicine, convolutional neural networks are used to analyze medical images like mammograms or CT scans and identify signs of cancer that might be missed by the human eye. They can also help doctors detect abnormalities in MRI scans or X-ray images, helping make a faster and more accurate diagnosis.
AINU detects and analyzes tiny structures inside cells at the molecular level. The researchers trained the model by feeding it with nanoscale-resolution images of the nucleus of many different types of cells in different states. The model learned to recognize specific patterns in cells by analyzing how nuclear components are distributed and arranged in three-dimensional space.
For example, cancer cells have distinct changes in their nuclear structure compared to normal cells, such as alterations to how their DNA is organized or the distribution of enzymes within the nucleus. After training, AINU could analyze new images of cell nuclei and classify them as cancerous or normal based on these features alone.
The nanoscale resolution of the images enabled the AI to detect changes in a cell’s nucleus as soon as one hour after it was infected by the herpes simplex virus type-1. The model could detect the presence of the virus by finding slight differences in how tightly DNA is packed, which happens when a virus starts to alter the structure of the cell’s nucleus.
“Our method can detect cells that have been infected by a virus very soon after the infection starts. Normally, it takes time for doctors to spot an infection because they rely on visible symptoms or larger changes in the body. But with AINU, we can see tiny changes in the cell’s nucleus right away,” says Ignacio Arganda-Carreras, co-corresponding author of the study and Ikerbasque Research Associate at UPV/EHU and affiliated with the FBB-Biofisika Institute and the DIPC in San Sebastián/Donostia.
“Researchers can use this technology to see how viruses affect cells almost immediately after they enter the body, which could help in developing better treatments and vaccines. In hospitals and clinics, AINU could be used to quickly diagnose infections from a simple blood or tissue sample, making the process faster and more accurate,” adds Limei Zhong, co-first author of the study and researcher at the Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (GDPH) in Guangzhou, China.
Laying the groundwork for clinical readiness
The researchers have to overcome important limitations before the technology is ready to be tested or deployed in a clinical setting. For example, STORM images can only be taken with specialized equipment normally only found in biomedical research labs. Setting up and maintaining the imaging systems required by the AI is a significant investment in both equipment and technical expertise.
Another constraint is that STORM imaging typically analyzes only a few cells at a time. For diagnostic purposes, especially in clinical settings where speed and efficiency are crucial, doctors would need to capture many more numbers of cells in a single image to be able to detect or monitor a disease.
“There are many rapid advances in the field of STORM imaging which mean that microscopes may soon be available in smaller or less specialized labs, and eventually, even in the clinic. The limitations of accessibility and throughput are more tractable problems than we previously thought and we hope to carry out preclinical experiments soon,” says Dr. Cosma.
Though clinical benefits might be years away, AINU is expected to accelerate scientific research in the short term. The researchers found the technology could identify stem cells with very high precision. Stem cells can develop into any type of cell in the body, an ability known as pluripotency. Pluripotent cells are studied for their potential in helping repair or replace damaged tissues.
AINU can make the process of detecting pluripotent cells quicker and more accurate, helping make stem cell therapies safer and more effective.
“Current methods to detect high-quality stem cells rely on animal testing. However, all our AI model needs to work is a sample that is stained with specific markers that highlight key nuclear features. As well as being easier and faster, it can accelerate stem cell research while contributing to the shift in reducing animal use in science,” says Davide Carnevali, first author of the research and researcher at the CRG.
More information: A deep learning method that identifies cellular heterogeneity using nanoscale nuclear features, Nature Machine Intelligence (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s42256-024-00883-x
News
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard it is for scientists to [...]
Are Pesticides Breeding the Next Pandemic? Experts Warn of Fungal Superbugs
Fungicides used in agriculture have been linked to an increase in resistance to antifungal drugs in both humans and animals. Fungal infections are on the rise, and two UC Davis infectious disease experts, Dr. George Thompson [...]