AI algorithms outperformed traditional clinical risk models in a large-scale study, predicting five-year breast cancer risk more accurately. These models use mammograms as the single data source, offering potential advantages in individualizing patient care and enhancing prediction efficiency.
In a large study of thousands of mammograms, artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms outperformed the standard clinical risk model for predicting the five-year risk for breast cancer. The results of the study were published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
A woman’s risk of breast cancer is typically calculated using clinical models such as the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium (BCSC) risk model, which uses self-reported and other information on the patient—including age, family history of the disease, whether she has given birth, and whether she has dense breasts—to calculate a risk score.

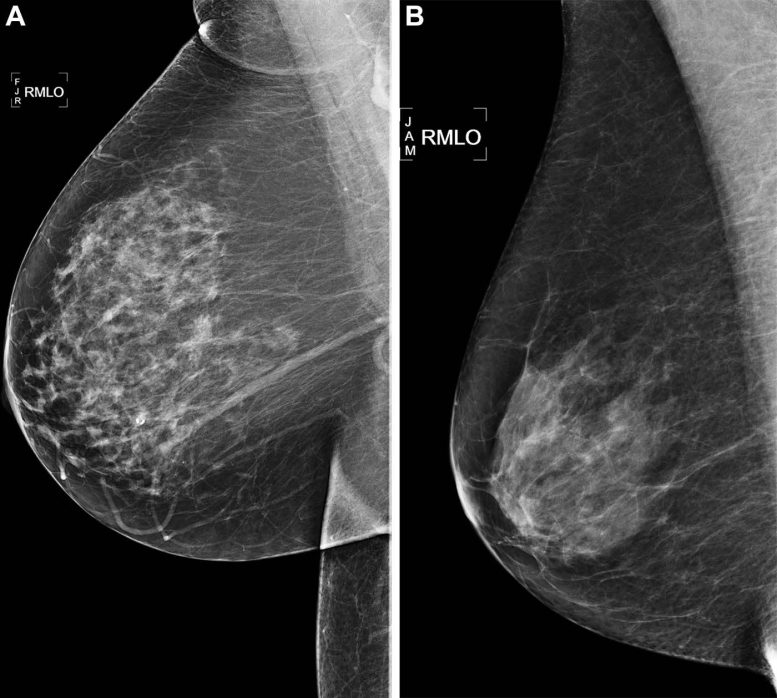
Right medial lateral oblique (RMLO) screening mammograms show negative results from 2016 in (A) a 73-year-old woman with Mirai artificial intelligence (AI) risk score with more than 90th percentile risk who developed right breast cancer in 2021 at 5 years of follow-up and (B) a 73-year-old woman with Mirai AI risk score with less than 10th percentile risk who did not develop cancer at 5 years after 5 years of follow-up. Credit: Radiological Society of North America
“We selected from the entire year of screening mammograms performed in 2016, so our study population is representative of communities in Northern California,” Dr. Arasu said.
The researchers divided the five-year study period into three time periods: interval cancer risk, or incident cancers diagnosed between 0 and 1 years; future cancer risk, or incident cancers diagnosed from between one and five years; and all cancer risk, or incident cancers diagnosed between 0 and 5 years.
Using the 2016 screening mammograms, risk scores for breast cancer over the five-year period were generated by five AI algorithms, including two academic algorithms used by researchers and three commercially available algorithms. The risk scores were then compared to each other and to the BCSC clinical risk score.
“All five AI algorithms performed better than the BCSC risk model for predicting breast cancer risk at 0 to 5 years,” Dr. Arasu said. “This strong predictive performance over the five-year period suggests AI is identifying both missed cancers and breast tissue features that help predict future cancer development. Something in mammograms allows us to track breast cancer risk. This is the ‘black box’ of AI.”
“[AI] is a tool that could help us provide personalized, precision medicine on a national level..” — Vignesh A. Arasu, M.D., Ph.D.
Some of the AI algorithms excelled at predicting patients at high risk of interval cancer, which is often aggressive and may require a second reading of mammograms, supplementary screening, or short-interval follow-up imaging. When evaluating women with the highest 10% risk as an example, AI predicted up to 28% of cancers compared to 21% predicted by BCSC.
Even AI algorithms trained for short time horizons (as low as 3 months) were able to predict the future risk of cancer up to five years when no cancer was clinically detected by screening mammography. When used in combination, the AI and BCSC risk models further improved cancer prediction.
“We’re looking for an accurate, efficient and scalable means of understanding a women’s breast cancer risk,” Dr. Arasu said. “Mammography-based AI risk models provide practical advantages over traditional clinical risk models because they use a single data source: the mammogram itself.”
Dr. Arasu said some institutions are already using AI to help radiologists detect cancer on mammograms. A person’s future risk score, which takes seconds for AI to generate, could be integrated into the radiology report shared with the patient and their physician.
“AI for cancer risk prediction offers us the opportunity to individualize every woman’s care, which isn’t systematically available,” he said. “It’s a tool that could help us provide personalized, precision medicine on a national level.”
Reference: “Comparison of Mammography AI Algorithms with a Clinical Risk Model for 5-year Breast Cancer Risk Prediction: An Observational Study” by Vignesh A. Arasu, Laurel A. Habel, Ninah S. Achacoso, Diana S. M. Buist, Jason B. Cord, Laura J. Esserman, Nola M. Hylton, M. Maria Glymour, John Kornak, Lawrence H. Kushi, Donald A. Lewis, Vincent X. Liu, Caitlin M. Lydon, Diana L. Miglioretti, Daniel A. Navarro, Albert Pu, Li Shen, Weiva Sieh, Hyo-Chun Yoon and Catherine Lee, 6 June 2023, Radiology.
DOI: 10.1148/radiol.222733
News
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]





















