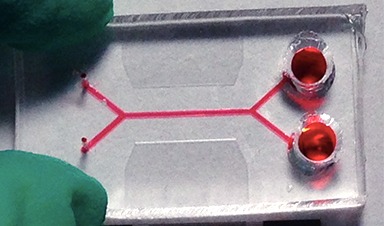
Circulating tumour cells (CTCs) are cancer cells that escape from primary tumour sites and enter the bloodstream. This metastasis is responsible for the majority of deaths from cancer. Monitoring the level of CTC levels in blood is thus important but has proved difficult to do. A team of researchers in China and the US has now developed a new way to isolate these cells using a technique called size-amplified acoustofluidics in which the CTCs selectively bind to microbeads.
The bound cancer cells are significantly different in terms of size and physical properties (they are stiffer, for example) compared to normal cells, explain the researchers led by Feng Guo of Indiana University in Bloomington in the US. This means that their acoustic radiation force is a 100-fold higher than that of bare CTCs or normal blood cells. They can thus be efficiently sorted from blood using microbeads (the “size-amplifiers”) in a travelling acoustic wave microfluidic device, and then released from the amplifiers by being degraded with enzymes.
The technique is 77% efficient and produces CTCs with a 96% yield.
Image Credit: Huiqin Liu
News This Week
Scientists Discover Simple Saliva Test That Reveals Hidden Diabetes Risk
Researchers have identified a potential new way to assess metabolic health using saliva instead of blood. High insulin levels in the blood, known as hyperinsulinemia, can reveal metabolic problems long before obvious symptoms appear. It is [...]
One Nasal Spray Could Protect Against COVID, Flu, Pneumonia, and More
A single nasal spray vaccine may one day protect against viruses, pneumonia, and even allergies. For decades, scientists have dreamed of creating a universal vaccine capable of protecting against many different pathogens. The idea [...]
New AI Model Predicts Cancer Spread With Incredible Accuracy
Scientists have developed an AI system that analyzes complex gene-expression signatures to estimate the likelihood that a tumor will spread. Why do some tumors spread throughout the body while others remain confined to their [...]
Scientists Discover DNA “Flips” That Supercharge Evolution
In Lake Malawi, hundreds of species of cichlid fish have evolved with astonishing speed, offering scientists a rare opportunity to study how biodiversity arises. Researchers have identified segments of “flipped” DNA that may allow fish to adapt rapidly [...]
Our books now available worldwide!
Online Sellers other than Amazon, Routledge, and IOPP Indigo Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artifcial Intelligence Global Health Care Equivalency In The Age Of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine And Artificial [...]
Scientists Discover Why Some COVID Survivors Still Can’t Taste Food Years Later
A new study provides the first direct biological evidence explaining why some people continue to experience taste loss long after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers have uncovered specific biological changes in taste buds that could help [...]
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]













Leave A Comment