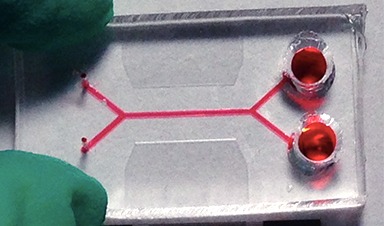
Circulating tumour cells (CTCs) are cancer cells that escape from primary tumour sites and enter the bloodstream. This metastasis is responsible for the majority of deaths from cancer. Monitoring the level of CTC levels in blood is thus important but has proved difficult to do. A team of researchers in China and the US has now developed a new way to isolate these cells using a technique called size-amplified acoustofluidics in which the CTCs selectively bind to microbeads.
The bound cancer cells are significantly different in terms of size and physical properties (they are stiffer, for example) compared to normal cells, explain the researchers led by Feng Guo of Indiana University in Bloomington in the US. This means that their acoustic radiation force is a 100-fold higher than that of bare CTCs or normal blood cells. They can thus be efficiently sorted from blood using microbeads (the “size-amplifiers”) in a travelling acoustic wave microfluidic device, and then released from the amplifiers by being degraded with enzymes.
The technique is 77% efficient and produces CTCs with a 96% yield.
Image Credit: Huiqin Liu
News This Week
New Once-a-Week Shot Promises Life-Changing Relief for Parkinson’s Patients
A once-a-week shot from Australian scientists could spare people with Parkinson’s the grind of taking pills several times a day. The tiny, biodegradable gel sits under the skin and releases steady doses of two [...]
Weekly injectable drug offers hope for Parkinson’s patients
A new weekly injectable drug could transform the lives of more than eight million people living with Parkinson's disease, potentially replacing the need for multiple daily tablets. Scientists from the University of South Australia [...]
Most Plastic in the Ocean Is Invisible—And Deadly
Nanoplastics—particles smaller than a human hair—can pass through cell walls and enter the food web. New research suggest 27 million metric tons of nanoplastics are spread across just the top layer of the North [...]
Repurposed drugs could calm the immune system’s response to nanomedicine
An international study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has identified a promising strategy to enhance the safety of nanomedicines, advanced therapies often used in cancer and vaccine treatments, [...]
Nano-Enhanced Hydrogel Strategies for Cartilage Repair
A recent article in Engineering describes the development of a protein-based nanocomposite hydrogel designed to deliver two therapeutic agents—dexamethasone (Dex) and kartogenin (KGN)—to support cartilage repair. The hydrogel is engineered to modulate immune responses and promote [...]
New Cancer Drug Blocks Tumors Without Debilitating Side Effects
A new drug targets RAS-PI3Kα pathways without harmful side effects. It was developed using high-performance computing and AI. A new cancer drug candidate, developed through a collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), BridgeBio Oncology [...]
Scientists Are Pretty Close to Replicating the First Thing That Ever Lived
For 400 million years, a leading hypothesis claims, Earth was an “RNA World,” meaning that life must’ve first replicated from RNA before the arrival of proteins and DNA. Unfortunately, scientists have failed to find [...]
Why ‘Peniaphobia’ Is Exploding Among Young People (And Why We Should Be Concerned)
An insidious illness is taking hold among a growing proportion of young people. Little known to the general public, peniaphobia—the fear of becoming poor—is gaining ground among teens and young adults. Discover the causes [...]













Leave A Comment