The rising concern of plastic pollution and the increase in nanoplastics, which are small plastic debris particles with nanoscale sizes between 1 and 1000 nm, have become a field of research that has garnered popularity over recent years. Innovative research published in the journal, ACS Omega, has investigated the effect of nanoplastics on developing zebrafish embryos.
Nanoplastic Pollution
Nanoplastic pollution is a significant rising concern for public health and the environment.
Plastics, which have become a ubiquitous waste material found in landfills and the oceans, have been a growing concern due to their lack of biodegradability. Additionally, the eroding of large plastics into nanosize can be more detrimental for the environment and human health, with nanosized particles causing more damage.
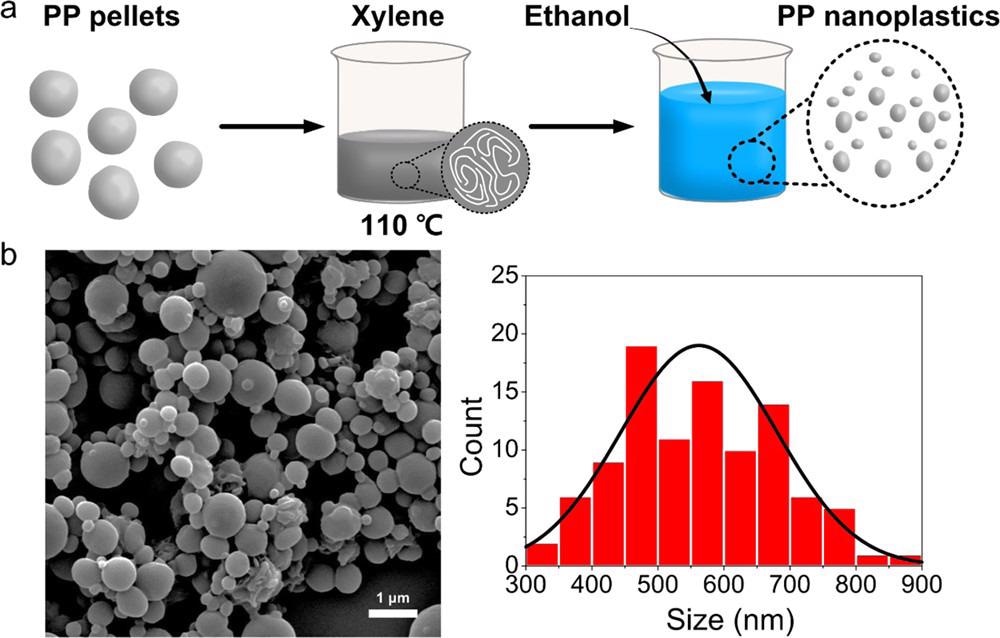
(a) Scheme for preparation of the polypropylene nanoplastics (PPNPs) using a modified nonsolvent-induced phase separation (NIPS) method. (b) SEM images and the size distribution (n = 100). © Lee, W., Kim, H., Sim, Y., Kang, T. and Jeong, J., (2022)
With physiochemical properties associated with nanosized plastics, they can interact with biological systems, leading to disastrous effects. Additionally, nanoplastic pollution may not be purified by wastewater treatment systems.
It can be found in drinking water, causing them to be ingested; resultant oxidative stress and inflammation have been reported in diverse organisms. This can also occur through its ability to penetrate human tissue by crossing the lungs, skin and gastrointestinal barriers – which can be deleterious for health.
Plastic types that are a risk and constitute plastic debris include polystyrene, polyethylene, and polypropylene (PP). Polystyrene has largely been responsible for the risk that nanoplastics hold due to its commercial availability of various sizes and surface charges; however, while this plastic has high usage, polyethylene and polypropylene are ubiquitously detected in plastic debris in the environment.
While polypropylene is abundant in the environment, there are limited studies on this plastic type. Regardless, its incorporation as the most used plastic, such as within food packaging, automotive components, and even personal protective equipment (PPE), including masks that have increased during the COVID-19 pandemic, raises the concern for plastic pollution.
The accumulation of PP into microplastics such as UV radiation, oxidation, and biofilms can be a health risk with the detection of PP being found gastrointestinal tracts of sea turtles on the Atlantic coastline of Florida after only being post-hatched for 96 hours. Additionally, PP microplastics were found to induce cytotoxicity, proinflammatory cytokine production, oxidative stress and intestinal damage in human-derived cell and animal models such as zebrafish.
With the disastrous effect of microplastics on both the environment and human health, fragmentation into nanosized particles could be potentially further hazardous. This plastic pollution, which is a major concern due to associated plastic manufacturing, requires further research to understand the effects of polypropylene nanoplastics.
Innovative Nanoplastic Research
The researchers of this innovative study aimed to investigate the biological effects of nanoscale polypropylene in an animal model utilizing developing zebrafish embryos.
The team produced PPNPs utilizing a high yield method, including nonsolvent-induced phase separation; they fabricated PPNPs within a spherical shape with an average diameter of 562.15 ± 118.47 nm. They were then fluorescently labeled utilizing the combined swelling-diffusion method to investigate and observe the biodistribution of these particles after being exposed to developing zebrafish embryos.
Interestingly, the researchers found the fluorescent-labeled polypropylene nanoplastics internalized through ingestion and found even in the intestines of developing zebrafish embryos before being eventually excreted.
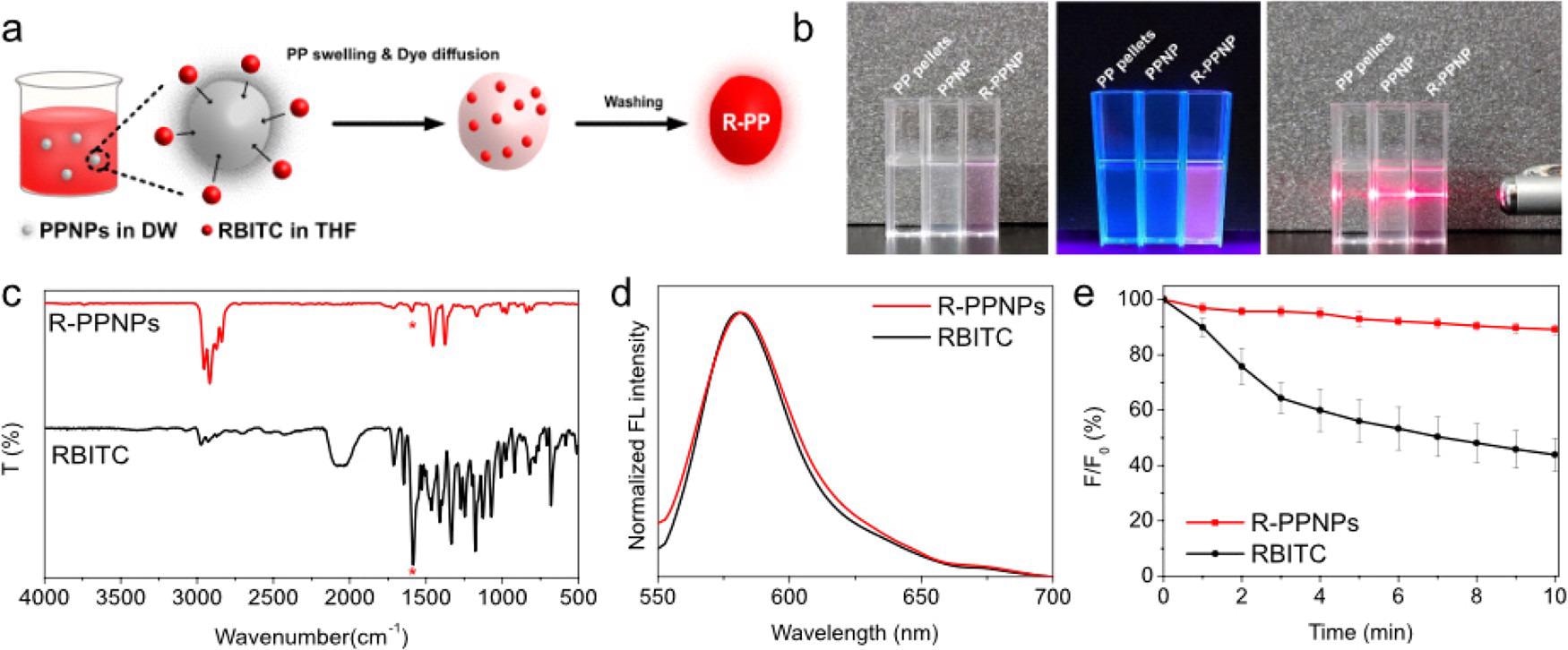
(a) Scheme of fluorescence labeling of PPNPs by the CSD method. (b) Photographs of PP pellets, PPNPs, and R-PPNP suspension in DW under visible light (left), UV light (365 nm, middle), and visible light with laser beam (right). (c) FT-IR spectra, (d) fluorescence spectra, and (e) fluorescence stability of RBITC and R-PPNPs. © Lee, W., Kim, H., Sim, Y., Kang, T. and Jeong, J., (2022)
Significant Implications for Environmental and Human Health
Overcoming the limitations of prior investigations into polypropylene plastic pollution, this novel research has uncovered the significant effect that nanoplastics can have on biological systems.
The team has raised awareness of the biodistribution of nanoplastics, especially polypropylene, which is found significantly in plastic debris within the environment. This study can be a basis for further research into the effect that nanoplastics can have on biological systems, such as focusing on oxidative stress and potential interactions that may cause harm for human health if ingested.
The research team can also aid in bringing awareness to the significance of nanoplastic pollution and its effects on the environment, with microplastic awareness being provided with traction. This can translate to reducing the manufacturing of polypropylene-based plastics, including finding other biodegradable plastics for applications, including PPE, which has become an increasing concern for plastic pollution.
Creating biodegradable plastics can ease plastic pollution and advancement in wastewater treatments can reduce any harmful effects these plastics can have on animal and human health.
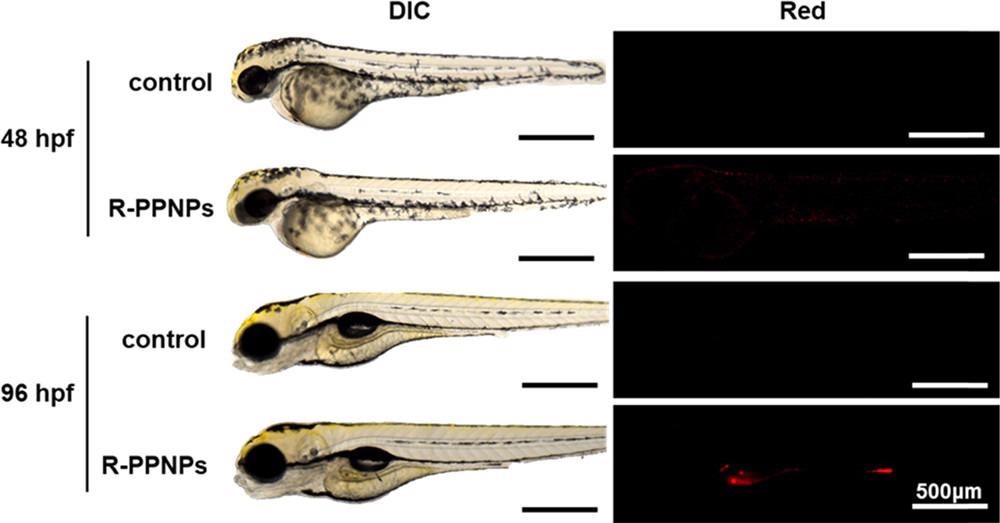
Optical and fluorescence images of zebrafish embryos with or without R-PPNP treatments at 24 and 72 hpf. These images were taken after 24 h exposure. © Lee, W., Kim, H., Sim, Y., Kang, T. and Jeong, J., (2022)
News
This Viral RNA Structure Could Lead to a Universal Antiviral Drug
Researchers identify a shared RNA-protein interaction that could lead to broad-spectrum antiviral treatments for enteroviruses. A new study from the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC), published in Nature Communications, explains how enteroviruses begin reproducing [...]
New study suggests a way to rejuvenate the immune system
Stimulating the liver to produce some of the signals of the thymus can reverse age-related declines in T-cell populations and enhance response to vaccination. As people age, their immune system function declines. T cell [...]
Nerve Damage Can Disrupt Immunity Across the Entire Body
A single nerve injury can quietly reshape the immune system across the entire body. Preclinical research from McGill University suggests that nerve injuries may lead to long-lasting changes in the immune system, and these [...]
Fake Science Is Growing Faster Than Legitimate Research, New Study Warns
New research reveals organized networks linking paper mills, intermediaries, and compromised academic journals Organized scientific fraud is becoming increasingly common, ranging from fabricated research to the buying and selling of authorship and citations, according [...]
Scientists Unlock a New Way to Hear the Brain’s Hidden Language
Scientists can finally hear the brain’s quietest messages—unlocking the hidden code behind how neurons think, decide, and remember. Scientists have created a new protein that can capture the incoming chemical signals received by brain [...]
Does being infected or vaccinated first influence COVID-19 immunity?
A new study analyzing the immune response to COVID-19 in a Catalan cohort of health workers sheds light on an important question: does it matter whether a person was first infected or first vaccinated? [...]
We May Never Know if AI Is Conscious, Says Cambridge Philosopher
As claims about conscious AI grow louder, a Cambridge philosopher argues that we lack the evidence to know whether machines can truly be conscious, let alone morally significant. A philosopher at the University of [...]
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]
What could the future of nanoscience look like?
Society has a lot to thank for nanoscience. From improved health monitoring to reducing the size of electronics, scientists’ ability to delve deeper and better understand chemistry at the nanoscale has opened up numerous [...]
Scientists Melt Cancer’s Hidden “Power Hubs” and Stop Tumor Growth
Researchers discovered that in a rare kidney cancer, RNA builds droplet-like hubs that act as growth control centers inside tumor cells. By engineering a molecular switch to dissolve these hubs, they were able to halt cancer [...]
Platelet-inspired nanoparticles could improve treatment of inflammatory diseases
Scientists have developed platelet-inspired nanoparticles that deliver anti-inflammatory drugs directly to brain-computer interface implants, doubling their effectiveness. Scientists have found a way to improve the performance of brain-computer interface (BCI) electrodes by delivering anti-inflammatory drugs directly [...]
After 150 years, a new chapter in cancer therapy is finally beginning
For decades, researchers have been looking for ways to destroy cancer cells in a targeted manner without further weakening the body. But for many patients whose immune system is severely impaired by chemotherapy or radiation, [...]
Older chemical libraries show promise for fighting resistant strains of COVID-19 virus
SARS‑CoV‑2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to mutate, with some newer strains becoming less responsive to current antiviral treatments like Paxlovid. Now, University of California San Diego scientists and an international team of [...]
Lower doses of immunotherapy for skin cancer give better results, study suggests
According to a new study, lower doses of approved immunotherapy for malignant melanoma can give better results against tumors, while reducing side effects. This is reported by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in the Journal of the National [...]