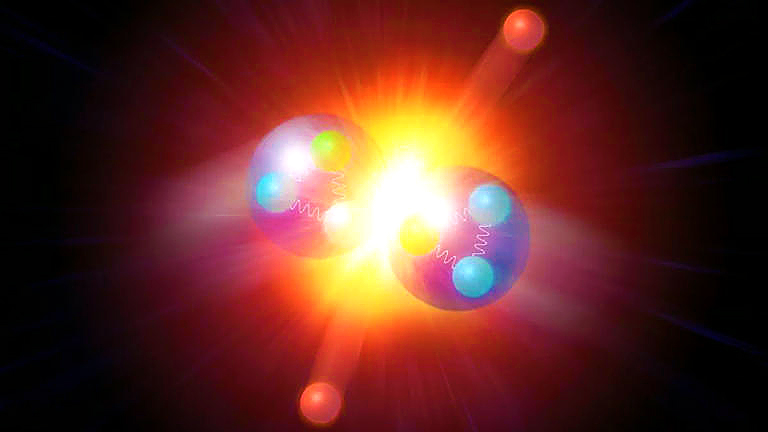
A proton is one of the subatomic particles that make up the nucleus of an atom. As small as protons are, they are composed of even tinier elementary particles known as quarks, which come in a variety of "flavors," or types: up, down, strange, charm, bottom and top. Typically, a proton is thought to be made of two up quarks and one down quark.
But a new study finds it's more complicated than that. Protons can also contain a charm quark, an elementary particle that's 1.5 times the mass of the proton itself. Even weirder, when the proton does contain the charm quark, the heavy particle still only carries about half the proton's mass.
The finding all comes down to the probabilistic world of quantum physics. Though the charm quark is heavy, the chance of it popping into existence in a proton is fairly small, so the high mass and small chance basically cancel each other out. Put another way, the full mass of the charm quark doesn't get taken up by the proton, even if the charm quark is there, Science News reported.
Though protons are fundamental to the structure of atoms — which make up all matter — they're also very complicated. Physicists don't actually know protons' fundamental structure. Quantum physics holds that beyond the up and down quarks known to be present, other quarks might pop into protons now and then, Stefano Forte, a physicist at the University of Milan, told the podcast Nature Briefing. Forte was a co-author of the new paper showing evidence for the charm quark in protons, published in the journal Nature Aug. 17.
There are six types of quarks. Three are heavier than protons and three are lighter than protons. The charm quark is the lightest of the heavy batch, so researchers wanted to start with that one to find out whether a proton could contain a quark heavier than itself. They did this by taking a new approach to 35 years of particle-smashing data.
To learn about the structure of subatomic and elementary particles, researchers fling particles against each other at blistering speeds at particle accelerators such as the Large Hadron Collider, the world's largest atom smasher, located near Geneva. Scientists with the nonprofit NNPDF collaboration gathered this particle-smashing data going back to the 1980s, including examples of experiments in which photons, electrons, muons, neutrinos and even other protons were crashed into protons. By looking at the debris from these collisions, researchers can reconstruct the original state of the particles.
In the new study, the scientists handed over all of this collision data to a machine-learning algorithm designed to look for patterns without any preconceived notions of how the structures might look. The algorithm returned possible structures and the likelihood that they might actually exist.
The study found a "small but not negligible" chance of finding a charm quark, Forte told Nature Briefing. The level of evidence wasn't high enough for the researchers to declare the undeniable discovery of the charm quark in protons, but the results are the "first solid evidence" that it can be there, Forte said.
The structure of the proton is important, Forte said, because to discover new elementary particles, physicists will have to uncover minuscule differences in what theories suggest and what's actually observed. This requires extremely precise measurements of subatomic structures.
For now, physicists still need more data on the elusive "charm" within a proton. Future experiments, such as the planned Electron-Ion Collider at Brookhaven National Laboratory in Upton, New York, may help, Tim Hobbs, a theoretical physicist at Fermilab in Batavia, Illinois, told Science News.
News
The Brain’s Strange Way of Computing Could Explain Consciousness
Consciousness may emerge not from code, but from the way living brains physically compute. Discussions about consciousness often stall between two deeply rooted viewpoints. One is computational functionalism, which holds that cognition can be [...]
First breathing ‘lung-on-chip’ developed using genetically identical cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and AlveoliX have developed the first human lung-on-chip model using stem cells taken from only one person. These chips simulate breathing motions and lung disease in an individual, [...]
Cell Membranes May Act Like Tiny Power Generators
Living cells may generate electricity through the natural motion of their membranes. These fast electrical signals could play a role in how cells communicate and sense their surroundings. Scientists have proposed a new theoretical [...]
This Viral RNA Structure Could Lead to a Universal Antiviral Drug
Researchers identify a shared RNA-protein interaction that could lead to broad-spectrum antiviral treatments for enteroviruses. A new study from the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC), published in Nature Communications, explains how enteroviruses begin reproducing [...]
New study suggests a way to rejuvenate the immune system
Stimulating the liver to produce some of the signals of the thymus can reverse age-related declines in T-cell populations and enhance response to vaccination. As people age, their immune system function declines. T cell [...]
Nerve Damage Can Disrupt Immunity Across the Entire Body
A single nerve injury can quietly reshape the immune system across the entire body. Preclinical research from McGill University suggests that nerve injuries may lead to long-lasting changes in the immune system, and these [...]
Fake Science Is Growing Faster Than Legitimate Research, New Study Warns
New research reveals organized networks linking paper mills, intermediaries, and compromised academic journals Organized scientific fraud is becoming increasingly common, ranging from fabricated research to the buying and selling of authorship and citations, according [...]
Scientists Unlock a New Way to Hear the Brain’s Hidden Language
Scientists can finally hear the brain’s quietest messages—unlocking the hidden code behind how neurons think, decide, and remember. Scientists have created a new protein that can capture the incoming chemical signals received by brain [...]
Does being infected or vaccinated first influence COVID-19 immunity?
A new study analyzing the immune response to COVID-19 in a Catalan cohort of health workers sheds light on an important question: does it matter whether a person was first infected or first vaccinated? [...]
We May Never Know if AI Is Conscious, Says Cambridge Philosopher
As claims about conscious AI grow louder, a Cambridge philosopher argues that we lack the evidence to know whether machines can truly be conscious, let alone morally significant. A philosopher at the University of [...]
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]
What could the future of nanoscience look like?
Society has a lot to thank for nanoscience. From improved health monitoring to reducing the size of electronics, scientists’ ability to delve deeper and better understand chemistry at the nanoscale has opened up numerous [...]
Scientists Melt Cancer’s Hidden “Power Hubs” and Stop Tumor Growth
Researchers discovered that in a rare kidney cancer, RNA builds droplet-like hubs that act as growth control centers inside tumor cells. By engineering a molecular switch to dissolve these hubs, they were able to halt cancer [...]
Platelet-inspired nanoparticles could improve treatment of inflammatory diseases
Scientists have developed platelet-inspired nanoparticles that deliver anti-inflammatory drugs directly to brain-computer interface implants, doubling their effectiveness. Scientists have found a way to improve the performance of brain-computer interface (BCI) electrodes by delivering anti-inflammatory drugs directly [...]