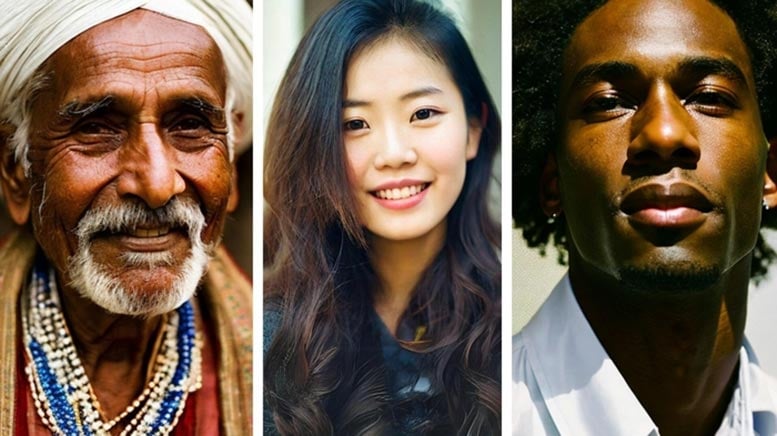
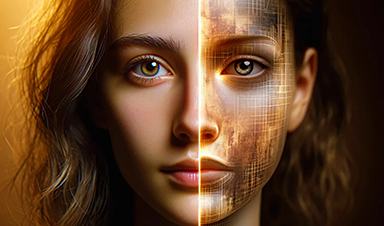
Research shows survey participants duped by AI-generated images nearly 40 percent of the time.
If you recently had trouble figuring out if an image of a person is real or generated through artificial intelligence (AI), you're not alone.
A new study from University of Waterloo researchers found that people had more difficulty than was expected distinguishing who is a real person and who is artificially generated.
The Waterloo study saw 260 participants provided with 20 unlabeled pictures: 10 of which were of real people obtained from Google searches, and the other 10 generated by Stable Diffusion or DALL-E, two commonly used AI programs that generate images.
Participants were asked to label each image as real or AI-generated and explain why they made their decision. Only 61 percent of participants could tell the difference between AI-generated people and real ones, far below the 85 percent threshold that researchers expected.
Misleading Indicators and Rapid AI Development
"People are not as adept at making the distinction as they think they are," said Andreea Pocol, a PhD candidate in Computer Science at the University of Waterloo and the study's lead author.
Participants paid attention to details such as fingers, teeth, and eyes as possible indicators when looking for AI-generated content – but their assessments weren't always correct.
Pocol noted that the nature of the study allowed participants to scrutinize photos at length, whereas most internet users look at images in passing.
"People who are just doomscrolling or don't have time won't pick up on these cues," Pocol said.
Pocol added that the extremely rapid rate at which AI technology is developing makes it particularly difficult to understand the potential for malicious or nefarious action posed by AI-generated images. The pace of academic research and legislation isn't often able to keep up: AI-generated images have become even more realistic since the study began in late 2022.
The Threat of AI-Generated Disinformation
These AI-generated images are particularly threatening as a political and cultural tool, which could see any user create fake images of public figures in embarrassing or compromising situations.
"Disinformation isn't new, but the tools of disinformation have been constantly shifting and evolving," Pocol said. "It may get to a point where people, no matter how trained they will be, will still struggle to differentiate real images from fakes. That's why we need to develop tools to identify and counter this. It's like a new AI arms race."
The study, "Seeing Is No Longer Believing: A Survey on the State of Deepfakes, AI-Generated Humans, and Other Nonveridical Media," was published in the journal Advances in Computer Graphics.
Reference: "Seeing Is No Longer Believing: A Survey on the State of Deepfakes, AI-Generated Humans, and Other Nonveridical Media" by Andreea Pocol, Lesley Istead, Sherman Siu, Sabrina Mokhtari and Sara Kodeiri, 29 December 2023, Advances in Computer Graphics.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-50072-5_34
News
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]