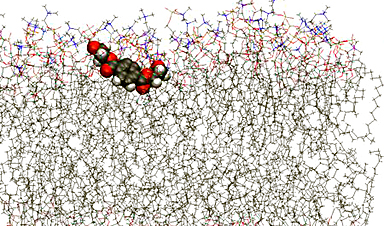
The occurrence of microplastics in nature has been studied extensively, also at the University of Eastern Finland. However, little is known about the health effects of microplastics, and understanding of their transport into the human body is also lacking. Any adverse health effects possibly associated with plastics may be caused by the plastic compound itself, or by the environmental toxins it carries. Many known fat-soluble environmental toxins and heavy metals are known to be able to attach to the surface of small plastic particles. This is why it is important to investigate the transport mechanisms of microplastics into the human body. However, not enough research methods have been developed for the study of this transport. Another key challenge in microplastics research is the lack of standardized methods.
The cell membrane permeability of pulverized PE and PET plastics was also examined using the Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay method, PAMPA. The method is usually used to investigate passive absorption of medicines, but it hasn’t been used to study microplastics before. The PAMPA method was used to investigate the amount of matter permeating the membrane. The amount of plastic permeating the artificial membrane was measured by NMR spectroscopy at certain intervals.
In both experiments, the movement of molecules was controlled only by concentration differences on different sides of the membrane, and by occasional movement induced by heat. In other words, the methods provided information on the passive permeation of molecules through the membranes.
In the computer simulations, PE particles were found to prefer the center of the lipid membrane as their location. In the PAMPA experiments, PE plastic partially permeated the membrane, but membrane permeability slowed down significantly over time, probably due to the accumulation of plastic in the membrane. In the simulations, the preferred location of PET particles was, to a certain degree, the surface part of the membrane, and in the experiments, they permeated the membrane fairly well. According to this study, the properties of the membrane structures were not significantly affected by individual plastics.
The study provides a starting point for the further development of computer simulations and experimental methods for the needs of microplastics research. Significantly more information is still needed on the active transport of microplastics, such as their binding to transporter proteins, possible phagocytosis, and toxic effects on cells.
News
New Book! NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Miller School Researchers Pioneer Nanovanilloid-Based Brain Cooling for Traumatic Injury
A multidisciplinary team at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine has developed a breakthrough nanodrug platform that may prove beneficial for rapid, targeted therapeutic hypothermia after traumatic brain injury (TBI). Their work, published in ACS [...]
COVID-19 still claims more than 100,000 US lives each year
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers report national estimates of 43.6 million COVID-19-associated illnesses and 101,300 deaths in the US during October 2022 to September 2023, plus 33.0 million illnesses and 100,800 deaths [...]
Nanomedicine in 2026: Experts Predict the Year Ahead
Progress in nanomedicine is almost as fast as the science is small. Over the last year, we've seen an abundance of headlines covering medical R&D at the nanoscale: polymer-coated nanoparticles targeting ovarian cancer, Albumin recruiting nanoparticles for [...]
Lipid nanoparticles could unlock access for millions of autoimmune patients
Capstan Therapeutics scientists demonstrate that lipid nanoparticles can engineer CAR T cells within the body without laboratory cell manufacturing and ex vivo expansion. The method using targeted lipid nanoparticles (tLNPs) is designed to deliver [...]
The Brain’s Strange Way of Computing Could Explain Consciousness
Consciousness may emerge not from code, but from the way living brains physically compute. Discussions about consciousness often stall between two deeply rooted viewpoints. One is computational functionalism, which holds that cognition can be [...]
First breathing ‘lung-on-chip’ developed using genetically identical cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and AlveoliX have developed the first human lung-on-chip model using stem cells taken from only one person. These chips simulate breathing motions and lung disease in an individual, [...]
Cell Membranes May Act Like Tiny Power Generators
Living cells may generate electricity through the natural motion of their membranes. These fast electrical signals could play a role in how cells communicate and sense their surroundings. Scientists have proposed a new theoretical [...]
This Viral RNA Structure Could Lead to a Universal Antiviral Drug
Researchers identify a shared RNA-protein interaction that could lead to broad-spectrum antiviral treatments for enteroviruses. A new study from the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC), published in Nature Communications, explains how enteroviruses begin reproducing [...]
New study suggests a way to rejuvenate the immune system
Stimulating the liver to produce some of the signals of the thymus can reverse age-related declines in T-cell populations and enhance response to vaccination. As people age, their immune system function declines. T cell [...]
Nerve Damage Can Disrupt Immunity Across the Entire Body
A single nerve injury can quietly reshape the immune system across the entire body. Preclinical research from McGill University suggests that nerve injuries may lead to long-lasting changes in the immune system, and these [...]
Fake Science Is Growing Faster Than Legitimate Research, New Study Warns
New research reveals organized networks linking paper mills, intermediaries, and compromised academic journals Organized scientific fraud is becoming increasingly common, ranging from fabricated research to the buying and selling of authorship and citations, according [...]
Scientists Unlock a New Way to Hear the Brain’s Hidden Language
Scientists can finally hear the brain’s quietest messages—unlocking the hidden code behind how neurons think, decide, and remember. Scientists have created a new protein that can capture the incoming chemical signals received by brain [...]
Does being infected or vaccinated first influence COVID-19 immunity?
A new study analyzing the immune response to COVID-19 in a Catalan cohort of health workers sheds light on an important question: does it matter whether a person was first infected or first vaccinated? [...]
We May Never Know if AI Is Conscious, Says Cambridge Philosopher
As claims about conscious AI grow louder, a Cambridge philosopher argues that we lack the evidence to know whether machines can truly be conscious, let alone morally significant. A philosopher at the University of [...]
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]