In an article recently published in the open-access MDPI journal nanomaterials, researchers investigated the mechanism of interaction between nanoscale materials and specific cells for biomedical applications, primarily related to targeted delivery and tracing.
Here, the localization, cellular uptake quantity, and response time of gold nanorods in MCF-7 and SKBR-3 breast cancer cells were measured.
Background
The amalgamation of biotechnology and nanotechnology has been a quite fascinating field of research for the last few years.
Currently, nanomaterials are extensively used in biomedical applications such as drug delivery, magnetic or fluorescent bio-imaging, tissue engineering, tracing pathogens in sensitive organs, cancer chemotherapy, and many more. However, each nanomaterial interacts differently with a particular type of cell.
Many studies have shown cellular uptake of gold nanorods by cancer cells. MCF-7 and SKBR-3 cancer cell lines represent HER2-negative and HER2-positive breast cancer models, respectively. These cells intake gold nanorods through a mechanism occurring at the surface of the cell membrane, called endocytosis.
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) can measure the efficiency of targeted delivery and cellular uptake of these nanoparticles, while transmission electron microscopy (TEM) can be used to investigate their localization.
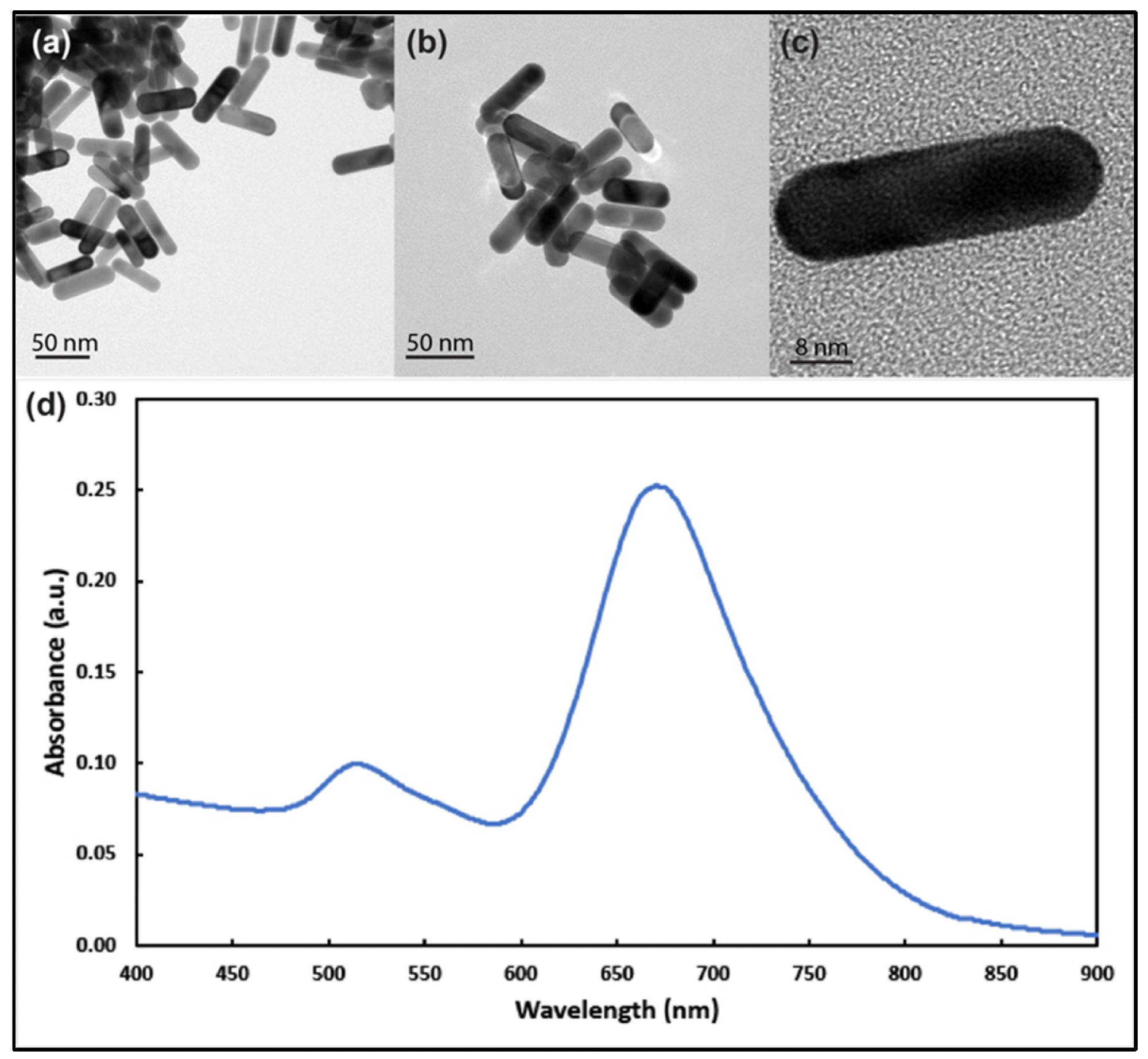
Figure 1. Transmission electron microscope images of gold nanorods with aspect ratio around 3 at different magnifications (a–c). (d) UV–visible spectrum analysis of the prepared gold nanorods showing longitudinal and transverse plasmons around 690 nm and 514 nm, respectively. © White, B., White, M., Nima Alsudani, Z., Watanabe, F., Biris, A., Ali, N., (2022)
About the Study
In this article, researchers investigated the interaction mechanism of gold nanorods (Au NRs) in two types of breast cancer cell lines namely, MCF-7 and SKBR-3. More than 200 Au NRs with an average length and diameter of 36 and 12 nm, respectively, were synthesized using the silver ion-assisted seed-mediated method. Subsequently, MCF-7 and SKBR-3 cells were cultured in a conducive medium and allowed to bind with different concentrations of Au NRs for 1 and 2 days.
The excess Au NRs were washed away from the treated cancels using phosphate buffer saline (PBS) solution followed by treating with the (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) (MTT) reagent. Finally, ICP-MS and TEM analyses were performed to investigate the interaction mechanism.
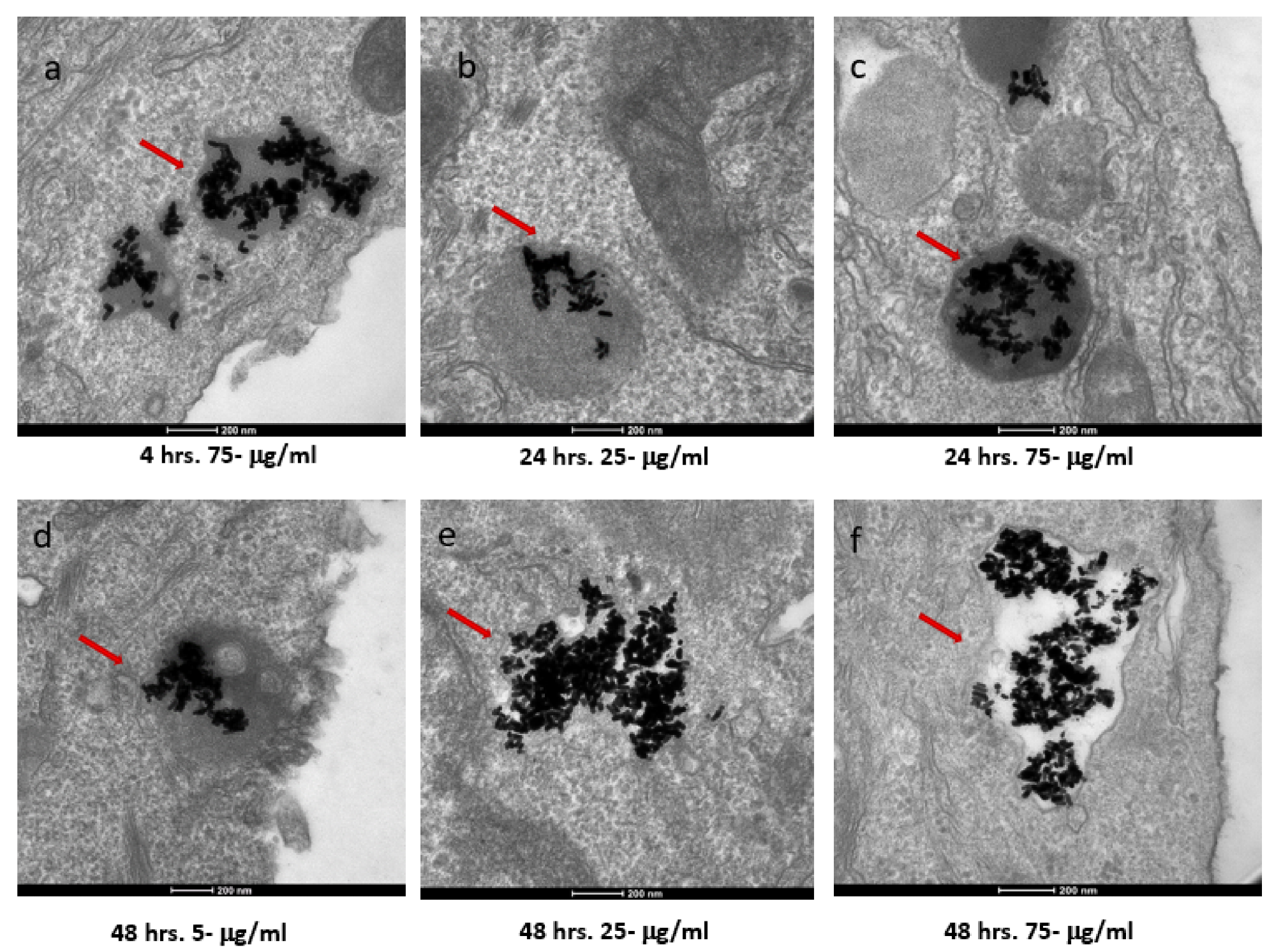
Figure 2. TEM images of AuNRs in SKBR-3 cells at different time points and concentrations. SKBR-3 cells were treated with 5, 25, and 75 μg/mL of AuNRs for 1, 4, 24, and 48 h. Internalization of nanorods was observed starting at 4hourincubation with 75 μg/mL (a). After 24hourof incubation, internalization was observed with the 25 μg/mL (b) and 75 μg/mL concentrations (c). For cells incubated for 48 h, we observed internalization with 5, 25, and 75 μg/mL concentrations (d, e, and f, respectively). Red arrows point to gold nanorods localized in SKBR-3 cells. Electron photomicrographs shown are representative of at least three independent experiments with similar conditions. © White, B., White, M., Nima Alsudani, Z., Watanabe, F., Biris, A., Ali, N., (2022)
Observations
TEM images showed Au NRs had longitudinal and transverse plasmon resonances at around 680 and 514 nm, respectively. The average zeta potential of the NRs was −47.18 ± 4.26 mV. Au NRs did not show any cytotoxicity in healthy human cells. MTT methods indicated that the MCF-7 cells were less sensitive to Au NR exposure than the SKBR-3 cells for longer exposure times at higher concentrations. The SKBR-3 cells exhibited a drop in cell vitality due to higher sensitivity, whereas the MCF-7 cells had almost no drop in cell viability.
Both types of cells demonstrated a different pattern in cellular uptake of Au NRs for different exposure times and concentrations. The SKBR-3 cells had a constant cellular uptake between one to four hours, but 25 μg/mL Au NRs concentration had a higher uptake than the 75 μg/mL sample, i.e. lower concentration had a higher cellular uptake. In contrast, in MCF-7 cells, the 75 μg/mL AuNR-treated cell samples exhibited higher cellular uptake than 5 and 25 μg/mL samples, i.e. higher concentration samples had higher cellular uptake than lower concentration samples.
Furthermore, TEM analysis showed that the Au NRs interacted with the cell membrane of both cancer cells starting from one to 48 hours of exposure time. However, the Au NRs entered into the cell (i.e. internalized) for the samples with concentrations of 25 and 75 μg/mL. The 5 μg/mL concentration samples were never internalized. Moreover, the minimum exposure time for internalization was one hour and four hours for the MCF-7 and SKBR-3 cells, respectively.
The mechanism for the cellular uptake of the Au NRs was primarily micropinocytosis instead of receptor-mediated endocytosis. These Au NRs-carrying macropinosomes further interacted with the lysosomes inside the cells.
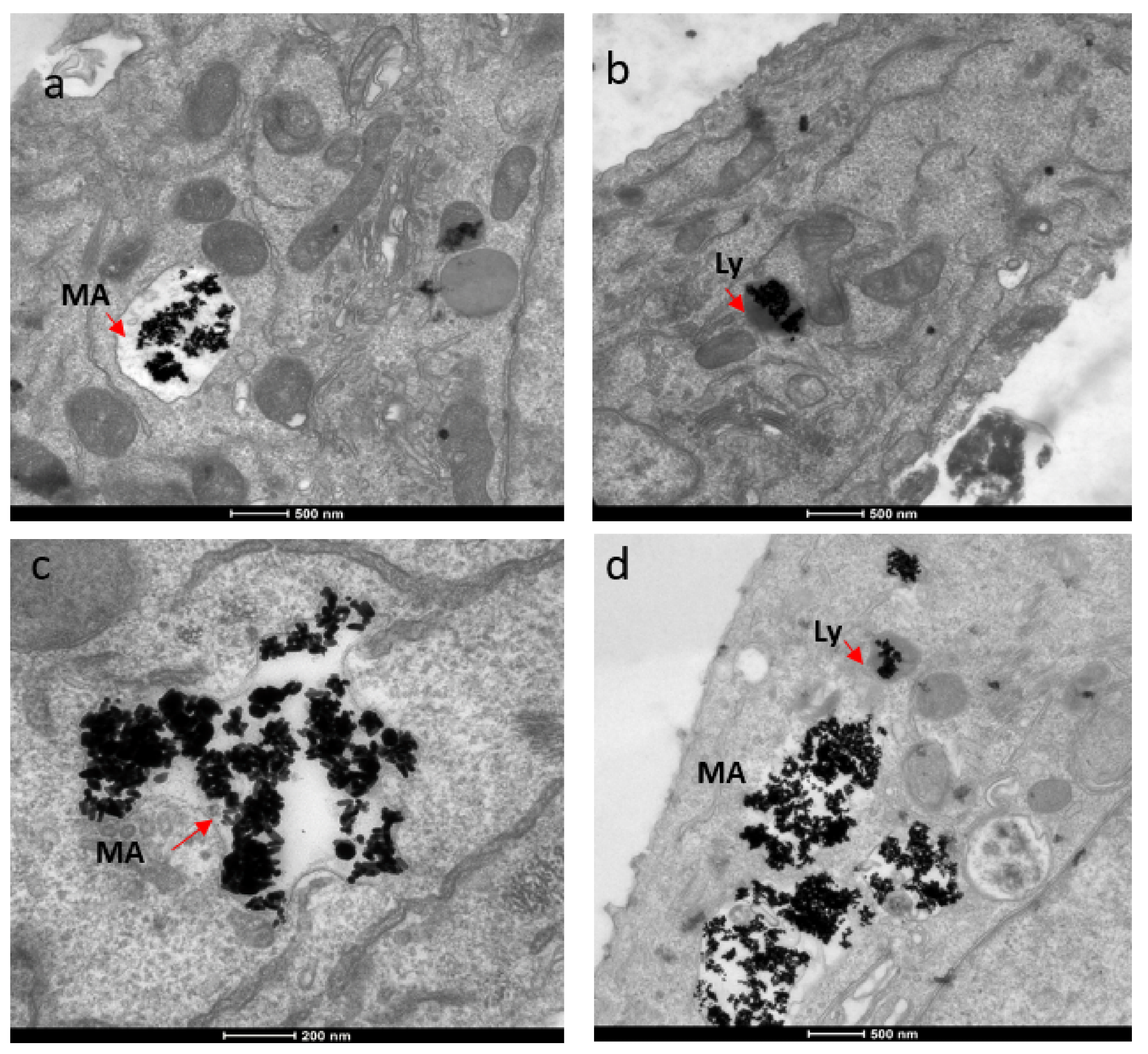
Figure 3. TEM images showing localization of gold nanorods in macropinosomes and lysosomes in both SKBR-3 and MCF-7 cell lines. AuNR localization in (a) macropinosomes (MA) and (b) lysosomes (Ly) of SKBR-3 cells. (c) Macropinosomes (MA) containing gold nanorods in MCF-7 and (d) lysosomes (Ly) containing gold nanorods in MCF-7. Red arrows point out macropinosomes and lysosomes containing gold nanorods in each image. Electron photomicrographs shown are representative of at least three independent experiments with similar conditions. © White, B., White, M., Nima Alsudani, Z., Watanabe, F., Biris, A., Ali, N., (2022)
Conclusions
To conclude, the researchers of this study investigated the interaction of Au NRs in two types of breast cancer cell lines, i.e. MCF-7 and SKBR-3. The shape, size, and zeta potential of Au NRs had different effects on cell vitality and toxicity of different cancer cells. Additionally, both cell types had different patterns of cellular uptake for Au NRs at different concentrations and exposure times.
The Au NRs did not enter into the cancer cells for samples with lower concentrations of NRs or lower exposure time. Also, the cellular uptake mechanism was primarily driven by micropinocytosis. These findings will help improve biomedical applications related to targeted drug delivery, tracing, and bio-imaging involving nanomaterials.
News
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]