An enormous meteor spelled doom for most dinosaurs 65 million years ago. But not all. In the aftermath of the extinction event, birds — technically dinosaurs themselves — flourished.
Scientists have spent centuries trying to organize and sort some 10,000 species of birds into one clear family tree to understand how the last surviving dinosaurs filled the skies. Cheap DNA sequencing should have made this simple, as it has for countless other species.
But birds were prepared to deceive us.
In a pair of new research papers released today, April 1, scientists reveal that another event 65 million years ago misled them about the true family history of birds. They discovered that a section of one chromosome spent millions of years frozen in time, and it refused to mix together with nearby DNA as it should have.
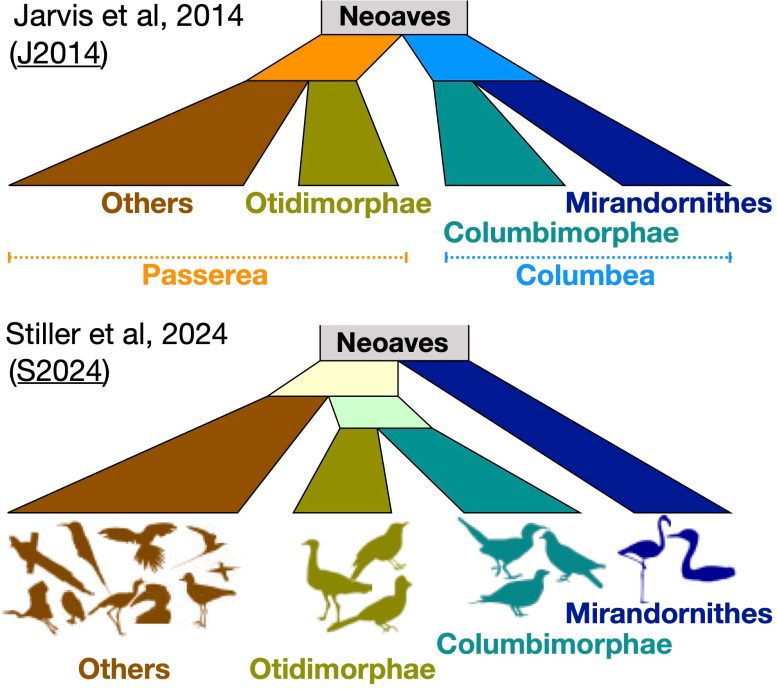
This section, just two percent of the bird genome, convinced scientists that most birds could be grouped into two major categories, with flamingos and doves as evolutionary cousins. The more accurate family tree, which accounts for the misleading section of the genome, identifies four main groups and identifies flamingos and doves as more distantly related.
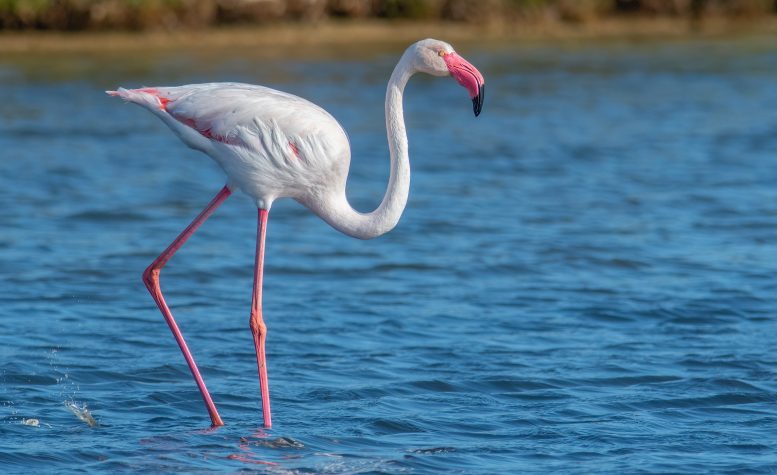
A greater flamingo in Mallorca, Spain. Unraveling a genetic mystery revealed that flamingos and doves are more distantly related than previously thought. Credit: Daniel J. Field
Breakthrough in Bird Evolution Research
"My lab has been chipping away at this problem of bird evolution for longer than I want to think about," said Edward Braun, Ph.D., the senior author of the paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences and a professor of biology at the University of Florida. "We had no idea there would be a big chunk of the genome that behaved unusually. We kind of stumbled onto it."
Braun supervised an international team of collaborators led by Siavash Mirarab, a professor of computer engineering at the University of California San Diego, to publish their evidence that this sticky chunk of DNA muddied the true history of bird evolution. Mirarab and Braun also contributed to a companion paper published in Nature that outlines the updated bird family tree, which was led by Josefin Stiller at the University of Copenhagen.
Both papers are part of the B10K avian genomics project led by Guojie Zhang of Zhejiang University, Erich Jarvis of Rockefeller University, and Tom Gilbert of the University of Copenhagen.
Two mutually exclusive bird family trees. The top family tree lumps flamingos and doves, in blue and teal respectively, closely together, while the bottom family tree does not. The top family tree was built around distortions in bird genomes that date back to the extinction of the dinosaurs. The bottom family tree is likely more accurate, after accounting for these genomic anomalies. Credit: Edward Braun
Genetic Anomalies and Evolutionary Insights
Ten years ago, Braun and his collaborators pieced together a family tree for the Neoaves, a group that includes the vast majority of bird species. Based on the genomes of 48 species, they split the Neoaves into two big categories: doves and flamingos in one group, all the rest in the other. When repeating a similar analysis this year using 363 species, a different family tree emerged that split up doves and flamingos into two distinct groups.
With two mutually exclusive family trees in hand, the scientists went hunting for explanations that could tell them which tree was correct.
"When we looked at the individual genes and what tree they supported, all of a sudden it popped out that all the genes that support the older tree, they're all in one spot. That's what started the whole thing," Braun said.
Investigating this spot, Braun's team noticed it was not as mixed together as it should have been over millions of years of sexual reproduction. Like humans, birds combine genes from a father and a mother into the next generation. But birds and humans alike first mix the genes they inherited from their parents when creating sperm and eggs. This process is called recombination, and it maximizes a species' genetic diversity by making sure no two siblings are quite the same.
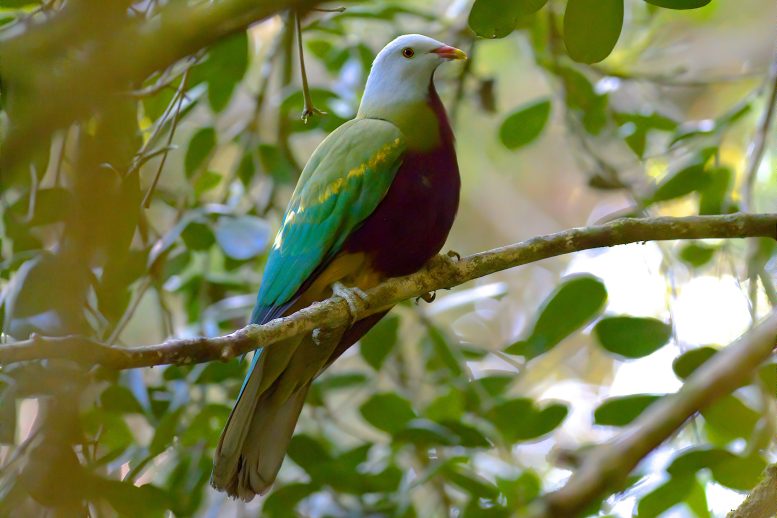
A wompoo fruit-dove in Queensland, Australia. Unraveling a genetic mystery revealed that flamingos and doves are more distantly related than previously thought. Credit: Daniel J. Field
Braun's team found evidence that one section of one bird chromosome had suppressed this recombination process for a few million years around the time the dinosaurs disappeared. Whether the extinction event and the genomic anomalies are related is unclear.
The result was that the flamingos and doves looked similar to one another in this chunk of frozen DNA. But taking into account the full genome, it became clear that the two groups are more distantly related.
"What's surprising is that this period of suppressed recombination could mislead the analysis," Braun said. "And because it could mislead the analysis, it was actually detectable more than 60 million years in the future. That's the cool part."
Such a mystery could be lurking in the genomes of other organisms as well.
"We discovered this misleading region in birds because we put a lot of energy into sequencing birds' genomes," Braun said. "I think there are cases like this out there for other species that are just not known right now."
References:
"Complexity of avian evolution revealed by family-level genomes" by Josefin Stiller, Shaohong Feng, Al-Aabid Chowdhury, Iker Rivas-González, David A. Duchêne, Qi Fang, Yuan Deng, Alexey Kozlov, Alexandros Stamatakis, Santiago Claramunt, Jacqueline M. T. Nguyen, Simon Y. W. Ho, Brant C. Faircloth, Julia Haag, Peter Houde, Joel Cracraft, Metin Balaban, Uyen Mai, Guangji Chen, Rongsheng Gao, Chengran Zhou, Yulong Xie, Zijian Huang, Zhen Cao, Zhi Yan, Huw A. Ogilvie, Luay Nakhleh, Bent Lindow, Benoit Morel, Jon Fjeldså, Peter A. Hosner, Rute R. da Fonseca, Bent Petersen, Joseph A. Tobias, Tamás Székely, Jonathan David Kennedy, Andrew Hart Reeve, Andras Liker, Martin Stervander, Agostinho Antunes, Dieter Thomas Tietze, Mads Bertelsen, Fumin Lei, Carsten Rahbek, Gary R. Graves, Mikkel H. Schierup, Tandy Warnow, Edward L. Braun, M. Thomas P. Gilbert, Erich D. Jarvis, Siavash Mirarab and Guojie Zhang, 32 March 2024, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07323-1
"A region of suppressed recombination misleads neoavian phylogenomics" by Siavash Mirarab, Iker Rivas-González, Shaohong Feng, Josefin Stiller, Qi Fang, Uyen Mai, Glenn Hickey, Guangji Chen, Nadolina Brajuka, Olivier Fedrigo, Giulio Formenti, Jochen B. W. Wolf, Kerstin Howe, Agostinho Antunes, Mikkel H. Schierup, Benedict Paten, Erich D. Jarvis, Guojie Zhang and Edward L. Braun, 1 April 2024, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2319506121
This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation.
News
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]
Scientists Develop Spray-On Powder That Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds
KAIST scientists have created a fast-acting, stable powder hemostat that stops bleeding in one second and could significantly improve survival in combat and emergency medicine. Severe blood loss remains the primary cause of death from [...]
Oceans Are Struggling To Absorb Carbon As Microplastics Flood Their Waters
New research points to an unexpected way plastic pollution may be influencing Earth’s climate system. A recent study suggests that microscopic plastic pollution is reducing the ocean’s capacity to take in carbon dioxide, a [...]
Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine – New book from Frank Boehm
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]