A novel study published in the journal, Foods, describes edible nanoparticle-based antibacterial agents to control foodborne diseases.
This research comprises a ternary nanoparticle with two active ingredients and a carrier material that was prepared from rosemary essential oil, nisin and Lycium barbarum polysaccharides.
Using Edible Nanoparticles
Interestingly, the use of functional nanoparticles with food-grade biological macromolecules including protein and polysaccharides has become a popular research area for novel food additives.
This is due to these molecules consisting of components that have a large surface area, a simple preparation process as well as having a flexible structure.
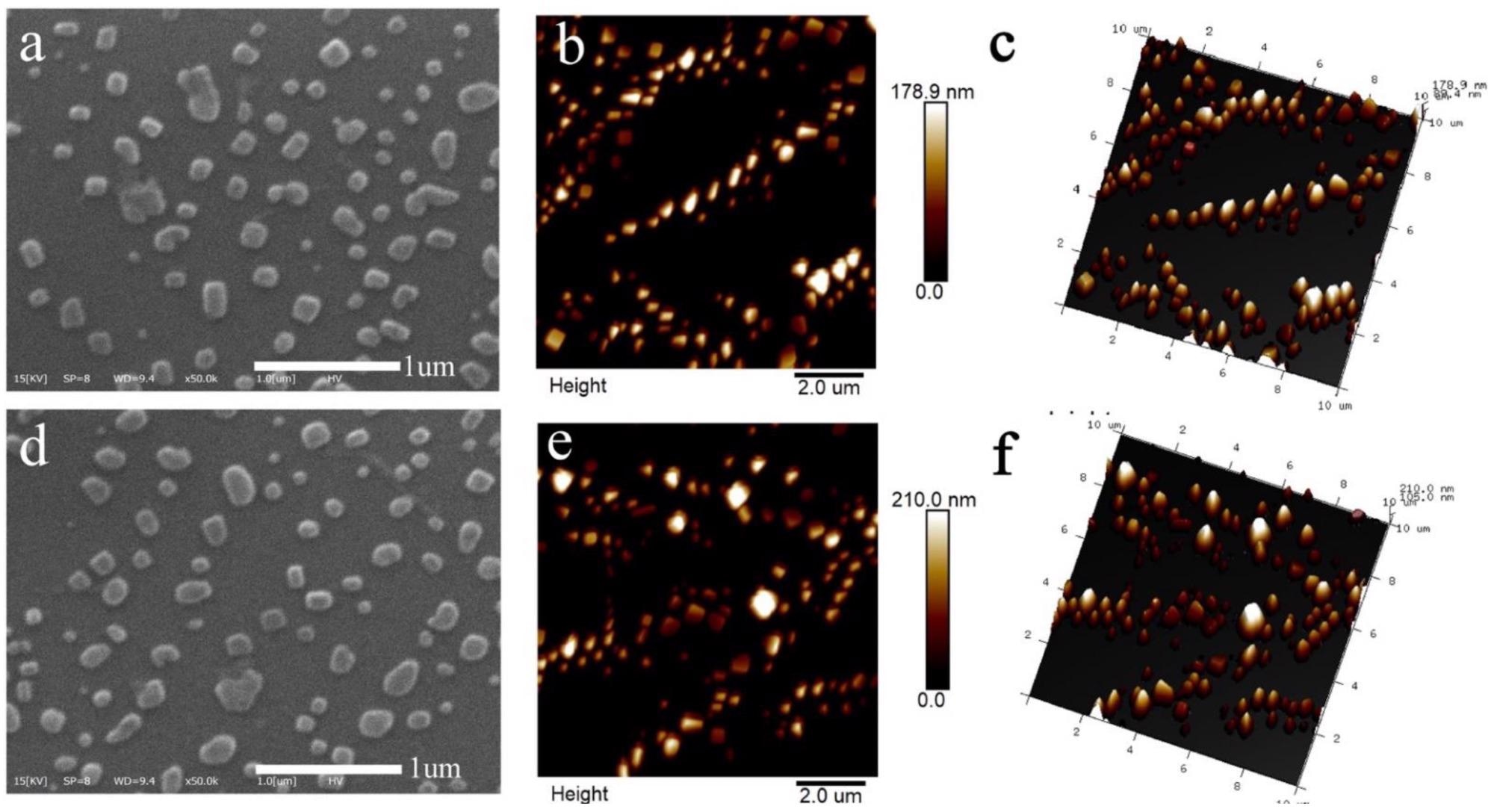
Figure 1. The morphology of nanoparticles including SEM-micrographs and surface, 3-Dimensional AFM images of RNNP (a–c) and TNP (d–f). © Lin, L., Luo, C., Li, C., Chen, X. and Cui, H., (2022)
This is especially significant for the application against foodborne diseases that can be attributed to pathogenic microorganism contamination, resulting in high mortality and morbidity on a global scale.
These pathogenic microorganisms that can infect food and result in severe infections in humans mainly consist of, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has reported 600 million foodborne disease occurrences on an annual basis with more than approximately 420,000 lives lost, illustrating the significance in this area of research to reduce and prevent foodborne diseases.
Previous research on this food health crisis includes novel antibacterial strategies, including the development of new packaging and coating materials that consist of natural antibacterial agents.
Incorporating nanotechnology has furthered this research area through the use of biomaterials and nanocarrier technology via nanoparticles, nanoemulsions, nanohydrogels, and nanoliposomes.
For example, metal oxide nanoparticles have been synthesized as intelligent food packaging; findings indicated increased antibacterial activity.
Ternary Nanoparticle Research
The novel advancement in this field has now encompassed the use of ternary nanoparticles (TNP) comprising two active ingredients and a carrier material prepared from rosemary essential oil (REO), nisin and Lycium barbarum polysaccharides (LBP).
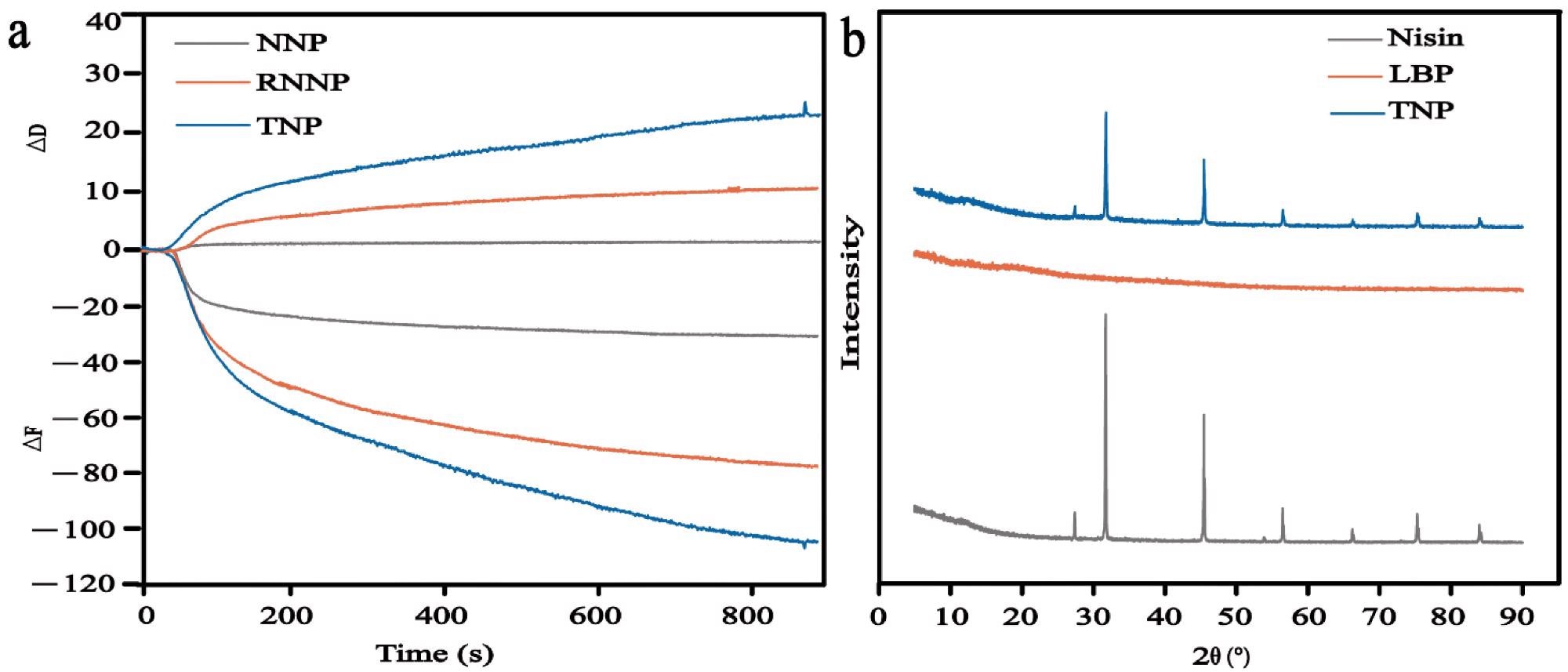
Figure 2. QCM of NNP, RNNP and TNP (a); XRD of Nisin, LBP and TNP(b). © Lin, L., Luo, C., Li, C., Chen, X. and Cui, H., (2022)
Rosemary essential oil was utilized in this research study as the main active ingredient, due to its high antibacterial and antioxidant effects.
These properties have illustrated the potential of REO to be used as an alternative ‘green’ antibacterial agent within food preservation and safety as a method to inhibit foodborne pathogens.
Additionally, the use of nisin as an active ingredient can also enhance the antibacterial and antioxidant activity within food as well as having the role of encapsulating REO due to its peptide-based material that can be used to form nanoparticles.
However, due to being easily degradable by enzymes within food ingredients, nisin can be combined with biopolymers or by incorporated into nisin-loaded nanoparticles.
The potential of LBP for use as a stabilizer for REO and nisin can increase the stability and efficiency of this effective combination of active ingredients.
The novelty of this research can be found in the dual ability of these nanoparticles to improve both the antibacterial and antioxidant effects within beef but also have thermal and storage stability within this food application.
The results of this research study included a reduction in in vitro populations of S. aureus and E.coli when treated with TNP compared to the control group.
The use of TNP as an antibacterial agent on beef was also found to have positive results with favorable preservation effects as well as a lack of change in color or texture, illustrating its potential for use in real-world applications.
Translatory Significance
The high encapsulation efficiency and stability of this ternary nanoparticle combination with multiple ingredients were able to demonstrate how protein nanoparticle instability can be improved.
Additionally, it also illustrated a novel strategy of addressing foodborne pathogens and the use of ‘green’ alternatives to increase the antibacterial and antioxidant activity and reduce bacteria populations.
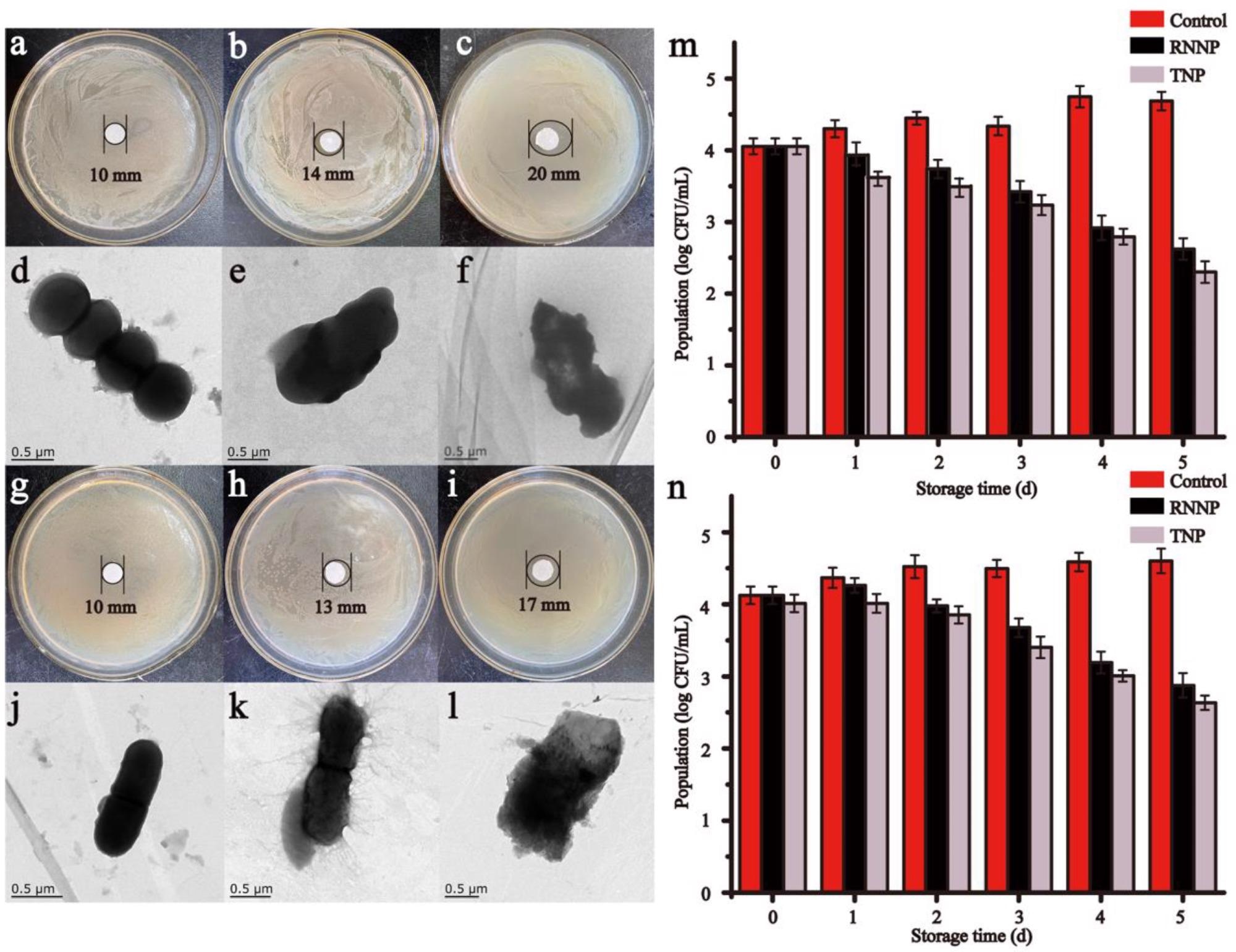
Figure 3. The antibacterial effect of nanoparticles including the inhibition zones, TEM and time-kill curve of control, RNNP and TNP on S. aureus (a–f,m) and E. coli O157:H7 (g–l,n). © Lin, L., Luo, C., Li, C., Chen, X. and Cui, H., (2022)
If translated, the significance of this research could help in reducing the number of infections from pathogenic microorganism contamination, aiding a reduction in overall levels of mortality and morbidity.
This is especially critical on a global scale with less economically developed countries that are more likely to harbor pathogenic contamination, and less likely to have access to medical care.
The use of ternary nanoparticles within the food industry may have the potential to aid with food preservation and reduction in pathogens, not only for beef but for all types of food, further reducing the likelihood of foodborne diseases from pathogenic contamination.
News
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]
What could the future of nanoscience look like?
Society has a lot to thank for nanoscience. From improved health monitoring to reducing the size of electronics, scientists’ ability to delve deeper and better understand chemistry at the nanoscale has opened up numerous [...]
Scientists Melt Cancer’s Hidden “Power Hubs” and Stop Tumor Growth
Researchers discovered that in a rare kidney cancer, RNA builds droplet-like hubs that act as growth control centers inside tumor cells. By engineering a molecular switch to dissolve these hubs, they were able to halt cancer [...]
Platelet-inspired nanoparticles could improve treatment of inflammatory diseases
Scientists have developed platelet-inspired nanoparticles that deliver anti-inflammatory drugs directly to brain-computer interface implants, doubling their effectiveness. Scientists have found a way to improve the performance of brain-computer interface (BCI) electrodes by delivering anti-inflammatory drugs directly [...]
After 150 years, a new chapter in cancer therapy is finally beginning
For decades, researchers have been looking for ways to destroy cancer cells in a targeted manner without further weakening the body. But for many patients whose immune system is severely impaired by chemotherapy or radiation, [...]
Older chemical libraries show promise for fighting resistant strains of COVID-19 virus
SARS‑CoV‑2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to mutate, with some newer strains becoming less responsive to current antiviral treatments like Paxlovid. Now, University of California San Diego scientists and an international team of [...]
Lower doses of immunotherapy for skin cancer give better results, study suggests
According to a new study, lower doses of approved immunotherapy for malignant melanoma can give better results against tumors, while reducing side effects. This is reported by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in the Journal of the National [...]
Researchers highlight five pathways through which microplastics can harm the brain
Microplastics could be fueling neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, with a new study highlighting five ways microplastics can trigger inflammation and damage in the brain. More than 57 million people live with dementia, [...]
Tiny Metal Nanodots Obliterate Cancer Cells While Largely Sparing Healthy Tissue
Scientists have developed tiny metal-oxide particles that push cancer cells past their stress limits while sparing healthy tissue. An international team led by RMIT University has developed tiny particles called nanodots, crafted from a metallic compound, [...]
Gold Nanoclusters Could Supercharge Quantum Computers
Researchers found that gold “super atoms” can behave like the atoms in top-tier quantum systems—only far easier to scale. These tiny clusters can be customized at the molecular level, offering a powerful, tunable foundation [...]
A single shot of HPV vaccine may be enough to fight cervical cancer, study finds
WASHINGTON -- A single HPV vaccination appears just as effective as two doses at preventing the viral infection that causes cervical cancer, researchers reported Wednesday. HPV, or human papillomavirus, is very common and spread [...]
New technique overcomes technological barrier in 3D brain imaging
Scientists at the Swiss Light Source SLS have succeeded in mapping a piece of brain tissue in 3D at unprecedented resolution using X-rays, non-destructively. The breakthrough overcomes a long-standing technological barrier that had limited [...]
Scientists Uncover Hidden Blood Pattern in Long COVID
Researchers found persistent microclot and NET structures in Long COVID blood that may explain long-lasting symptoms. Researchers examining Long COVID have identified a structural connection between circulating microclots and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). The [...]
This Cellular Trick Helps Cancer Spread, but Could Also Stop It
Groups of normal cbiells can sense far into their surroundings, helping explain cancer cell migration. Understanding this ability could lead to new ways to limit tumor spread. The tale of the princess and the [...]