Several difficulties have been associated with developing robust nanoscale coating on the surface of electrospun nanofibers. In a recent study published in Nature Communications, scientists have successfully produced a facile, controllable, and versatile method to develop superlubricated nano-skin (SLNS) on the single electrospun nanofiber in situ.
Electrospun Nanofibers
Nanofibers synthesized through electrospinning are commonly applied in several areas, including biomedical engineering, energy, and the environment. This is because electrospinning is responsible for producing highly controllable structures with specific functions.
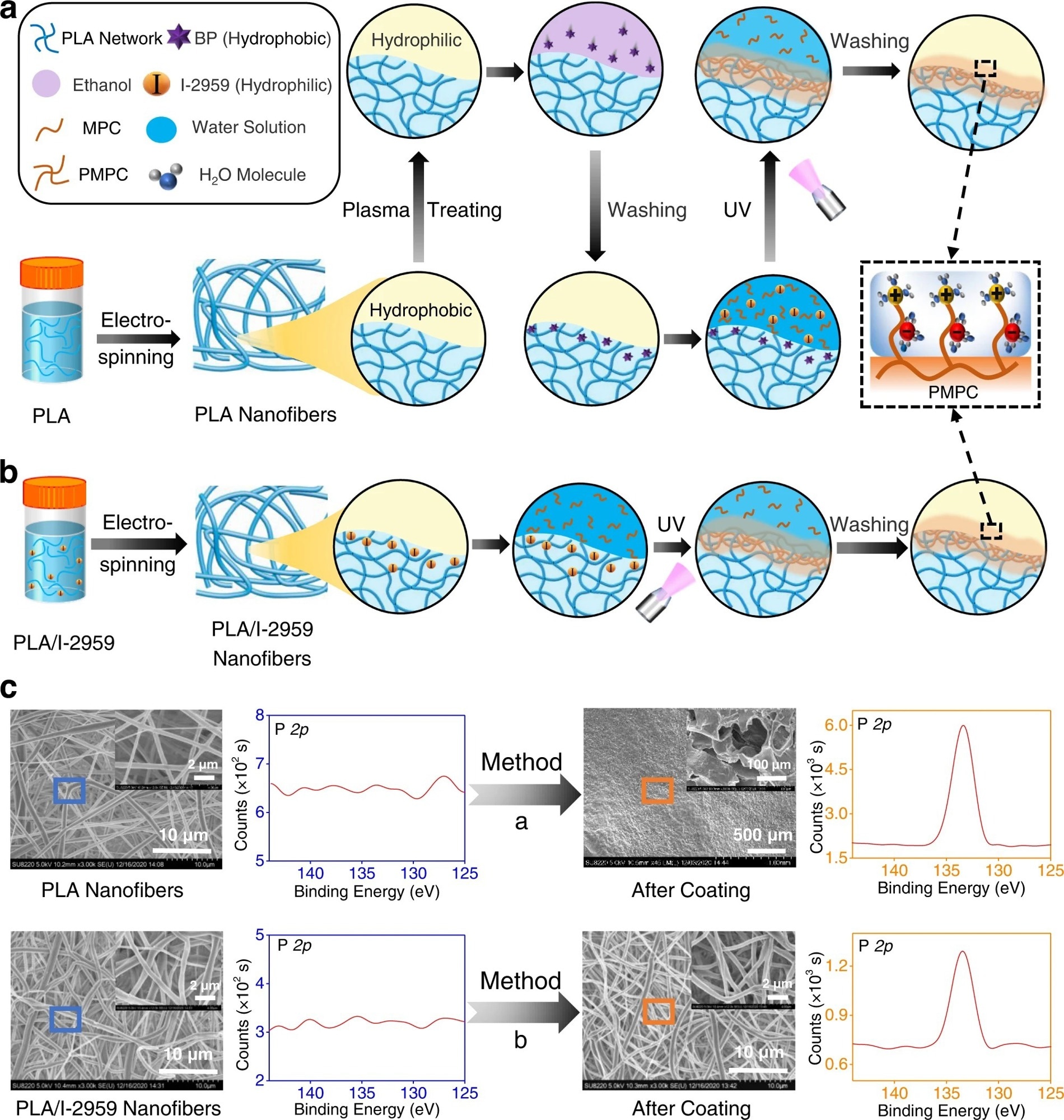
Figure 1. The comparison of our developed surface coating strategy to construct superlubricated nano-skin on electrospun nanofibers with previously reported method. a Schematic diagram of a slightly changed procedure from previous method17,18. PLA polylactic acid, BP benzophenone, MPC 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine, PMPC poly MPC, UV ultraviolet. b Schematic diagram of our optimized method of subsurface-initiated polymerization. c Representative SEM and XPS results of electrospun nanofibers for the comparison of surface morphology and elemental composition between the method in a and in b. The experiments are replicated three times independently with similar results. © Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Zhai, W. et al. (2022)
These nanofibrous membranes are also used for in vivo treatments that require direct human tissue contact. The effectiveness of the application of electrospun nanofibers depends on their surface performance. The electrospun nanofiber’s surface properties, such as patterned structure and fiber orientation, are effectively adjusted via various methods.
The incorporation of these properties improves the cell growth capacity on the fiber surface along with cellular adhesion, which plays an important role in the acceleration of the tissue regeneration process. Nevertheless, uncontrolled cell growth and adhesion to adjacent tissues lead to irretrievable consequences.
Non-Specific Cell Adhesion Property of Electrospun Membranes
Electrospun polylactic acid (PLA)-based membranes (e.g., DK-film) are clinically used for anti-adhesion purposes. This membrane forms a barrier between the injured tissues. However, one of the disadvantages of this membrane is that it adheres to the tissue surface. Therefore, it is extremely crucial to create an electrospun membrane with superior non-adhesive surface properties to prevent post-operative adhesion.
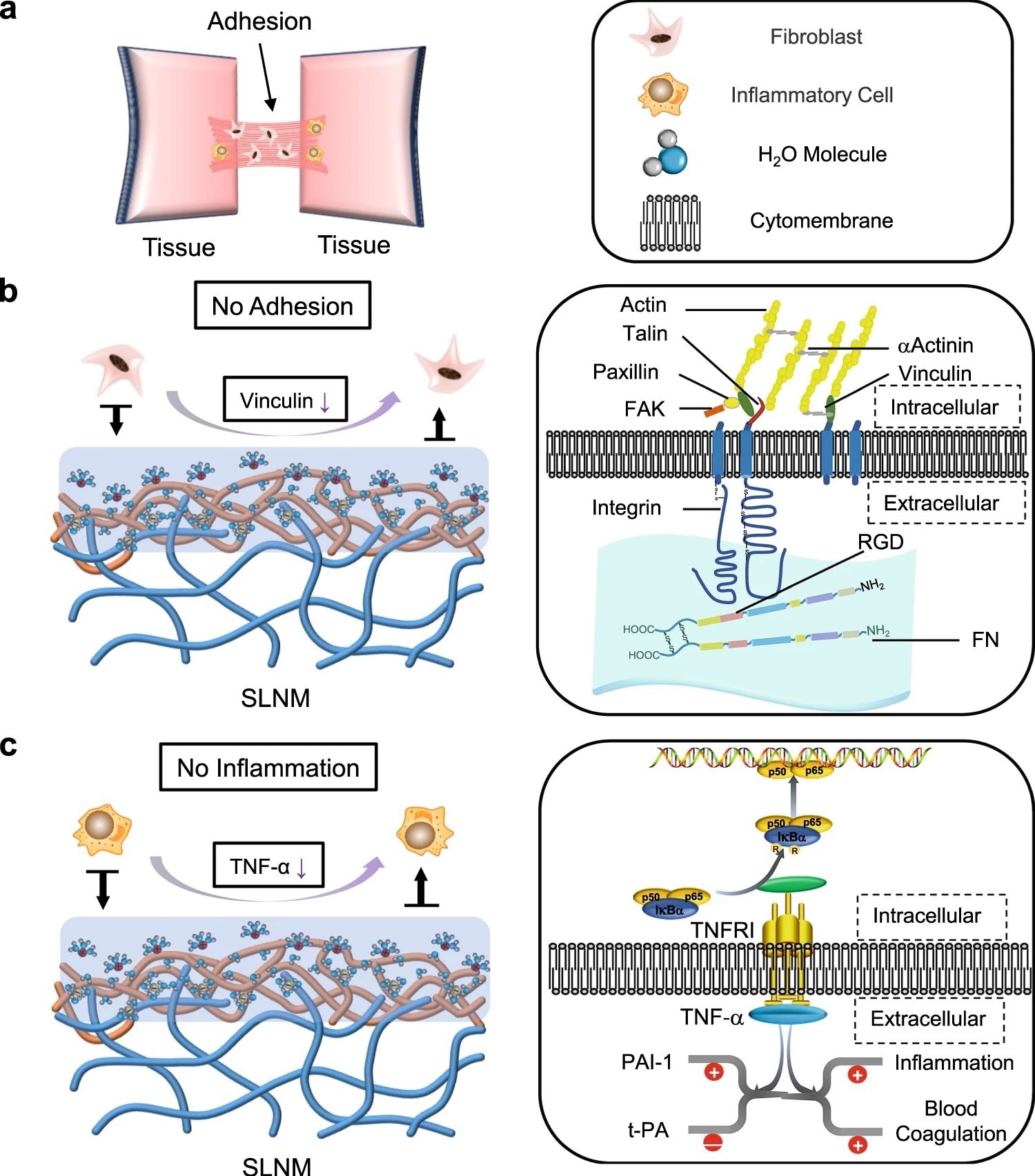
Hydration lubrication could be effectively used to develop nanofibrous membranes with non-adhesive surfaces. Mechanistically, polyelectrolyte polymers (e.g., poly (2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) (PMPC)) exhibit strong adsorption to the hydration layer due to the zwitterionic charges and, subsequently, promote an extremely low coefficient of friction (COF) between the sliding surfaces. This condition prevents non-specific cell adhesion.
Optimization of the interfacial bonding between the substrate polymer chains of nanofibers and the zwitterionic polymer chains in the coating is a challenging task. Although surface modification methods (e.g., grafting polymer chains) are used for this purpose, they cannot develop strong zwitterionic coatings. This is because PLA is sensitive to organic solvents and gets dissolved during surface modification.
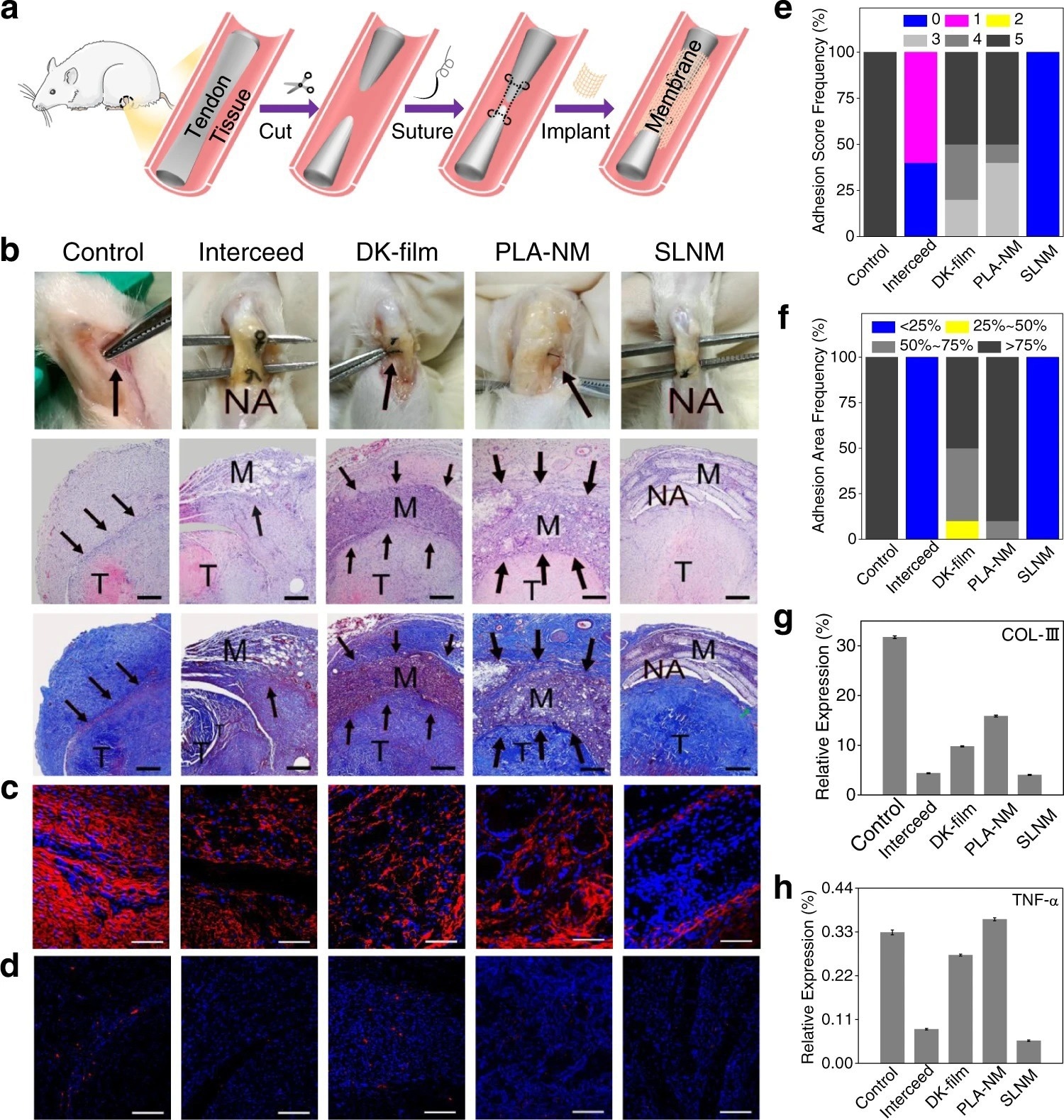
Figure 2. In vivo antitissue adhesion properties of the superlubricated electrospun nanofibrous membranes based on rat tendon adhesion model. a Schematic diagram showing the overall animal test process. b Photos of the harvested tendon on 14 d following implantation and H&E staining as well as Masson staining images. Scale bar: 500 µm. The black arrows point to adhesion site. M membrane. T tendon. NA no adhesion. Representative confocal laser scanning microscopic images for the immunofluorescent staining of c COL-III (scale bar: 100 µm) and d TNF-α (scale bar: 200 µm). Red color represents targeted protein and blue color represents cell nucleus. Comparison of e Adhesion score, f Adhesion area, and relative expression levels of g COL-III as well as h TNF-α for the control, Interceed, DK-film, PLA-NM, and SLNM groups, respectively. The experiments in b–d are replicated three times independently with similar results. © Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Zhai, W. et al. (2022)
Development of Superlubricated Nano-skin on Electrospun Nanofibers
In a previous method, after soaking in benzophenone, the electrospun nanofibrous membranes were immersed in an aqueous solution of methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine (MPC) monomer, which is a hydrophilic initiator 2-hydroxy-1-[4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)phenyl]-2-methyl-1-propanone (I-2959). The next step was to expose to ultraviolet light, for 30 minutes, on each side. The membrane was rinsed with enough deionized water to remove the weakly linked PMPC molecules. The newly synthesized surface-functionalized electrospun PLA nanofibers containing PMPC on the surface exhibited hydration lubrication performance.
Recently, in situ superlubricated nano-skin (SLNS) was grown (inside-out) on an electrospun nanofiber surface. During the electrospinning process, I-2959 (hydrophilic small molecules) self-arranged in the subsurface of the PLA nanofibers (hydrophobic polymer). The main advantage of this technique is that the second initiator outside the nanofibers is not required. As stated above, photopolymerization was performed by subjecting both sides of the electrospun PLA/I-2959 nanofibrous membranes to ultraviolet rays for 30 minutes, which was then immersed in an aqueous MPC monomer solution. The electrospun nanofiber membrane was rinsed with deionized water to remove unbound MPC and, thereby, superlubricated membranes were synthesized.
Both the techniques described were compared using various analytical tools, such as X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The surface elemental compositions of the newly synthesized superlubricated membranes were analyzed using XPS.
The electrospun nanofiber synthesized using the first method showed the presence of a phosphorous element, which originates from PMPC. Hence, XPS data indicated that PMPC coating was successfully prepared in the first method. However, a SEM analysis showed prominent damage to nanofibers, which strongly suggests that hydrogel-skin coating cannot be applied to nanofibers. Nevertheless, SEM and XPS data of the newly developed superlubricated nano-skin (SLNS) showed successful coating without destroying nanofiber structures.
Importantly, the in situ grown superlubricated coating formed on the electrospun nanofiber surface with a thickness of around 1 to 10 nm. Additionally, the COF was lower than 0.025. The newly developed nanofibrous membranes exhibited ideal tensile property and biocompatibility.
Figure 3. Potential antiadhesion mechanism of the superlubricated electrospun nanofibrous membranes. a Schematic diagram showing the occurrence of postoperative tissue adhesion. Interstitial fibrosis and inflammation are involved in this process. Schematic diagrams showing the mechanisms of b inhibiting fibrosis and c reducing inflammation based on the tenacious hydration layer formed surrounding the zwitterionic phosphorylcholine groups on the SLNM surface. © Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Zhai, W. et al. (2022)
Anti-adhesion Performance of Superlubricated Nano-Skin on Electrospun Nanofibers
The newly developed SLNM with the superlubricated nano-skin exhibited significant anti-adhesion performance. Importantly, compared to two commercially used anti-adhesion products, namely, DK-film and intercede, the newly synthesized material showed greater anti-adhesion performance with a lower production cost. This finding was validated using an in vitro anti-cell adhesion test and an in vivo study (anti-tissue adhesion test) was also performed using rat abdominal adhesion and tendon adhesion models. In the future, the application of the newly developed superlubricated biomaterial could prevent post-operative adhesion.
News
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]