A team of international researchers led by Prof Martin Hegner, Investigator in CRANN and Trinity’s School of Physics developed an automated diagnostic platform that indicates bleeding – and thrombotic risks in one drop of blood within seconds (Nanoscale, “Towards personalised rapid label free miRNA detection for cancer and liver injury diagnostics in cell lysates and blood based samples”).
They exploit micro-resonators for real-time measurements of the evolving blood plasma clot strength. Along with the clinically measured clotting time, other parameters, from specific factor deficiency to global coagulation parameters to assess fibrinolysis, can be extracted.
These technical developments now open up the possibility to introduce a miniaturized global haemostasis assay with capability to fine-tune anti-coagulation therapies.
In collaboration with the multinational Hoffman-la-Roche they report a novel strategy for quick, reliable and quantitative diagnostics of expression patterns of non-coding short RNA in blood plasma or cell cultures. They directly detect label-free specific miRNA biomarkers relevant to cancer and adverse drug effects in blood-based samples (right image).
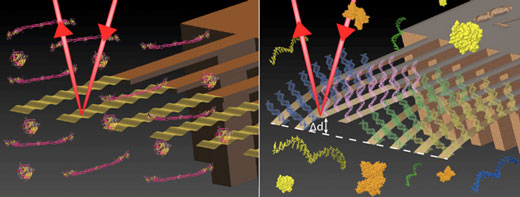
Image Credit: CRANN
News This Week
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]














Leave A Comment