Researchers have found that different facial temperatures correlate with chronic illnesses like diabetes and high blood pressure, and these can be detected using AI with thermal cameras.
They highlight the potential of this technology for promoting healthy aging by using thermal facial imaging to predict a person’s health status and biological age. The study also found that regular physical activities like jumping rope can decrease one’s thermal age, suggesting a possible link between exercise and thermal signs of aging.
A colder nose and warmer cheeks may be a telltale sign of rising blood pressure.
Researchers discovered that temperatures in different face regions are associated with various chronic illnesses, such as diabetes and high blood pressure. These temperature differences are not easily perceptible by one’s own touch but can instead be identified using specific AI-derived spatial temperature patterns that require a thermal camera and a data-trained model. The results were published recently in the journal Cell Metabolism. With further research, doctors could one day use this simple and non-invasive approach for early detection of diseases.
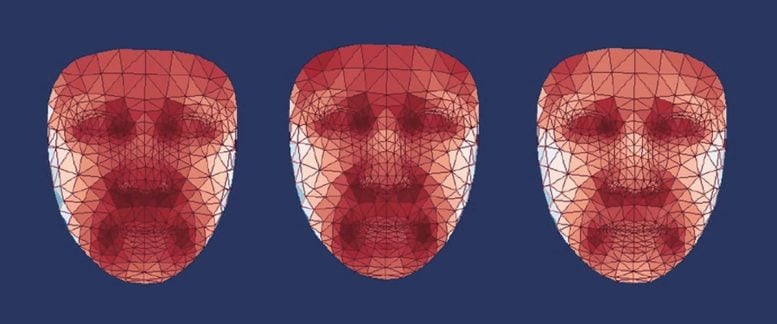
Average facial temperatures of three aging-status groups among women 50-60 years old. Credit: Zhengqing Yu and Jing-Dong J Han
Potential of Thermal Facial Imaging
“Aging is a natural process,” says Jing-Dong Jackie Han, the paper’s corresponding author at Peking University in Beijing. “But our tool has the potential to promote healthy aging and help people live disease-free.”
The team had previously used 3D facial structure to predict people’s biological age, which indicates how well the body is aging. Biological age is closely related to the risk of diseases, including cancer and diabetes. They were curious if other features of the face, such as temperature, could also predict aging rate and health status.
Age and Health Indicators Through Thermal Analysis
Han and her colleagues analyzed facial temperatures of more than 2,800 Chinese participants between the ages of 21 and 88. Then, the researchers used the information to train AI models that could predict a person’s thermal age. They identified several key facial regions where the temperatures were significantly related to age and health, including the nose, eyes and cheeks.
The team found the temperature of the nose decreases with age at a rate faster than other parts of the face, meaning people with warmer noses have a younger thermal age. At the same time, temperatures around the eyes tend to increase with age.
The team also found that people with metabolic disorders such as diabetes and fatty liver disease had faster thermal aging. They tended to have higher eye area temperatures than their healthy counterparts of the same age. People with elevated blood pressure also had higher cheek temperatures.
Exploring Thermal Aging and Disease Connections
By analyzing participants’ blood samples, the team revealed that the increase in temperatures around the eyes and cheeks was mainly because of an increase in cellular activities related to inflammation, such as repairing damaged DNAs and fighting infections. The increase in these activities led to a rise in temperatures in certain facial regions.
“The thermal clock is so strongly associated with metabolic diseases that previous facial imaging models were not able to predict these conditions,” Han says.
Thermal Imaging and Physical Activity
Due to this connection, the team set out to test if exercise could influence thermal age. They asked 23 participants to jump rope for at least 800 times daily for two weeks. To the team’s surprise, these participants reduced their thermal age by five years after just two weeks of exercise.
Next, the team wants to explore if they can use thermal facial imaging to predict other diseases, such as sleeping disorders or cardiovascular problems.
“We hope to apply thermal facial imaging in clinical settings, as it holds significant potential for early disease diagnosis and intervention,” Han says.
Reference: “Thermal facial image analyses reveal quantitative hallmarks of aging and metabolic diseases” by Zhengqing Yu, Yong Zhou, Kehang Mao, Bo Pang, Kai Wang, Tang Jin, Haonan Zheng, Haotian Zhai, Yiyang Wang, Xiaohan Xu, Hongxiao Liu, Yi Wang and Jing-Dong J. Han, 2 July 2024, Cell Metabolism.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.05.012
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China.
News
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]