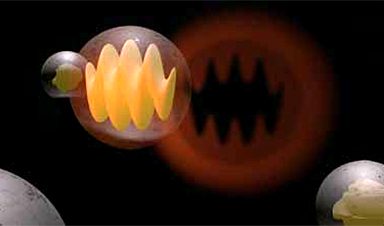
| Energy is information. Lengthening the time during which a system is capable of retaining energy before losing it to the local environment is a key goal for the development of quantum information. This interval is called the “coherence time”. Several studies have been performed with the aim of retarding decoherence. | |
| A study conducted by researchers at the University of Campinas’s Gleb Wataghin Institute of Physics (IFGW-UNICAMP) in São Paulo State, Brazil, in partnership with colleagues at the University of Michigan’s Physics Department in Ann Arbor, USA, and Sungkyunkwan University’s Advanced Institute of Nanotechnology (SAINT SKKU) in Seoul, South Korea, set out to understand the decoherence process on the femtosecond (10-15 s) timescale. | |
| An article describing the results was published in Physical Review Letters (“Non-Markovian Exciton-Phonon Interactions in Core-Shell Colloidal Quantum Dots at Femtosecond Timescales”). |
| In the study, interactions between excitons (excited electrons) and phonons (quantum units of vibrational energy in a crystal lattice) were observed on the femtosecond timescale. A femtosecond is one quadrillionth of a second. | |
| The use of a revolutionary ultrafast spectroscopy technique with high temporal and spectral resolution was fundamental to the success of the study, which was supported by FAPESP via a Young Investigator Grant awarded to Lázaro Aurélio Padilha Junior and a project conducted in partnership with the University of Michigan under the aegis of the São Paulo Research Foundation – FAPESP program São Paulo Researchers in International Collaboration (SPRINT). | |
| Padilha was one of the principal investigators for the project, and Diogo Burigo Almeida, then a postdoctoral fellow at Michigan, was one of the main authors. The experiment was performed with semiconducting nanocrystals dispersed in a colloidal solution at cryogenic temperatures. | |
| “We found that when the material is excited [by light], the light it emits changes color in under 200 femtoseconds. This is due to interaction between excitons and phonons. The excitons transfer part of the energy they receive to the crystal lattice. This causes a change of frequency and hence a change of emission color,” Padilha told. |
Image Credit: Image courtesy of the researchers
News This Week
COVID-19 still claims more than 100,000 US lives each year
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers report national estimates of 43.6 million COVID-19-associated illnesses and 101,300 deaths in the US during October 2022 to September 2023, plus 33.0 million illnesses and 100,800 deaths [...]
Nanomedicine in 2026: Experts Predict the Year Ahead
Progress in nanomedicine is almost as fast as the science is small. Over the last year, we've seen an abundance of headlines covering medical R&D at the nanoscale: polymer-coated nanoparticles targeting ovarian cancer, Albumin recruiting nanoparticles for [...]
Lipid nanoparticles could unlock access for millions of autoimmune patients
Capstan Therapeutics scientists demonstrate that lipid nanoparticles can engineer CAR T cells within the body without laboratory cell manufacturing and ex vivo expansion. The method using targeted lipid nanoparticles (tLNPs) is designed to deliver [...]
The Brain’s Strange Way of Computing Could Explain Consciousness
Consciousness may emerge not from code, but from the way living brains physically compute. Discussions about consciousness often stall between two deeply rooted viewpoints. One is computational functionalism, which holds that cognition can be [...]
First breathing ‘lung-on-chip’ developed using genetically identical cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and AlveoliX have developed the first human lung-on-chip model using stem cells taken from only one person. These chips simulate breathing motions and lung disease in an individual, [...]
Cell Membranes May Act Like Tiny Power Generators
Living cells may generate electricity through the natural motion of their membranes. These fast electrical signals could play a role in how cells communicate and sense their surroundings. Scientists have proposed a new theoretical [...]
This Viral RNA Structure Could Lead to a Universal Antiviral Drug
Researchers identify a shared RNA-protein interaction that could lead to broad-spectrum antiviral treatments for enteroviruses. A new study from the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC), published in Nature Communications, explains how enteroviruses begin reproducing [...]
New study suggests a way to rejuvenate the immune system
Stimulating the liver to produce some of the signals of the thymus can reverse age-related declines in T-cell populations and enhance response to vaccination. As people age, their immune system function declines. T cell [...]
Nerve Damage Can Disrupt Immunity Across the Entire Body
A single nerve injury can quietly reshape the immune system across the entire body. Preclinical research from McGill University suggests that nerve injuries may lead to long-lasting changes in the immune system, and these [...]
Fake Science Is Growing Faster Than Legitimate Research, New Study Warns
New research reveals organized networks linking paper mills, intermediaries, and compromised academic journals Organized scientific fraud is becoming increasingly common, ranging from fabricated research to the buying and selling of authorship and citations, according [...]
Scientists Unlock a New Way to Hear the Brain’s Hidden Language
Scientists can finally hear the brain’s quietest messages—unlocking the hidden code behind how neurons think, decide, and remember. Scientists have created a new protein that can capture the incoming chemical signals received by brain [...]
Does being infected or vaccinated first influence COVID-19 immunity?
A new study analyzing the immune response to COVID-19 in a Catalan cohort of health workers sheds light on an important question: does it matter whether a person was first infected or first vaccinated? [...]
We May Never Know if AI Is Conscious, Says Cambridge Philosopher
As claims about conscious AI grow louder, a Cambridge philosopher argues that we lack the evidence to know whether machines can truly be conscious, let alone morally significant. A philosopher at the University of [...]
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]