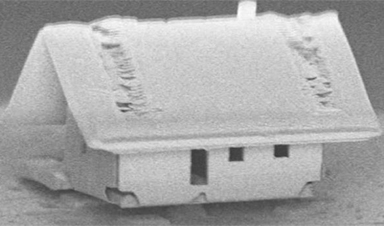
Scientists have assembled the world’s smallest house by using a combination of robotics and nanotechnology. The micro-house even has a door that a house mite can fit through.
The house has been devised, according to Engadget, as a proof-of-concept study from a nanorobotics team based at the Femto-ST Institute in Besancon, France. The researchers successfully assembled a new microbotics system termed the μRobotex nanofactory. By deploying tiny robots the researchers can construct microstructures within a large vacuum chamber. Within this they can fix components onto optical fiber tips at a level of nanometer accuracy.
The idea behind the microhouse construction was in order to demonstrate that the latest advances in optical sensing technologies can be used to manipulate ion guns (via gas injection), electron beams and finely controlled robotic piloting, so that a variety of different constructs can be rendered. As an example of the complexity and tiny scale of operations, the ion gun focuses on an area only 300 micrometers by 300 micrometers so that it can to fire ions onto the fiber tip and silica membrane.
This forms part of the area of lab-on-fiber technologies. In the early stages of this technology there were no robotic actuators available for for nanoassembly, which limited what engineers could achieve in terms of creating microstructures at the nano-scale. A recent advance in miniaturtized-sensing elements has addressed this. These sensing elements can be fitted onto fiber tips, allowing scientists to manipulate different components.
The technology allows enables scientists to insert optical fibers as thin as a strand of human hair into previously inaccessible locations such as jet engines, to detect radiation levels, or into human blood vessels to detect viral particles.
Image Credit: FEMTO-ST Institute
News This Week
COVID-19 still claims more than 100,000 US lives each year
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers report national estimates of 43.6 million COVID-19-associated illnesses and 101,300 deaths in the US during October 2022 to September 2023, plus 33.0 million illnesses and 100,800 deaths [...]
Nanomedicine in 2026: Experts Predict the Year Ahead
Progress in nanomedicine is almost as fast as the science is small. Over the last year, we've seen an abundance of headlines covering medical R&D at the nanoscale: polymer-coated nanoparticles targeting ovarian cancer, Albumin recruiting nanoparticles for [...]
Lipid nanoparticles could unlock access for millions of autoimmune patients
Capstan Therapeutics scientists demonstrate that lipid nanoparticles can engineer CAR T cells within the body without laboratory cell manufacturing and ex vivo expansion. The method using targeted lipid nanoparticles (tLNPs) is designed to deliver [...]
The Brain’s Strange Way of Computing Could Explain Consciousness
Consciousness may emerge not from code, but from the way living brains physically compute. Discussions about consciousness often stall between two deeply rooted viewpoints. One is computational functionalism, which holds that cognition can be [...]
First breathing ‘lung-on-chip’ developed using genetically identical cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and AlveoliX have developed the first human lung-on-chip model using stem cells taken from only one person. These chips simulate breathing motions and lung disease in an individual, [...]
Cell Membranes May Act Like Tiny Power Generators
Living cells may generate electricity through the natural motion of their membranes. These fast electrical signals could play a role in how cells communicate and sense their surroundings. Scientists have proposed a new theoretical [...]
This Viral RNA Structure Could Lead to a Universal Antiviral Drug
Researchers identify a shared RNA-protein interaction that could lead to broad-spectrum antiviral treatments for enteroviruses. A new study from the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC), published in Nature Communications, explains how enteroviruses begin reproducing [...]
New study suggests a way to rejuvenate the immune system
Stimulating the liver to produce some of the signals of the thymus can reverse age-related declines in T-cell populations and enhance response to vaccination. As people age, their immune system function declines. T cell [...]











Leave A Comment