One-dimensional (1D) nanostructures exhibit distinct properties that vary from those of bulk materials. They provide significant benefits in designing next-generation batteries due to facile electronic and ionic transport and strong tolerance to stress changes. Thus, contributing to the high performance of energy storage systems.
A review article published in Advanced Functional Materials systematically reviewed the latest research on rechargeable battery-based 1D nanostructures. This review highlighted a few important 1D nanostructuring methods and summarized in situ 1D nanostructure-based structural characterizations that facilitate atomic-scale monitoring of the structural evolution dynamics and reaction kinetics of electrode materials.
The stabilization of metal anodes and 1D nanostructuring in solid-state electrolytes have also been highlighted because they are not only vital for prevailing battery research trends but are also rarely covered in earlier studies.
1D Nanostructures in Batteries
Low-dimensional nanomaterials have unique properties that are not observed in macroscale materials and have applications in rechargeable batteries. Electrode materials with 1D nanostructures facilitate fast ion or electron transport, along with large contact areas between the electrode and electrolyte.
Incorporating 1D nanostructures with hierarchical, interfacial, or tubular porous geometries further accelerates electrochemical reactions by providing several active sites, short ion diffusion lengths, and strain relaxation.
The high aspect ratio of 1D nanostructures enables self-integration, which promotes the development of three-dimensional (3D) functional structures for additional battery components. However, such self-integration is unachievable through zero-dimensional (0D) or two-dimensional (2D) nanostructures owing to their low aspect ratio.
1D nanostructures stabilized metal anodes in rechargeable batteries by rendering lithiophilic 3D interlinked nanofiber-based scaffolds, which facilitate uniform metal deposition, enhance stability during stripping and metal plating, and provide adequate channels for ion transportation.
Additionally, 1D nanostructures offer novel experimental techniques and tools for the practical determination of the physicochemical characteristics of electrode materials, providing guidelines for developing high-performance batteries.
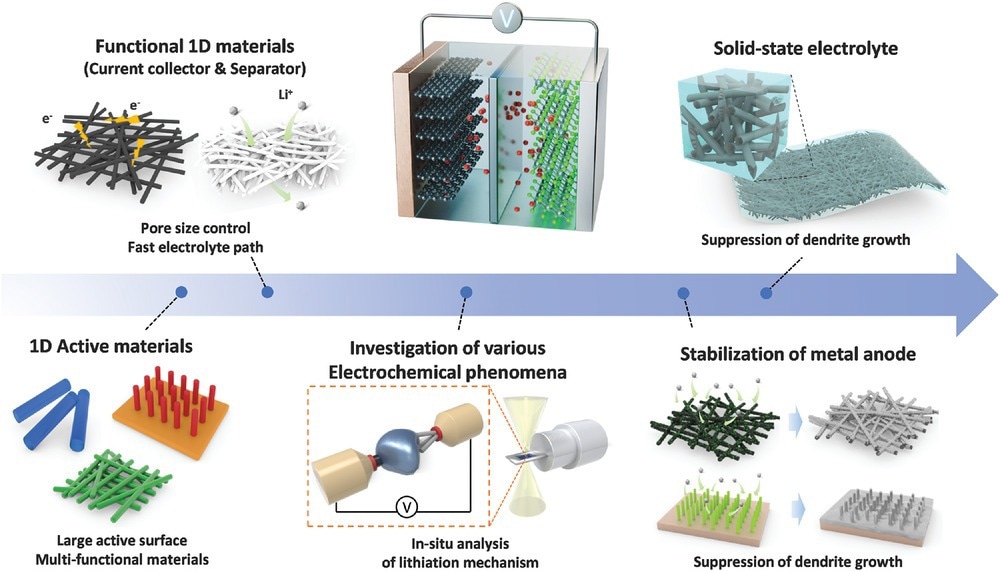
Schematic illustration on the employment of 1D nanostructures for multifunctional applications, ranging from active materials to solid-state electrolyte. © Cheong, J. Y., Cho, S.H., Lee, J., Jung, J.W., Kim, C., Kim, I.D. (2022).
Synthetic Methodologies Towards 1D Nanostructures and Their Limitations
Among the methodologies for synthesizing 1D nanostructures, solvothermal and hydrothermal synthetic strategies face several challenges, including structural predictability and control, which remain elusive in compositionally complex systems obtained via these synthetic routes. Hence, it is challenging to synthesize amorphous structures using solvothermal and hydrothermal methods.
Moreover, the formation and evolution mechanisms of various inorganic semiconducting nanostructures have been limited to hypothetical interpretations. Thus, integrating in situ transmission electron microscopy (TEM) or X-ray diffraction (XRD) into an autoclave enables the observation of reaction dynamics during crystal formation.
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is more favorable than the solvothermal or hydrothermal synthesis of 1D nanostructures because it allows precise or controlled synthesis. Moreover, their low production efficiency can be fixed by increasing the heating zones of the device to produce sufficient material. Although most CVD processes occur at high temperatures, synthesizing 1D nanostructures via plasma-enhanced CVD enables the process at a lower temperature.
On the other hand, the key advantages of the electrodeposition approach are low-temperature synthesis and applicability to diverse metal substrates. Nevertheless, this method is limited by the difficulty in uniformly controlling the morphology. In addition, it is challenging to employ an insulating substrate for electrodeposition using a template or a template-free method.
Although the sol-gel process is efficient, it requires a high-quality gel precursor and additional post-reaction steps to remove by-products. Electrospinning selectively facilitates the production of continuous 1D nanofibers. However, the insolubility of polymer precursors restricts their adaptability.
Alternatively, 3D printing and lithography techniques are the latest methods for preparing highly porous micro-sized lattice structures. However, these methods are limited by a lack of reliable processes for obtaining sufficient yields, a lack of suitable materials, and multistep processes in lithography techniques. Thus, by overcoming these limitations, 3D nano-printing and lithography techniques can achieve substantial development in terms of utilization and productivity in the design of energy devices.
Scope of 1D Nanostructures in Batteries
Novel battery systems such as spin- and quantum-phase batteries can be developed using 1D nanostructures. While conventional batteries provide a sustained voltage bias that can power electronic circuits by storing chemical energy, a phase-coherence-based quantum phase battery offers a quantum circuit wave function with persistent phase bias.
Owing to the unique characteristics of quantum mechanics, researchers have anticipated that batteries in the quantum phase would experience faster charging. Using 1D nanostructures has also proven the viability of rechargeable spin batteries. By applying a strong magnetic field to nanomagnets in a magnetic tunnel junction, spin batteries may store energy in magnets rather than through chemical processes.
Thus, 1D nanostructures provide enormous potential for developing new batteries and serve as a foundation for studying electrochemical dynamics using in situ or operando characterization techniques.
Conclusion
In summary, 1D nanostructures have substantially contributed to advances in battery science. The short pathways of ion or electron transport, large surface areas, and the ability for effective strain relaxation of 1D nanostructures offer excellent electrochemical performances that are not found in bulk materials.
Furthermore, constructing a nanoscale probe with a single 1D nanostructure helps investigate the electrochemical dynamics and fundamental mechanism with high resolution. This will contribute to the development of future batteries.
In addition to electrochemical analysis, integrating artificial intelligence (AI) technology is expected to contribute to significant advancements in 1D nanostructuring for real-world battery applications.
News
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
Scientists Discover Simple Saliva Test That Reveals Hidden Diabetes Risk
Researchers have identified a potential new way to assess metabolic health using saliva instead of blood. High insulin levels in the blood, known as hyperinsulinemia, can reveal metabolic problems long before obvious symptoms appear. It is [...]
One Nasal Spray Could Protect Against COVID, Flu, Pneumonia, and More
A single nasal spray vaccine may one day protect against viruses, pneumonia, and even allergies. For decades, scientists have dreamed of creating a universal vaccine capable of protecting against many different pathogens. The idea [...]
New AI Model Predicts Cancer Spread With Incredible Accuracy
Scientists have developed an AI system that analyzes complex gene-expression signatures to estimate the likelihood that a tumor will spread. Why do some tumors spread throughout the body while others remain confined to their [...]
Scientists Discover DNA “Flips” That Supercharge Evolution
In Lake Malawi, hundreds of species of cichlid fish have evolved with astonishing speed, offering scientists a rare opportunity to study how biodiversity arises. Researchers have identified segments of “flipped” DNA that may allow fish to adapt rapidly [...]
Our books now available worldwide!
Online Sellers other than Amazon, Routledge, and IOPP Indigo Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artifcial Intelligence Global Health Care Equivalency In The Age Of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine And Artificial [...]
Scientists Discover Why Some COVID Survivors Still Can’t Taste Food Years Later
A new study provides the first direct biological evidence explaining why some people continue to experience taste loss long after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers have uncovered specific biological changes in taste buds that could help [...]
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]





















