The impact of different kinds of commercial metallic nanoparticles (nanosized zero valent iron (nZVI), bimetal nZVI-Pd, and nano-magnetite (nFe3O4)) for the recovery of soil co-contaminated with Cr and PCBs are evaluated in a recent article published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The implementation of restoration solutions for soil degraded with a combination of pollutants (metal(loid)s and chemical products) has rarely been studied. The results suggest that the introduction of nZVI or nZVI-Pd, as well as pseudo-anaerobic settings, may well be employed to restore Cr and PCB-contaminated soil.
Soil Contamination Due to Chromium
Soil contamination is a global problem. It degrades the ecological functions supplied by the soil, reduces agricultural production, and has a negative influence on human health.
The bulk of contaminants come from man-made sources such as commercial activities, quarrying, public transit, and sewer waste treatment on soil.
The primary pollutants detected in European soils are metals and metalloids. As environmental pollutants, they are non-biodegradable and hence linger for long durations.
Due to its highly anti-corrosive characteristics, chromium (Cr) is extensively employed in a variety of industrial applications. Metallurgical operations, tanneries, wood processing, galvanizing, and petrochemical industries are just a few examples.
Cr (III), which presents as impermeable oxide and hydroxide cations, and Cr (VI), which emerges as oxyanion, are by far the most frequent types of Cr found as soil minerals.
Cr (III) is rejected by the electrostatic repulsion of soil and so stays in soil solution, accessible to crops and other creatures. As a result of its high mobility and bioavailability, Cr (VI) is 1000 times more hazardous than Cr (III).
Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs): A Major Soil Pollutant
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs), like metallic materials, are biological chemical compounds that are permanent, extremely poisonous, and micropollutants, posing a concern to the ecosystem.
PCBs are a class of synthetic organic chemicals classified as POPs by the Stockholm Convention of 2001 owing to their high public health hazard and breakdown resilience. PCBs may be created inadvertently as by-products in a variety of biochemical procedures that use chlorine and hydrocarbons.
PCBs have been linked to spillage from power equipment, waste distribution to soil, garbage furnace fumes, leaks during transportation, evaporation and sedimentation from surface waterways, and leakage from improper treatment and disposal.
Use of Nanoparticles for Soil Remediation
Compared to conventional physio-chemical approaches, nanoscience has recently allowed the development of new cost-effective and ecologically sound restoration solutions.
The increased particular surface area of nanoparticles leads to faster reaction kinetics with contaminants. Many distinct nanomaterials, such as carbon nanotubes, inorganic materials, and activated carbons, have been explored for cleanup purposes, but nano zero valent iron (nZVI) particulates are the most extensively deployed.
The application of magnetized nanomaterials, such as nano magnetite (nFe3O4), for the rehabilitation of metal(loid) contaminated streams has gained popularity in recent decades. This is because of their higher absorption capabilities and magnetic characteristics, which allow for better membrane separation from the solid material.
The major goal of this research was to compare the efficacy of three kinds of commercial magnetite nanoparticles (nZVI, nZVI-Pd, and nFe3O4) for the restoration of industrialized soil polluted with Cr and PCBs.
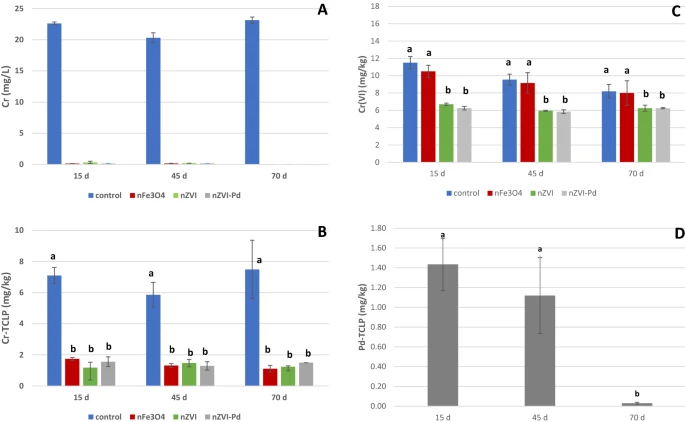
(A) Mean concentration of Cr (mg/L) in the aqueous extracts at the different sampling times. (B) Mean concentration of Cr (mg/kg) in TCLP extracts at the different sampling times. (C) Mean concentration of Cr(VI) (mg/kg) in soil samples at the different sampling times. For each sampling time, bars with the same letter do not differ significantly (p < 0.05). (D) Mean concentration of Pd (mg/kg) in TCLP extracts at the different sampling times for nZVI-Pd treated soils. Bars with the same letter do not differ significantly (p < 0.05). © Gil-Díaz, M., Pérez, R., Alonso, J., Miguel, E., Diez-Pascual, S. and Lobo, M., (2022)
Research Findings and Conclusion
When nZVI, nZVI-Pd, or nFe3O4 were added to soil polluted with Cr and PCBs, the leakage of Cr in the soil was greatly decreased, and the immobilization remained stable over a period of 70 days under the simulated conditions.
When contrasted to nFe3O4, Te nZVI and nZVI-Pd were more successful in converting Cr (VI) to Cr (III). The PCB levels in soils sprayed with the three kinds of iron nanoparticles fell considerably after 15 days of engagement between soil and nanoparticles.
Control soils demonstrated a drop in PCBs content during the 45-day sample period due to environmental remediation, reaching levels comparable to those seen in soil amended with nZVI and nZVI-Pd. In this case, biodegradation might be possible if the soil was just poisoned with PCBs, but not if it also included metals like Cr.
Tus, nZVI-based nanoparticles show modest performance in PCB-polluted soil cleanup. Both nZVI particles, on the other hand, achieved effective Cr absorption in soils.
The findings show that the introduction of nZVI or nZVI-Pd, as well as pseudo-anaerobic settings, might be employed to recover Cr and PCB-contaminated soils.
News
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]
Scientists Develop Spray-On Powder That Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds
KAIST scientists have created a fast-acting, stable powder hemostat that stops bleeding in one second and could significantly improve survival in combat and emergency medicine. Severe blood loss remains the primary cause of death from [...]
Oceans Are Struggling To Absorb Carbon As Microplastics Flood Their Waters
New research points to an unexpected way plastic pollution may be influencing Earth’s climate system. A recent study suggests that microscopic plastic pollution is reducing the ocean’s capacity to take in carbon dioxide, a [...]
Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine – New book from Frank Boehm
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
New Book! NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artificial Intelligence
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
Miller School Researchers Pioneer Nanovanilloid-Based Brain Cooling for Traumatic Injury
A multidisciplinary team at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine has developed a breakthrough nanodrug platform that may prove beneficial for rapid, targeted therapeutic hypothermia after traumatic brain injury (TBI). Their work, published in ACS [...]
COVID-19 still claims more than 100,000 US lives each year
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers report national estimates of 43.6 million COVID-19-associated illnesses and 101,300 deaths in the US during October 2022 to September 2023, plus 33.0 million illnesses and 100,800 deaths [...]
Nanomedicine in 2026: Experts Predict the Year Ahead
Progress in nanomedicine is almost as fast as the science is small. Over the last year, we've seen an abundance of headlines covering medical R&D at the nanoscale: polymer-coated nanoparticles targeting ovarian cancer, Albumin recruiting nanoparticles for [...]
Lipid nanoparticles could unlock access for millions of autoimmune patients
Capstan Therapeutics scientists demonstrate that lipid nanoparticles can engineer CAR T cells within the body without laboratory cell manufacturing and ex vivo expansion. The method using targeted lipid nanoparticles (tLNPs) is designed to deliver [...]