| Researchers at Duke University have developed a unique type of nanoparticle called a “nanorattle” that greatly enhances light emitted from within its outer shell. | |
| Loaded with light scattering dyes called Raman reporters commonly used to detect biomarkers of disease in organic samples, the approach can amplify and detect signals from separate types of nanoprobes without needing an expensive machine or medical professional to read the results. | |
| In a small proof-of-concept study, the nanorattles accurately identified head and neck cancers through an AI-enabled point-of-care device that could revolutionize how these cancers and other diseases are detected in low-resource areas to improve global health. | |
| The results appear in the Journal of Raman Spectroscopy (“Machine Learning Using Convolutional Neural Networks for SERS Analysis of Biomarkers in Medical Diagnostics”). |
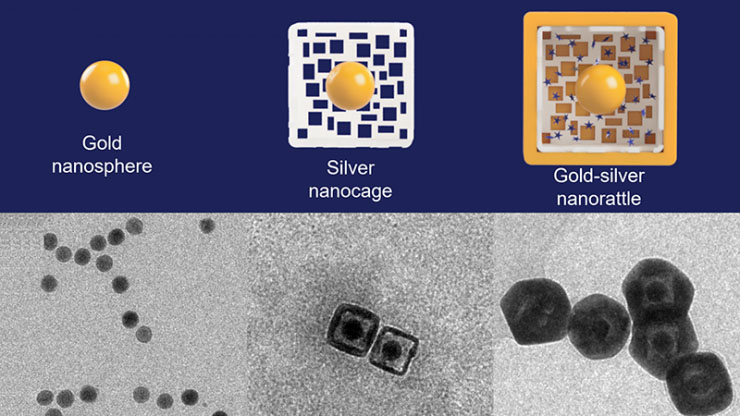
The starting gold nanosphere seeds (left) are surrounded by a hollow, porous silver cage (middle) and become a nanorattle filled with light-scattering dyes inside a gold outer shell (right). The nanorattles can amplify and detect signals from separate types of nanoprobes without needing an expensive machine or medical professional to read the results. (Image: Duke University)
| “The concept of trapping Raman reporters in these so-called nanorattles has been done before, but most platforms had difficulty controlling the interior dimensions,” said Tuan Vo-Dinh, the R. Eugene and Susie E. Goodson Distinguished Professor of Biomedical Engineering at Duke. | |
| “Our group has developed a new type of probe with a precisely tunable gap between the interior core and outer shell, which allows us to load multiple types of Raman reporters and amplify their emission of light called surface-enhanced Raman scattering,” Vo-Dinh said. | |
| To make nanorattles, researchers start with a solid gold sphere about 20 nanometers wide. After growing a layer of silver around the gold core to make a larger sphere (or cube), they use a corrosion process called galvanic replacement that hollows out the silver, creating a cage-like shell around the core. The structure is then soaked in a solution containing positively charged Raman reporters, which are drawn into the outer cage by the negatively charged gold core. The outer hulls are then covered by an extremely thin layer of gold to lock the Raman reporters inside. | |
| The result is a nanosphere (or nanocube) about 60 nanometers wide with an architecture that resembles a rattle—a gold core trapped within a larger outer silver-gold shell. The gap between the two is only about a few nanometers, which is just large enough to fit the Raman reporters. | |
| Those tight tolerances are essential to controlling the Raman signal enhancement the nanorattles produce. | |
| When a laser shines on the nanorattles, it travels through the extremely thin outer shell and hits the Raman reporters within, causing them to emit light of their own. Because of how close the surfaces of the gold core and the outer gold/silver shell are together, the laser also excites groups of electrons on the metallic structures, called plasmons. These groups of electrons create an extremely powerful electromagnetic field due to the plasmons’ interaction of the metallic core-shell architecture, a process called plasmonic coupling, which amplifies the light emitted by the Raman reporters millions of times over. | |
| “Once we had the nanorattles working, we wanted to make biosensing devices to detect infectious diseases or cancers before people even know they’re sick,” Vo-Dinh said. “With how powerful the signal enhancement of the nanorattles is, we thought we could make a simple test that could be easily read by anybody at the point-of-care.” | |
| In the new paper, Vo-Dinh and his collaborators apply the nanorattle technology to a lab-on-a-stick device capable of detecting head and neck cancers, which appear anywhere between the shoulders and the brain, typically in the mouth, nose and throat. Survival rate for these cancers have hovered between 40 and 60 percent for decades. While those statistics have improved in recent years in the United States, they have gotten worse in low-resource settings, where risk factors such as smoking, drinking and betel nut chewing are much more prevalent. | |
| “In low-resource settings, these cancers often present in advanced stages and result in poor outcomes due in part to limited examination equipment, lack of trained healthcare workers and essentially non-existent screening programs,” said Walter Lee, professor of head and neck surgery & communication sciences and radiation oncology at Duke, and a collaborator on the research. | |
| “Having the ability to detect these cancers early should lead to earlier treatment and improvement in outcomes, both in survival and quality of life,” Lee said. “This approach is exciting since it does not depend on a pathologist review and potentially could be used at the point of care.” | |
| The prototype device uses specific genetic sequences that act like Velcro for the biomarkers the researchers are looking for — in this case, a specific mRNA that is overly abundant in people with head and neck cancers. When the mRNA in question is present, it acts like a tether that binds nanorattles to magnetic beads. These beads are then concentrated and held in place by another magnet while everything else gets rinsed away. Researchers can then use a simple, inexpensive handheld device to look for light emitted from the nanorattles to see if any biomarkers were caught. | |
| In the experiments, the test determined whether or not 20 samples came from patients that had head and neck cancer with 100% accuracy. The experiments also showed that the nanorattle platform is capable of handling multiple types of nanoprobes, thanks to a machine learning algorithm that can tease apart the separate signals, meaning they can target multiple biomarkers at once. This is the goal of the group’s current project funded by the National Institutes of Health. | |
| “Many mRNA biomarkers are overly abundant in multiple types of cancers, while other biomarkers can be used to evaluate patient risk and future treatment outcome,” Vo-Dinh said. “Detecting multiple biomarkers at once would help us differentiate between cancers, and also look for other prognostic markers such as Human Papillomavirus (HPV), and both positive and negative controls. Combining mRNA detection with novel nanorattle biosensing will result in a paradigm shift in achieving a diagnostic tool that could revolutionize how these cancers and other diseases are detected in low-resource areas”. |
News
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]





















