Increased water consumption worldwide has resulted in low-quality water resources utilized for crop irrigation in the agricultural sector; however, these sources tend to be contaminated. New research published in the MDPI sustainability explores whether the addition of nanofertilizers can enhance these water sources.
Here, the team investigated the effects of nanofertilizers on saline water sources in tomato crops.
Harmful Effects of Conventional Fertilizers
Owing to the extensive utilization of mineral fertilizers and pesticides, traditional fertilizers have produced several ecological threats, including food poisoning and soil deterioration.
Excess nitrogen in the air and water from fertilizers can cause respiratory problems, heart illness, and many malignancies, as well as hinder agricultural development and boost hypoallergenic pollen output.
Keeping in mind the low effectiveness of traditional fertilizer use (ranging from 20 to 40 %), a large proportion of these fertilizers eluted into aquifers and ultimately streams, causing financial damage, eutrophication, and public health complications.
Are Nanofertilizers a Viable Option?
Considering these limitations of conventional fertilizers, nano fertilizers are an advantageous alternative. Nanofertilizers are thought to be interesting substances because they exhibit the distinctive properties of nanoparticles at the nanoscale.
Many studies have found advantages regarding the usage of nanofertilizers on agricultural plants such as hay, soy, potatoes, maize, and oats. Benefits include improved quality of the fruit, production, and storability, as well as reduced nutrient leakage into the soil following harvesting of crops.
Iron, copper, selenium, and zinc are the most frequent minerals that are already used as nutrient-based nanofertilizers.
Why Quality of the Irrigation Water Matters?
Irrigation quality of water is a constraining element in the agriculture industry worldwide, with different irrigation water quality parameters such as salinity and sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), sodium, manganese as well as toxic substances.
When irrigation water has a high salt concentration and toxic substances, the water loses quality and accumulates in soil samples and produced crops. This problem has been exacerbated by the extensive use of wastewater in the cultivation of crops, which contains various toxins that may continue throughout the food chain.
Many substances, including hydrogel, biochar, and nanomaterials, have been used to purify water sources. Nanomaterials have been utilized to remove contaminants such as cadmium and chromium from polluted water; however, the usefulness of nanofertilizers in increasing the productivity of farmed plants watered with poor water quality requires additional investigation.
Why Tomato Plants?
Tomato plants (Solanum Lycopersicum L.) are regarded as one of the most important vegetable crops worldwide due to their great gastronomic and commercial importance, in addition to their nutritious significance. As a result of their high oxide concentration, tomatoes are naturally strong in antioxidants and may defend against prostate cancer as well as protect human skin from UV radiation.
This crop has a long growing season and high water demands, and it can yield under a variety of conditions, including salt stress, dehydration, copper neurotoxicity, and continual watering with salty water. As a result, the current study was designed to determine if nanofertilizers (Cu and Se), either individually or in combination, can reduce the influence of salty water on tomatoes’ productivity and quality.
Result Findings
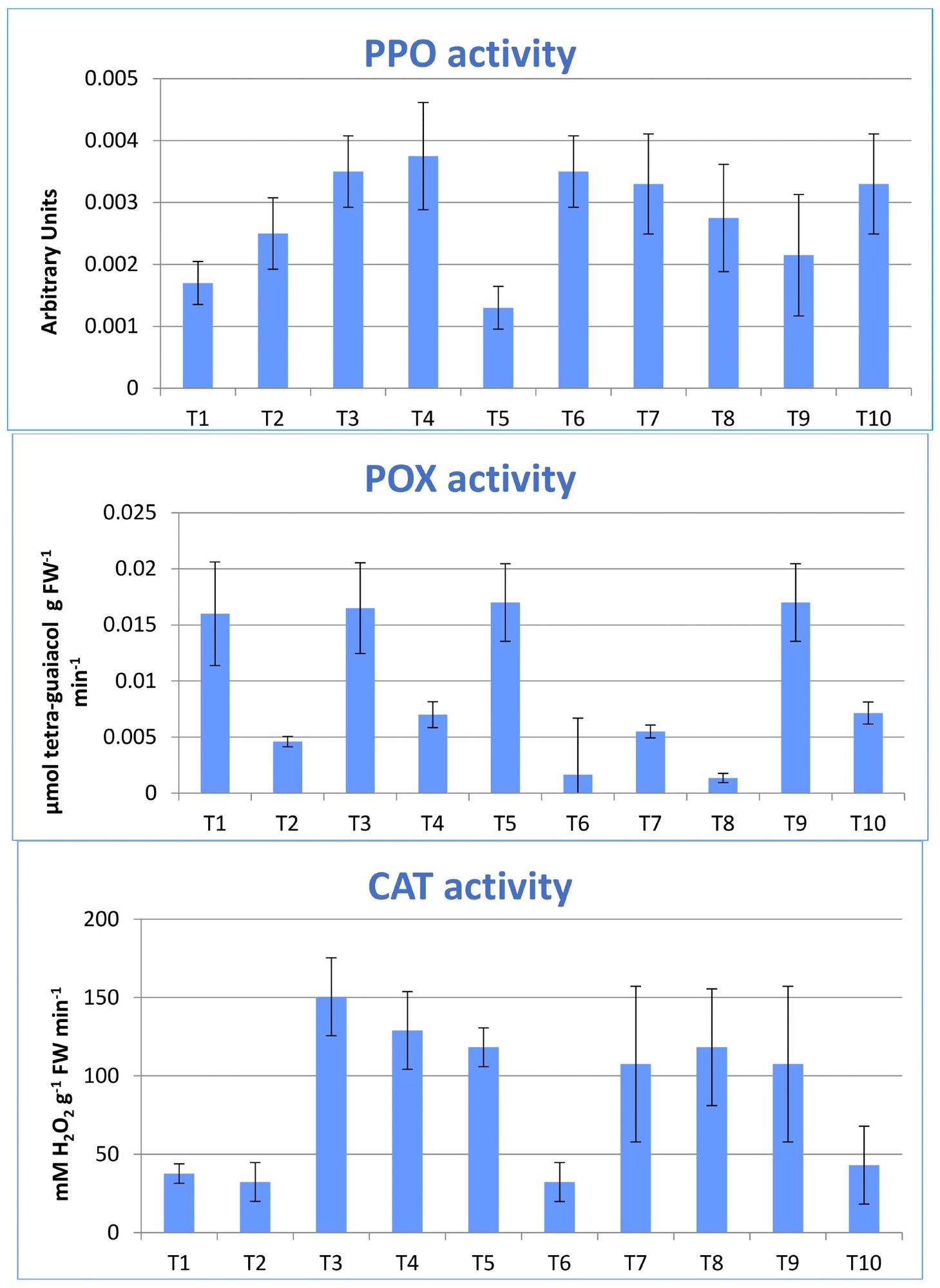
Undertreatment with average quality of water and coupled nano-Se, the longest branch growth (69.8 cm) was attained. The maximum chlorophyll concentration (79.7 SPAD) was measured following nano-Se administration and watering with low-quality water.
Among all tested properties, the number of branches per plant was the only one that had a non-significant influence on vegetative development. The highest amount of fruit yield (2.07 kg plant-1) and total soluble solid content (9.24 %) was acquired under irrigated agriculture using low quality of water (IW3) and 100 mg L-1 of nano-Cu.
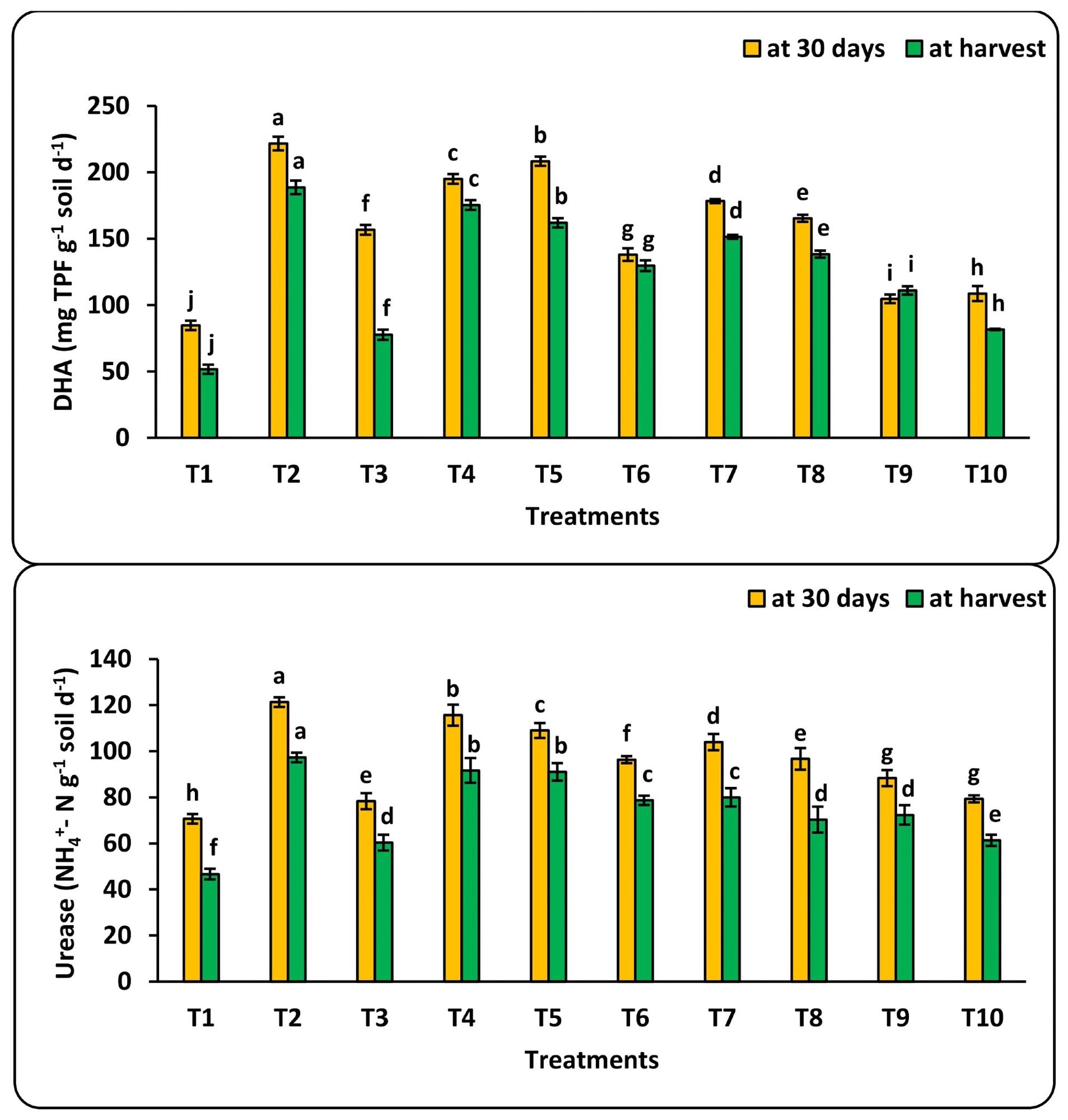
The highest value of vitamin C content (mg 100 g-1 FW) was achieved under fertigation using low water quality (IW3) and a combination of 100 mg L-1 of nano-Se and nano-Cu. Furthermore, the microbiological populations of bacterium, fungi, and actinobacteria increased after 30 days of transplantation and declined in all treatment at harvests due to the negative effect of poor irrigation water quality.
In short, the controlled utilization of bio-nano fertilizers was deemed successful in boosting the productivity as well as the quality of the produced crops.
News
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]





















