Doxorubicin (DOX) is a powerful anti-cancer medication, and efforts have been made to design nanostructures for delivering it to cancerous cells. The nanostructures increase the cytotoxic effects of DOX on cancerous cells, while reducing the negative effects on healthy cells.
In a research paper published in the journal Scientific Reports, layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanostructures were developed to administer DOX effectively.
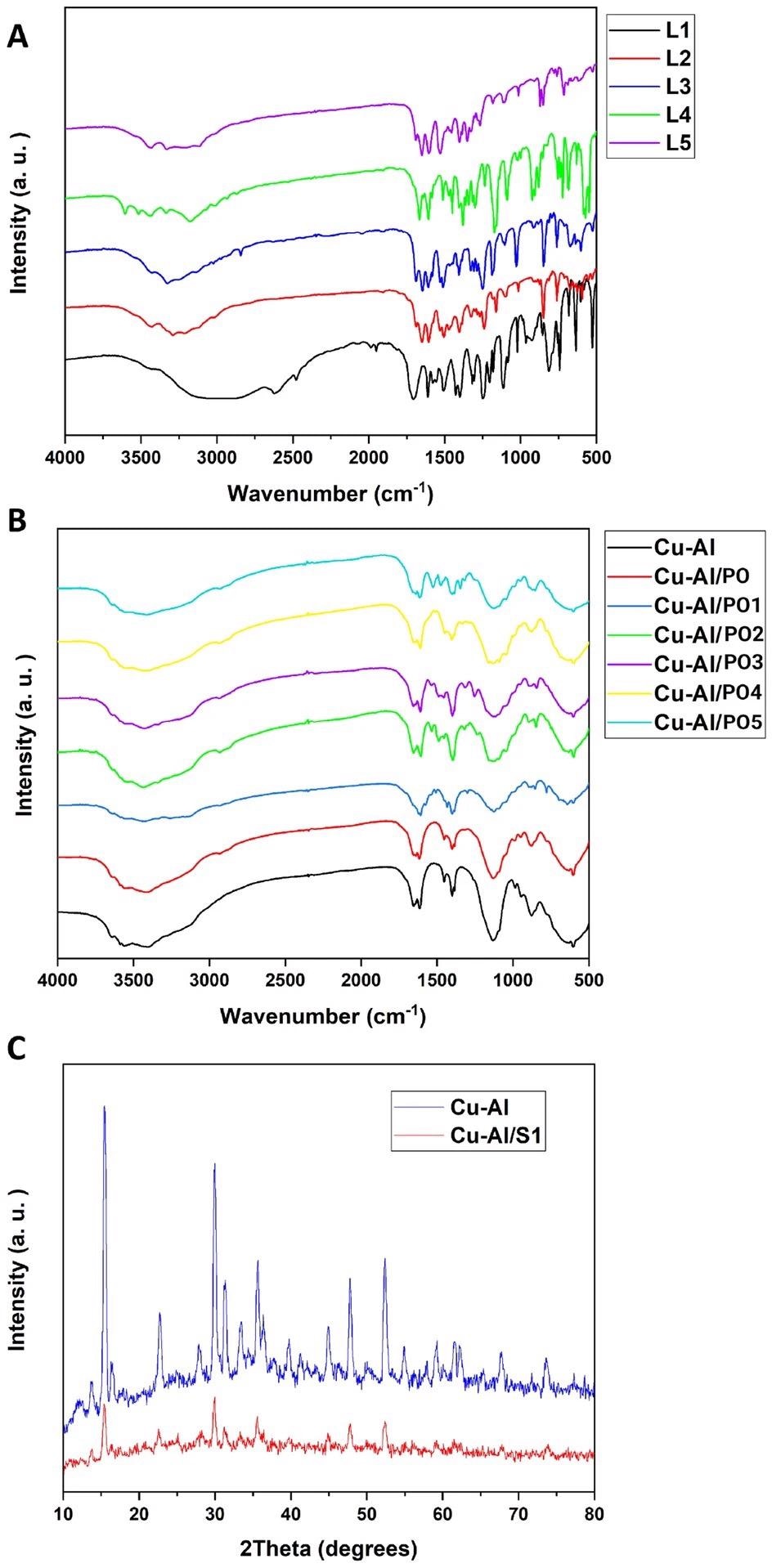
Figure 1. FTIR spectra of the synthesized nanomaterials (A,B). XRD results of the synthesized nanomaterials (C). S1 in part (C) stands for one of the PO’s. © Kiani, M., Bagherzadeh, M., Ghadiri, A. M., Makvandi, P., & Rabiee, N. (2022).
Cancer, and How Nanotechnology Can Help
Cancer accounts for the second-largest mortality rate after cardiac illnesses, with susceptibility to tumor development determined by multiple factors like age, family history and carcinogen exposure.
Chemotherapy is the most often used cancer treatment. However, complex encounters in the cancer microenvironment, as well as cancer cells’ capacity to proliferate and flip between molecular routes to guarantee their preservation, have led to the tumors developing resistance against treatments.
Doxorubicin (DOX) is widely used in tumor treatment because it may limit DNA replication by decreasing the action of topoisomerase enzymes, suppressing cell cycle progress and ultimately directing tumors towards cellular death.
Resistance against DOX has been caused by a range of factors, including discharge of doxorubicin by P-glycoprotein from tumor cells, Bcl-2 overexpression, apoptotic suppression, and abnormal expression of epigenetic and genetic variables. As a result, research has concentrated on developing nanostructured delivery mechanisms for doxorubicin to increase its cancer-suppressing effectiveness.
Benefits of LDH as Drug Deliver Systems
Nanotechnology offers fresh promise for reducing resistance against treatments and improving the efficacy of chemotherapy drugs in cancer treatment.
Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) are multilayer nanoscale structures and anion clays having a hydrotalcite crystalline structure generated by two metallic ions, comprising a trivalent and a divalent metallic ion, an -OH group, an H2O molecule, and an interlayer anion.
Due to their distinctive multilayer architecture and interlayer anion exchanging capability, LDH nanostructures have paved the way in the biomedicinal domain. One of the most significant uses of LDH nanostructures in the administration of drugs is the incorporation of a specific chemical into LDHs through an interlayer anionic exchange.
LDHs have excellent drug loading capability, a large surface area, great durability, and anion exchanging ability. These properties make them preferable for drug administration, especially when compared to other nanostructures like polymer nanoparticles (NPs).
More significantly, as LDHs have a dissoluble bulk layer at pH 5.0 (around the acidity level of the cancer microenvironment), they are great contenders for drug administration against tumors.
Advantages of Plantago Ovata
Plantago ovata (PO) is a classic botanical remedy with bioactive polysaccharides. It is an organically produced substance with advantages such as sustainable production, low cost, availability, and a good safety profile.
PO was initially employed to treat wounds. Subsequent research revealed that PO extracts possess a variety of medicinal properties, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammation, immunomodulation, and pain-relieving properties.
Important Findings of the Study
PO was utilized to modify the surfaces of Cu–Al LDH nanoscale structures to boost their capability as nanoscale drug administration systems. Doxorubicin, an anti-cancer medication, was stacked onto NPs once they were prepared, and characterization procedures showed proper fabrication and drug content.
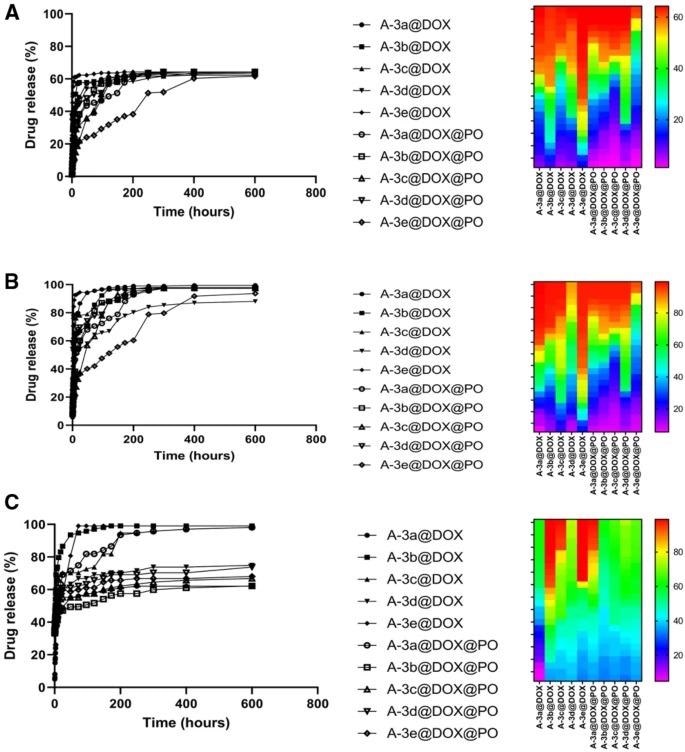
The drug discharge analysis indicated pH-sensitive discharge of doxorubicin from LDH NPs, with the largest discharge of anti-cancer medications occurring at pH 5.5 and the least amount of medication discharge occurring at pH 4.5, perhaps owing to the detrimental effect of lower and strongly acidic pH on NP architectures.
The MTT experiment exhibited great cytocompatibility of PO-incorporated Cu–Al LDH nanostructures, demonstrating partial and low cytotoxicity against HEK-293 and PC12 cells, while decreasing the viability of MCF-7 and HT-29 cells as cancerous cells.
Notably, the decrease in viability of HT-29 and MCF-7 cells was smaller in PO-incorporated LDH NPs than LDH nanoscale carriers without PO, which should be investigated further in future studies. The CLSM data demonstrated that LDH NPs delivered doxorubicin to the nucleus and cytoplasm of HEK-293 and MCF-7 cells.
Histological examination of renal tissue revealed no cellular deterioration, adequate cellular and tubular architecture, and zero bloodstream obstructions. This indicates the great cytocompatibility of PO-incorporated LDH nanostructures.
Antimicrobial testing revealed that Cu–Al LDH nanoparticles exhibited biotoxicity against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, and they may be used in treating microbial illnesses in future trials.
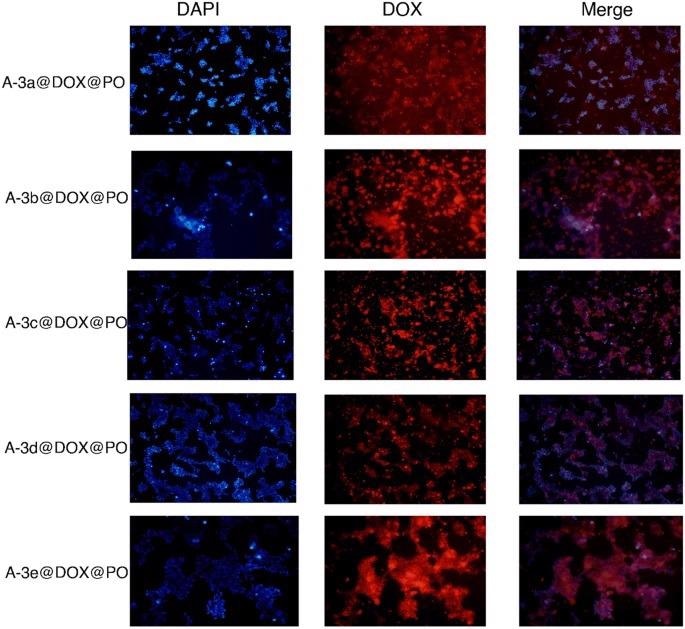
Figure 3. The CLSM images of the drug loaded nanocarriers-coated with leaf extracts treated with HEK-293 cell lines. The used concentration of the nanoparticles: 17.5 μg/mL. © Kiani, M., Bagherzadeh, M., Ghadiri, A. M., Makvandi, P., & Rabiee, N. (2022).
News
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
Scientists Discover Simple Saliva Test That Reveals Hidden Diabetes Risk
Researchers have identified a potential new way to assess metabolic health using saliva instead of blood. High insulin levels in the blood, known as hyperinsulinemia, can reveal metabolic problems long before obvious symptoms appear. It is [...]
One Nasal Spray Could Protect Against COVID, Flu, Pneumonia, and More
A single nasal spray vaccine may one day protect against viruses, pneumonia, and even allergies. For decades, scientists have dreamed of creating a universal vaccine capable of protecting against many different pathogens. The idea [...]
New AI Model Predicts Cancer Spread With Incredible Accuracy
Scientists have developed an AI system that analyzes complex gene-expression signatures to estimate the likelihood that a tumor will spread. Why do some tumors spread throughout the body while others remain confined to their [...]
Scientists Discover DNA “Flips” That Supercharge Evolution
In Lake Malawi, hundreds of species of cichlid fish have evolved with astonishing speed, offering scientists a rare opportunity to study how biodiversity arises. Researchers have identified segments of “flipped” DNA that may allow fish to adapt rapidly [...]
Our books now available worldwide!
Online Sellers other than Amazon, Routledge, and IOPP Indigo Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artifcial Intelligence Global Health Care Equivalency In The Age Of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine And Artificial [...]
Scientists Discover Why Some COVID Survivors Still Can’t Taste Food Years Later
A new study provides the first direct biological evidence explaining why some people continue to experience taste loss long after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers have uncovered specific biological changes in taste buds that could help [...]
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]





















