In an article published in the journal Scientific Reports, researchers presented the potentiostatic deposition used to electrodeposit nickel (Ni) and nickel-graphene (Ni-G) films on copper substrates. Myristic acid (MA) was employed to alter the plane of the electrodeposited coatings to create superhydrophobicity (SHP).
With water contact angles of 159° and 162°, respectively, the Ni-G films altered with MA (Ni-G-MA) and the Ni films altered with MA (Ni-MA) exhibited exceptional SHP qualities. When the surface morphology of the SHP films was examined with a scanning electron microscope (SEM), the findings showed that the Ni-G-MA and Ni-MA films had micro-nano structures.
The Fourier transform infrared spectrophotometer (FTIR) findings demonstrated that the grafting of the Ni-G-MA and Ni-MA films onto the copper metal was successful. Compared to Ni-MA, the Ni-G-MA film was more resistant to mechanical abrasion and had higher chemical stability.
The Ni-G-MA and Ni-MA films demonstrated long-term durability for about four months outdoors. Also, the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and potentiodynamic polarization results showed that the SHP film on the copper substrate had exceptional corrosion resistance in 0.5 molar sodium chloride (NaCl).
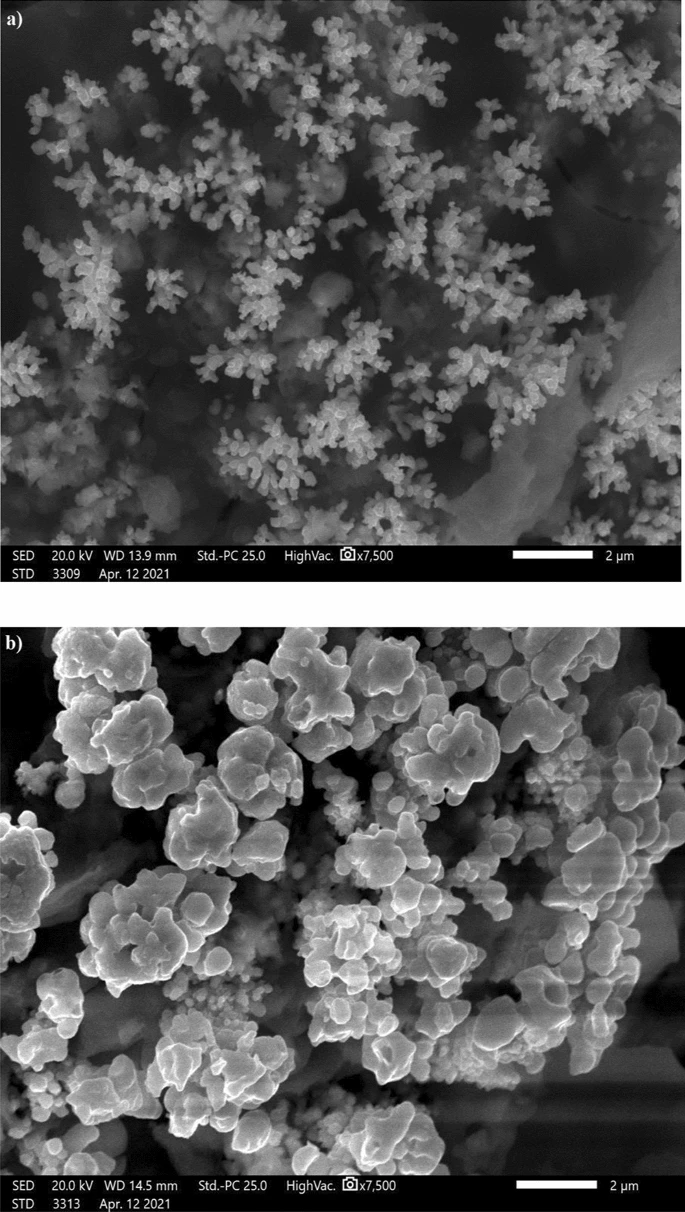

SEM images of copper grafted by (a) Ni-MA and (b) Ni-G-MA. Image Credit: Ragheb, D. M et al., Scientific Reports
Understanding the Makeup of Superhydrophobic Films
SHP surfaces have a slight sliding angle (SA) of less than 10° and a high contact angle (CA) greater than 150°. Lotuses, rice leaves, and roses are a few examples of the natural occurrences on which the SHP surface synthesis concepts are based. SHP surfaces have recently generated tremendous attention in academic research and potential commercial applications due to their applicability in drag reduction, self-cleaning capabilities, corrosion resistance, and water and oil separation.
A superhydrophobic surface requires two components, including a surface chemistry alteration with a low-free-energy covering and a rough surface texture with a specific binary structure. Several methods have been proposed for creating bio-inspired SHP surfaces by modifying chemical compositions and surface morphology. These techniques include sol-gel, chemical vapor deposition, electrodeposition, chemical etching, and spray. Most of these methods, however, have limitations due to the requirement for specialized machinery or challenging process control.
Producing SHP coatings on metals, conducting polymers, and metal oxides is simpler using electrodeposition. Due to its benefits, such as ease of control, scalability, low cost, simplicity, and production of a durable SHP coating, electrodeposition has emerged as a competitive way to generate superhydrophobic surfaces.
This study aimed to produce Ni and graphene-doped Ni films on a copper substrate using an electrodeposition method. These films were then altered with MA, a chemical with a negligible environmental impact, yielding SHP surfaces. Using an SEM and an FTIR, the chemical makeup and the surface topography of the synthesized SHP surfaces were investigated. The wettability, weather resistance, mechanical and chemical stability, and corrosion resistance of the manufactured SHP films were evaluated. The corrosion performance was examined in an aqueous medium of 0.5 molar NaCl.
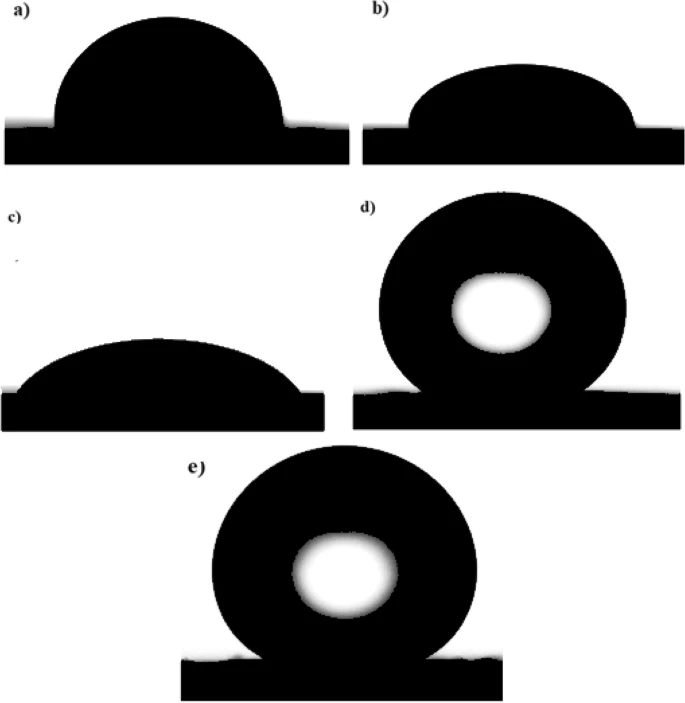
Experimental Set-Up
A copper plate measuring two centimeters by one centimeter by 0.3 centimeters was used as the working electrode. The authors used analytical-grade nickel chloride hexahydrate, sodium hydroxide, sulfuric acid, nickel sulfate, anhydrous ethanol, boric acid, and MA for the study.
The copper substrate was polished with various grades of silicon carbide (SiC) paper before electrodeposition, commencing with a sieve of grade 150 and working up to the superior 800 grade. Then the copper substrate was immersed in a soap solution for 10 minutes, followed by a 0.5 molar sulfuric acid (H2SO4) for one minute. Finally, the copper substrate was cleaned with distilled water before entering the electrodeposition bath.
SEM analysis was used to investigate the surface topography of the electrodeposited coating. Utilizing FTIR, the chemical makeup of the manufactured SHP coating was examined. The spectra were recorded between 400 and 4000 per centimeter.
The scratch, sand impact tests, and tape peeling were used to analyze the mechanical properties of the manufactured SHP films. This SHP film was applied to SiC paper of 1200 grade, which served as the abrasion surface, to conduct the scratch test.
A chemical stability test was conducted to validate that the created SHP films might be used in industrial applications. For one hour, several samples of copper grafted onto SHP films were submerged in aqueous solutions with pH ranges of one to 13. At every pH, the CAs and SAs were then calculated. The Ni-G-MA SHP-coated copper showed higher chemical stability than several previously observed values.
The potentiodynamic polarization method investigated the corrosion resistance of uncoated copper and copper coated with Ni, Ni-MA, Ni-G, and Ni-G-MA. Here, the findings showed that copper covered with Ni-G-MA film had a higher corrosion resistance. Thus, the prepared copper covered with Ni-G-MA had better protective efficacy than Ni-MA.
Findings and Significance of the Study
In this study, the authors effectively grafted Ni-G-MA and Ni-MA superhydrophobic films onto the copper substrate. Additionally, the mechanical strength and stability of the produced superhydrophobic films were evaluated through mechanical abrasion, sand impact testing, and tape peeling. The three methods demonstrated that the Ni-G-MA coating had more excellent mechanical stability compared to Ni-MA. Also, the Ni-G-MA films had more chemical stability than Ni-MA in basic and acidic conditions, according to the chemical stability assessment of the manufactured superhydrophobic films.
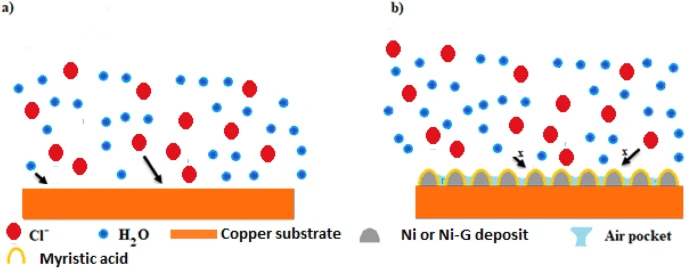
Schematic representation of the suggested mechanism for corrosion protection of the prepared SHP films. Image Credit: Ragheb, D. M et al., Scientific Reports
The findings revealed that adding graphene improved the mechanical and chemical stability of the resulting superhydrophobic coating. Also, the corrosion resistance of bare copper and copper coated with superhydrophobic material was studied using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) techniques and potentiodynamic polarisation. Finally, the findings demonstrated that the SHP coating on the copper surface prevented the diffusion of corrosive species into the copper surface and blocked active corrosion sites.
Therefore, the superhydrophobic coated copper had a strong corrosion resistance, particularly when the superhydrophobic coat was doped with graphene. Using the EIS approach, the manufacturing of superhydrophobic coatings’ continuing corrosion resistance was evaluated. The findings indicated that the manufactured superhydrophobic coatings showed excellent durability in 0.5 molar NaCl solution.
News
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]





















