Unprecedented views of the interior of cells and other nanoscale structures are now possible thanks to innovations in expansion microscopy. The advancements could help provide future insight into neuroscience, pathology, and many other biological and medical fields.
In the paper “Magnify is a universal molecular anchoring strategy for expansion microscopy,” published today (January 2, 2023) in the journal Nature Biotechnology, collaborators from Carnegie Mellon University, the University of Pittsburgh, and Brown University describe new protocols for dubbed Magnify.
“Magnify can be a potent and accessible tool for the biotechnology community,” said Yongxin (Leon) Zhao, the Eberly Family Career Development Associate Professor of Biological Sciences.
A video shows kidney cells. Expansion microscopy (ExM) provides unprecedented views of cell interiors. The emerging super-resolution imaging technique relies on physical — rather than optical — magnification. Advancements by Carnegie Mellon University’s Zhao Biophotonics Lab increases the expansion rate and allows many types of tissues to be viewed in 3D. Credit: Carnegie Mellon University
Magnify is a variant of expansion microscopy that allows researchers to use a new hydrogel formula, invented by Zhao’s team, that retains a spectrum of biomolecules, offers a broader application to a variety of tissues, and increases the expansion rate up to 11 times linearly or ~1,300 folds of the original volume.
“We overcame some of the longstanding challenges of expansion microscopy,” Zhao said. “One of the main selling points for Magnify is the universal strategy to keep the tissue’s biomolecules, including proteins, nucleus snippets, and carbohydrates, within the expanded sample.”
Zhao said that keeping different biological components intact matters because previous protocols required eliminating many various biomolecules that held tissues together. But these molecules could contain valuable information for researchers.
“In the past, to make cells really expandable, you need to use enzymes to digest proteins, so in the end, you had an empty gel with labels that indicate the location of the protein of interest,” he said. With the new method, the molecules are kept intact, and multiple types of biomolecules can be labeled in a single sample.
“Before, it was like having single-choice questions. If you want to label proteins, that would be the version one protocol. If you want to label nuclei, then that would be a different version,” Zhao said. “If you wanted to do simultaneous imaging, it was difficult. Now with Magnify, you can pick multiple items to label, such as proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates, and image them together.”
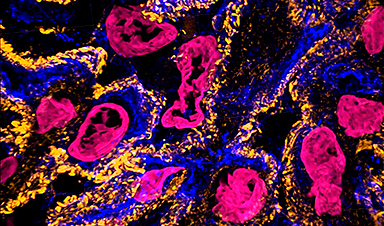
Example of (a) pre-expansion images of human kidney imaged at 60× and processed with SOFI compared to the same field of view (b) post-expansion with MAGNIFY taken at 40×. Magenta, DAPI; Orange, anti-alpha-actinin 4 (ACTN4); Blue, vimentin. Post expansion images are maximum intensity projected over 25 frames in z. (c-e) Root mean square (RMS) length measurement error as a function of measurement length for pre-expansion versus post expansion images for (c) DAPI, (d) ACTN4, and (e) Vimentin. Solid line, mean of channel; shaded area, standard error of mean (s.e.m); n = 5 technical replicates; average expansion factor, 8.64× (s.e.m 0.24). Example of (f) pre-expansion images of human prostate imaged at 60× and processed with SOFI compared to the same field of view (g) post-expansion with MAGNIFY taken at 40×. Magenta, DAPI; Green, Anti-ATPase Inhibitory Factor 1 (ATPIF). Post expansion images maximum intensity projected over 3 frames. (h-i) RMS length measurement error as a function of measurement length for pre-expansion versus post expansion images of (h) DAPI, and (i) ATPIF. Solid line, mean of channel; shaded area, s.e.m.; n = 4 technical replicates; average expansion factor, 10.38× (s.e.m 0.57). (j-o) Validation of MAGNIFY across multiple human tissue types. FFPE samples of human tissue were imaged at 40× (top left). Images were taken at 60×and processed with SOFI (bottom left). The white box indicates the field of view of the higher magnification images. The samples were then processed with the MAGNIFY protocol, and the same fields of view were imaged post-expansion in water at 10× (top right) and 40× (bottom right). Post expansion images were projected over 4-17 z slices. Magenta, DAPI; Green, ATPIF; Blue, Cytokeratin Pan Type I/II. Expansion factors in water were (j) Colon: 8.85×, (k) Breast: 9×, (l) Uterus: 8×, (m) Placenta: 8.75×, (n) Thymus: 10.00×, (o) Thyroid: 10.59×. (p-r) Example 3d images of human tissues: (p) kidney (Expansion factor 8.68×). Magenta, DAPI; Orange, ACTN4; Blue, WGA. (q) colon (Expansion factor 9.67×). Magenta, DAPI; Green, ATIPF; Blue, Cytokeratin Pan Type I/II. (r) Uterus (Expansion factor 8×). Magenta, DAPI; Green, ATIPF; Blue, Cytokeratin Pan Type I/II. Zoomed in regions indicated by dashed white box. Scale bars (yellow indicates post expansion images): (a) 5 μm; (b) 5 μm (physical scale post expansion: 40.75 μm; expansion factor: 8.15×); (f) 5 μm; (g) 5 μm (physical scale post expansion: 51.9 μm; expansion factor: 10.38×); (j-o) top: 10 μm; bottom: 1 μm; (p-t) 5 μm. Scale bars are all in biological scale. Credit: Courtesy of Carnegie Mellon University
Lab researchers Aleksandra Klimas, a postdoctoral researcher and Brendan Gallagher, a doctoral student, were first co-authors on the paper.
“This is an accessible way to image specimens in high resolution,” Klimas said. “Traditionally, you need expensive equipment and specific reagents and training. However, this method is broadly applicable to many types of sample preparations and can be viewed with standard microscopes that you would have in a biology laboratory.”
Gallagher, who has a background in neuroscience, said their goal was to make the protocols as compatible as possible for researchers who could benefit from adopting the Magnify as part of their toolkits.
“One of the key concepts that we tried to keep in mind was to meet researchers where they are and have them change as few things in their protocols as possible,” Gallagher said. “It works with different tissue types, fixation methods and even tissue that has been preserved and stored. It is very flexible, in that you don’t necessarily need to redesign experiments with Magnify in mind completely; it will work with what you have already.”
For researchers such as Simon Watkins, the founder and director of the Center for Biologic Imaging at the University of Pittsburgh and the Pittsburgh Cancer Institute, the fact that the new protocol is compatible with a broad range of tissue types — including preserved tissue sections — is important. For example, most expansion microscopy methods are optimized for brain tissue. In contrast, Magnify was tested on samples from various human organs and corresponding tumors including breast, brain and colon.
“Let’s say you have a tissue with dense and non-dense components, this gets around tissues that previously wouldn’t expand isometrically,” Watkins said. “Leon has been working hard on this to make this protocol work with tissues that have been archived.”
Xi (Charlie) Ren, an assistant professor of biomedical engineering at Carnegie Mellon, studies the lung tissue and how to model its morphogenesis and pathogenesis. Part of his research involves researching the motile cilia that function to clear mucus in the human conducting airway. At 200 nanometers in diameter and just a few micrometers in length, the structures are too small to see without time-intensive technology such as electron microscopy. Working in collaboration with Zhao’s lab, Ren’s team developed and delivered lung organoid models with specific defects in cilia ultrastructure and function to validate the ability of Magnify to visualize clinically relevant cilia pathology.
“With the latest Magnify techniques, we can expand those lung tissues and start to see some ultrastructure of the motile cilia even with a regular microscope, and this will expedite both basic and clinical investigations,” he said.
The researchers also were able to view defects in cilia in patient-specific lung cells known to have genetic mutations.
“The lung tissue engineering community always needs a better way to characterize the tissue system that we work with,” Ren said. He added that this work is an important first step and he hopes the collaborative work with Zhao’s lab will further be refined and applied to pathology samples found in tissue banks.
Finally, the hydrogel used in Magnify and developed in the Zhao lab is more robust than its predecessor, which was very fragile, causing breaks during the process.
“We are hoping to develop this technology to make it more accessible to the community,” he said. “There are different directions this can go. There’s a lot of interest in using this kind of tissue expansion technology for basic science.”
Alison Barth, the Maxwell H. and Gloria C. Connan Professor in the Life Sciences at Carnegie Mellon, studies synaptic connectivity during learning. She said the broad applications provided by the new methods will be a boon for researchers.
“The brain is a great place to take advantage of these super-resolution techniques,” said Barth, who collaborates with the Zhao Lab on several studies. “Microscopy methods will be beneficial for synaptic phenotyping and analysis across different brain conditions.
“One of the major advances in this paper is the method’s ability to work on many different types of tissue specimens.”
News
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]