Innovative research into DNA nanotechnology has been submitted to the journal, Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, comprising intelligent aptamer-incorporated DNA nanonetwork (Apt-Nnes). This novel technology can be used for imaging cancers as well as for increased drug delivery of chemotherapeutics.
The Need for DNA Nanotechnology
Nanoscale materials, which include materials that are within the nanoscale of 1 and 100 nm in size, have gained traction with the integration of nanotechnology into biomedical research.
Nanomaterials such as nanoparticles and nanocarriers have proven to have great potential when delivering drugs to target sites as they allow increased precision of drug release with a high concentration in the target areas. This also reduces systemic effects including toxicity, which is a major concern for chemotherapy drugs used for cancer therapeutics. The biodistribution of these drugs is non-specific and can cause secondary medical issues such as the elimination of healthy cells and tissue, and even affect organ functioning.
While there have been nanomaterials developed for this application such as liposomes and nanoparticles, these can also be associated with obstacles and limitations including the requirement of extensive surface functionalization to aid targetability as well compatibility with the immune system.
These drawbacks have increased research into DNA nanotechnology. This sector has illustrated benefits such as higher suitability for use in vivo as well as a high level of programmability. These advantages have made DNA nanotechnologies like aptamers potentially more suitable for use in cancer diagnostics and therapeutics such as bioimaging, biosensors and drug carriers.
Aptamers
Aptamers can be described as being short single-stranded oligonucleotides, which are usually 20-60 nucleotides long, with the ability to bind to target molecules with a high level of specificity and affinity.
These DNA molecules can bind a wide range of targets such as simple inorganic molecules, large proteins, and cells, as well as being cheaper nucleotide analogues of antibodies. This can enable aptamers to be used as a more cost-effective alternative, with the added benefit of being easily produced and non-toxic.
Applications of aptamer within DNA nanotechnology have led to innovative research into its suitability for cancer research and therapy.
Innovative Research
The pre-print article submitted to the journal Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine has undertaken research to develop a simplistic approach for constructing a versatile aptamer-incorporated DNA nanonetwork (Apt-Nnes) for carrying and delivering drugs with increased targetability.
This research has been developed for the application of carrying chemotherapy drugs such as doxorubicin (Dox), which can be loaded onto the Apt-Nnes carrier. This drug delivery carrier has a high cargo loading capacity as well as being suitable for biological systems without causing immunity issues or resulting in toxicity.
Additionally, the targetability of this DNA technology was tested for its potential use in cancer therapeutics by evaluating its specificity for the protein tyrosine kinase 7, which is overexpressed in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. The results of this research consisted of finding the binding affinity of this drug delivery carrier was heavily enhanced through the use of multivalent aptamers. Additionally, the structure itself was suitable for its purpose as its structural integrity was maintained in fetal bovine serum for eight hours.
The small size of this drug delivery carrier enables natural interaction with cancer cells, and this can allow its cancer-specific receptors to detect and enter cancer cells before releasing the chemotherapy drug with a high concentration within a localized area. Cytotoxicity within a localized tumor site using this DNA nanotechnology allow the preservation of heathy cells and tissue within the patient and this lack of systemic toxicity can allow patients to experience fewer adverse effects.
Future Outlook
Utilizing aptamers, this nano-based method can also enable a more patient-centered treatment approach, which can include potentially fewer chemotherapy treatment sessions, especially if sustained drug release can be enabled. The use of smaller doses of the chemotherapy drug is also a possibility with the drug being released in the target area, a larger dose is no longer required to ensure the site is reached. This can be beneficial for health care systems as the requirement of the overall drug treatment dose per patient is reduced and there this can be cheaper for the hospital, allowing the treatment of a larger number of patients.
The quality of life of these patients that are able to experience reduced toxicity is also a benefit of this novel approach and with further research, this research, while in its infancy, may be able to enter clinical practice and increase patient care.
News
Breakthrough in Antimicrobial Technology with Cinnamon-Based Nanokiller
The need for innovative antimicrobial agents has become increasingly urgent due to the rise of antibiotic-resistant pathogens and the persistent threat of infections acquired during hospital stays. Traditional antibiotics and antiseptics are often ineffective [...]
The Silent Battle Within: How Your Organs Choose Between Mom and Dad’s Genes
Research reveals that selective expression of maternal or paternal X chromosomes varies by organ, driven by cellular competition. A new study published today (July 26) in Nature Genetics by the Lymphoid Development Group at the MRC [...]
Study identifies genes increasing risk of severe COVID-19
Whether or not a person becomes seriously ill with COVID-19 depends, among other things, on genetic factors. With this in mind, researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn, in [...]
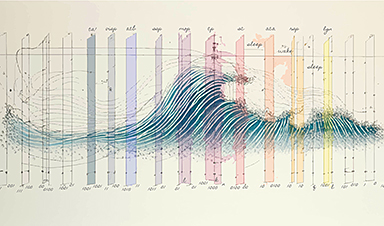
Small regions of the brain can take micro-naps while the rest of the brain is awake and vice versa
Sleep and wake: They're totally distinct states of being that define the boundaries of our daily lives. For years, scientists have measured the difference between these instinctual brain processes by observing brain waves, with [...]
Redefining Consciousness: Small Regions of the Brain Can Take Micro-Naps While the Rest of the Brain Is Awake
The study broadly reveals how fast brain waves, previously overlooked, establish fundamental patterns of sleep and wakefulness. Scientists have developed a new method to analyze sleep and wake states by detecting ultra-fast neuronal activity [...]
AI Reveals Health Secrets Through Facial Temperature Mapping
Researchers have found that different facial temperatures correlate with chronic illnesses like diabetes and high blood pressure, and these can be detected using AI with thermal cameras. They highlight the potential of this technology [...]
Breakthrough in aging research: Blocking IL-11 extends lifespan and improves health in mice
In a recent study published in the journal Nature, a team of researchers used murine models and various pharmacological and genetic approaches to examine whether pro-inflammatory signaling involving interleukin (IL)-11, which activates signaling molecules such [...]
Promise for a universal influenza vaccine: Scientists validate theory using 1918 flu virus
New research led by Oregon Health & Science University reveals a promising approach to developing a universal influenza vaccine—a so-called "one and done" vaccine that confers lifetime immunity against an evolving virus. The study, [...]
New Projects Aim To Pioneer the Future of Neuroscience
One study will investigate the alterations in brain activity at the cellular level caused by psilocybin, the psychoactive substance found in “magic mushrooms.” How do neurons respond to the effects of magic mushrooms? What [...]
Decoding the Decline: Scientific Insights Into Long COVID’s Retreat
Research indicates a significant reduction in long COVID risk, largely due to vaccination and the virus’s evolution. The study analyzes data from over 441,000 veterans, showing lower rates of long COVID among vaccinated individuals compared [...]
Silicon Transformed: A Breakthrough in Laser Nanofabrication
A new method enables precise nanofabrication inside silicon using spatial light modulation and laser pulses, creating advanced nanostructures for potential use in electronics and photonics. Silicon, the cornerstone of modern electronics, photovoltaics, and photonics, [...]
Caught in the actinium: New research could help design better cancer treatments
The element actinium was first discovered at the turn of the 20th century, but even now, nearly 125 years later, researchers still don't have a good grasp on the metal's chemistry. That's because actinium [...]
Innovative Light-Controlled Drugs Could Revolutionize Neuropathic Pain Treatment
A team of researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) has developed light-activated derivatives of the anti-epileptic drug carbamazepine to treat neuropathic pain. Light can be harnessed to target drugs to specific [...]
Green Gold: Turning E-Waste Into a Treasure Trove of Rare Earth Metals
Scientists are developing a process inspired by nature that efficiently recovers europium from old fluorescent lamps. The approach could lead to the long-awaited recycling of rare earth metals. A small molecule that naturally serves [...]
Cambridge Study: AI Chatbots Have an “Empathy Gap,” and It Could Be Dangerous
A new study suggests a framework for “Child Safe AI” in response to recent incidents showing that many children perceive chatbots as quasi-human and reliable. A study has indicated that AI chatbots often exhibit [...]
Nanoparticle-based delivery system could offer treatment for diabetics with rare insulin allergy
Up to 3% of people with diabetes have an allergic reaction to insulin. A team at Forschungszentrum Jülich has now studied a method that could be used to deliver the active substance into the [...]