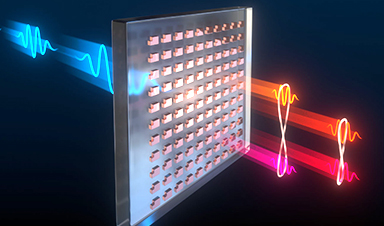
| An ultrathin invention could make future computing, sensing and encryption technologies remarkably smaller and more powerful by helping scientists control a strange but useful phenomenon of quantum mechanics, according to new research recently published in the journal Science (“Resonant metasurfaces for generating complex quantum states”). | |
| Scientists at Sandia National Laboratories and the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light have reported on a device that could replace a roomful of equipment to link photons in a bizarre quantum effect called entanglement. This device — a kind of nano-engineered material called a metasurface — paves the way for entangling photons in complex ways that have not been possible with compact technologies. |
| When scientists say photons are entangled, they mean they are linked in such a way that actions on one affect the other, no matter where or how far apart the photons are in the universe. It is an effect of quantum mechanics, the laws of physics that govern particles and other very tiny things. | |
| Although the phenomenon might seem odd, scientists have harnessed it to process information in new ways. For example, entanglement helps protect delicate quantum information and correct errors in quantum computing, a field that could someday have sweeping impacts in national security, science and finance. Entanglement is also enabling new, advanced encryption methods for secure communication. | |
| Research for the groundbreaking device, which is a hundred times thinner than a sheet of paper, was performed, in part, at the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies, a Department of Energy Office of Science user facility operated by Sandia and Los Alamos national laboratories. Sandia’s team received funding from the Office of Science, Basic Energy Sciences program. | |
Light goes in, entangled photons come out |
|
| The new metasurface acts as a doorway to this unusual quantum phenomenon. In some ways, it’s like the mirror in Lewis Carrol’s “Through the Looking-Glass,” through which the young protagonist Alice experiences a strange, new world. | |
| Instead of walking through their new device, scientists shine a laser through it. The beam of light passes through an ultrathin sample of glass covered in nanoscale structures made of a common semiconductor material called gallium arsenide. |
| “It scrambles all the optical fields,” said Sandia senior scientist Igal Brener, an expert in a field called nonlinear optics who led the Sandia team. Occasionally, he said, a pair of entangled photons at different wavelengths emerge from the sample in the same direction as the incoming laser beam. | |
| Brener said he is excited about this device because it is designed to produce complex webs of entangled photons — not just one pair at a time, but several pairs all entangled together, and some that can be indistinguishable from each other. Some technologies need these complex varieties of so-called multi-entanglement for sophisticated information processing schemes. | |
| Other miniature technologies based on silicon photonics can also entangle photons but without the much-needed level of complex, multi-entanglement. Until now, the only way to produce such results was with multiple tables full of lasers, specialized crystals and other optical equipment. | |
| “It is quite complicated and kind of intractable when this multi-entanglement needs more than two or three pairs,” Brener said. “These nonlinear metasurfaces essentially achieve this task in one sample when before it would have required incredibly complex optical setups.” | |
| The Science paper outlines how the team successfully tuned their metasurface to produce entangled photons with varying wavelengths, a critical precursor to generating several pairs of intricately entangled photons simultaneously. | |
| However, the researchers note in their paper that the efficiency of their device — the rate at which they can generate groups of entangled photons — is lower than that of other techniques and needs to be improved. | |
| Commercial industries, said Brener, are busy developing metasurfaces because they take up less space and can do more with light than, for instance, a traditional lens. | |
| “You now can replace lenses and thick optical elements with metasurfaces,” Brener said. “Those types of metasurfaces will revolutionize consumer products.” | |
| Sandia is one of the leading institutions in the world performing research in metasurfaces and metamaterials. Between its Microsystems Engineering, Science and Applications complex, which manufactures compound semiconductors, and the nearby Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies, researchers have access to all the specialized tools they need to design, fabricate and analyze these ambitious new materials. | |
| “The work was challenging as it required precise nanofabrication technology to obtain the sharp, narrowband optical resonances that seeds the quantum process of the work,” said Sylvain Gennaro, a former postdoctoral researcher at Sandia who worked on several aspects of the project. | |
| The device was designed, fabricated and tested through a partnership between Sandia and a research group led by physicist Maria Chekhova, an expert in the quantum entanglement of photons at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light. | |
| “Metasurfaces are leading to a paradigm shift in quantum optics, combining ultrasmall sources of quantum light with far reaching possibilities for quantum state engineering,” said Tomás Santiago-Cruz, a member of the Max Plank team and first author on the paper. | |
| Brener, who has studied metamaterials for more than a decade, said this newest research could possibly spark a second revolution — one that sees these materials developed not just as a new kind of lens, but as a technology for quantum information processing and other new applications. | |
| “There was one wave with metasurfaces that is already well established and on its way. Maybe there is a second wave of innovative applications coming,” he said. |
Breakthrough in Antimicrobial Technology with Cinnamon-Based Nanokiller
The need for innovative antimicrobial agents has become increasingly urgent due to the rise of antibiotic-resistant pathogens and the persistent threat of infections acquired during hospital stays. Traditional antibiotics and antiseptics are often ineffective [...]
The Silent Battle Within: How Your Organs Choose Between Mom and Dad’s Genes
Research reveals that selective expression of maternal or paternal X chromosomes varies by organ, driven by cellular competition. A new study published today (July 26) in Nature Genetics by the Lymphoid Development Group at the MRC [...]
Study identifies genes increasing risk of severe COVID-19
Whether or not a person becomes seriously ill with COVID-19 depends, among other things, on genetic factors. With this in mind, researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn, in [...]
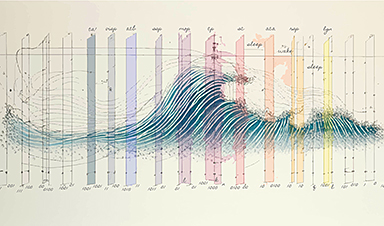
Small regions of the brain can take micro-naps while the rest of the brain is awake and vice versa
Sleep and wake: They're totally distinct states of being that define the boundaries of our daily lives. For years, scientists have measured the difference between these instinctual brain processes by observing brain waves, with [...]
Redefining Consciousness: Small Regions of the Brain Can Take Micro-Naps While the Rest of the Brain Is Awake
The study broadly reveals how fast brain waves, previously overlooked, establish fundamental patterns of sleep and wakefulness. Scientists have developed a new method to analyze sleep and wake states by detecting ultra-fast neuronal activity [...]
AI Reveals Health Secrets Through Facial Temperature Mapping
Researchers have found that different facial temperatures correlate with chronic illnesses like diabetes and high blood pressure, and these can be detected using AI with thermal cameras. They highlight the potential of this technology [...]
Breakthrough in aging research: Blocking IL-11 extends lifespan and improves health in mice
In a recent study published in the journal Nature, a team of researchers used murine models and various pharmacological and genetic approaches to examine whether pro-inflammatory signaling involving interleukin (IL)-11, which activates signaling molecules such [...]
Promise for a universal influenza vaccine: Scientists validate theory using 1918 flu virus
New research led by Oregon Health & Science University reveals a promising approach to developing a universal influenza vaccine—a so-called "one and done" vaccine that confers lifetime immunity against an evolving virus. The study, [...]
New Projects Aim To Pioneer the Future of Neuroscience
One study will investigate the alterations in brain activity at the cellular level caused by psilocybin, the psychoactive substance found in “magic mushrooms.” How do neurons respond to the effects of magic mushrooms? What [...]
Decoding the Decline: Scientific Insights Into Long COVID’s Retreat
Research indicates a significant reduction in long COVID risk, largely due to vaccination and the virus’s evolution. The study analyzes data from over 441,000 veterans, showing lower rates of long COVID among vaccinated individuals compared [...]
Silicon Transformed: A Breakthrough in Laser Nanofabrication
A new method enables precise nanofabrication inside silicon using spatial light modulation and laser pulses, creating advanced nanostructures for potential use in electronics and photonics. Silicon, the cornerstone of modern electronics, photovoltaics, and photonics, [...]
Caught in the actinium: New research could help design better cancer treatments
The element actinium was first discovered at the turn of the 20th century, but even now, nearly 125 years later, researchers still don't have a good grasp on the metal's chemistry. That's because actinium [...]
Innovative Light-Controlled Drugs Could Revolutionize Neuropathic Pain Treatment
A team of researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) has developed light-activated derivatives of the anti-epileptic drug carbamazepine to treat neuropathic pain. Light can be harnessed to target drugs to specific [...]
Green Gold: Turning E-Waste Into a Treasure Trove of Rare Earth Metals
Scientists are developing a process inspired by nature that efficiently recovers europium from old fluorescent lamps. The approach could lead to the long-awaited recycling of rare earth metals. A small molecule that naturally serves [...]
Cambridge Study: AI Chatbots Have an “Empathy Gap,” and It Could Be Dangerous
A new study suggests a framework for “Child Safe AI” in response to recent incidents showing that many children perceive chatbots as quasi-human and reliable. A study has indicated that AI chatbots often exhibit [...]
Nanoparticle-based delivery system could offer treatment for diabetics with rare insulin allergy
Up to 3% of people with diabetes have an allergic reaction to insulin. A team at Forschungszentrum Jülich has now studied a method that could be used to deliver the active substance into the [...]