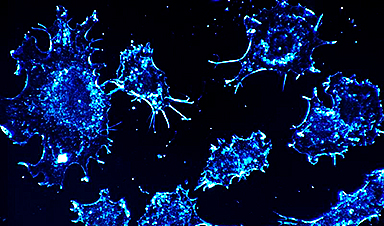
According to a new study by researchers at Penn Medicine, ketamine, which is well-known as an anesthetic and is becoming increasingly popular as an antidepressant, dramatically reorganizes activity in the brain, almost as if a switch were turned on. The study, published in Nature Neuroscience, found that after administering ketamine, there were drastic changes in the patterns of neuronal activity in the cerebral cortex of animal models. Neurons that were usually active were silenced, while others that were usually inactive suddenly became active.
This ketamine-induced activity switch in key brain regions tied to depression may impact our understanding of ketamine’s treatment effects and future research in the field of neuropsychiatry.
“Our surprising results reveal two distinct populations of cortical neurons, one engaged in normal awake brain function, the other linked to the ketamine-induced brain state,” said the co-lead and co-senior author Joseph Cichon, MD, Ph.D., an assistant professor of Anesthesiology and Critical Care and Neuroscience in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. “It’s possible that this new network induced by ketamine enables dreams, hypnosis, or some type of unconscious state. And if that is determined to be true, this could also signal that it is the place where ketamine’s therapeutic effects take place.”
In their new study, the researchers analyzed mouse behaviors before and after they were administered ketamine, comparing them to control mice who received placebo saline. One key observation was that those given ketamine, within minutes of injection, exhibited behavioral changes consistent with what is seen in humans on the drug, including reduced mobility, and impaired responses to sensory stimuli, which are collectively termed “dissociation.”
“We were hoping to pinpoint exactly what parts of the brain circuit ketamine affects when it’s administered so that we might open the door to better study of it and, down the road, more beneficial therapeutic use of it,” said co-lead and co-senior author Alex Proekt, MD, Ph.D., an associate professor of Anesthesiology and Critical Care at Penn.
Two-photon microscopy was used to image cortical brain tissue before and after ketamine treatment. By following individual neurons and their activity, they found that ketamine turned on silent cells and turned off previously active neurons.
The neuronal activity observed was traced to ketamine’s ability to block the activity of synaptic receptors — the junction between neurons — called NMDA receptors and ion channels called HCN channels. The researchers found that they could recreate ketamine’s effects without the medications by simply inhibiting these specific receptors and channels in the cortex. The scientists showed that ketamine weakens several sets of inhibitory cortical neurons that normally suppress other neurons. This allowed the normally quiet neurons, the ones usually being suppressed when ketamine wasn’t present, to become active.
The study showed that this dropout in inhibition was necessary for the activity switch in excitatory neurons — the neurons forming communication highways, and the main target of commonly prescribed antidepressant medications. More work will need to be undertaken to determine whether the ketamine-driven effects in excitatory and inhibitory neurons are the ones behind ketamine’s rapid antidepressant effects.
“While our study directly pertains to basic neuroscience, it does point at the greater potential of ketamine as a quick-acting antidepressant, among other applications,” said co-author Max Kelz, MD, Ph.D., a distinguished professor of Anesthesiology and vice chair of research in Anesthesiology and Critical Care. “Further research is needed to fully explore this, but the neuronal switch we found also underlies dissociated, hallucinatory states caused by some psychiatric illnesses.”
News
The Silent Battle Within: How Your Organs Choose Between Mom and Dad’s Genes
Research reveals that selective expression of maternal or paternal X chromosomes varies by organ, driven by cellular competition. A new study published today (July 26) in Nature Genetics by the Lymphoid Development Group at the MRC [...]
Study identifies genes increasing risk of severe COVID-19
Whether or not a person becomes seriously ill with COVID-19 depends, among other things, on genetic factors. With this in mind, researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn, in [...]
Small regions of the brain can take micro-naps while the rest of the brain is awake and vice versa
Sleep and wake: They're totally distinct states of being that define the boundaries of our daily lives. For years, scientists have measured the difference between these instinctual brain processes by observing brain waves, with [...]
Redefining Consciousness: Small Regions of the Brain Can Take Micro-Naps While the Rest of the Brain Is Awake
The study broadly reveals how fast brain waves, previously overlooked, establish fundamental patterns of sleep and wakefulness. Scientists have developed a new method to analyze sleep and wake states by detecting ultra-fast neuronal activity [...]
AI Reveals Health Secrets Through Facial Temperature Mapping
Researchers have found that different facial temperatures correlate with chronic illnesses like diabetes and high blood pressure, and these can be detected using AI with thermal cameras. They highlight the potential of this technology [...]
Breakthrough in aging research: Blocking IL-11 extends lifespan and improves health in mice
In a recent study published in the journal Nature, a team of researchers used murine models and various pharmacological and genetic approaches to examine whether pro-inflammatory signaling involving interleukin (IL)-11, which activates signaling molecules such [...]
Promise for a universal influenza vaccine: Scientists validate theory using 1918 flu virus
New research led by Oregon Health & Science University reveals a promising approach to developing a universal influenza vaccine—a so-called "one and done" vaccine that confers lifetime immunity against an evolving virus. The study, [...]
New Projects Aim To Pioneer the Future of Neuroscience
One study will investigate the alterations in brain activity at the cellular level caused by psilocybin, the psychoactive substance found in “magic mushrooms.” How do neurons respond to the effects of magic mushrooms? What [...]
Decoding the Decline: Scientific Insights Into Long COVID’s Retreat
Research indicates a significant reduction in long COVID risk, largely due to vaccination and the virus’s evolution. The study analyzes data from over 441,000 veterans, showing lower rates of long COVID among vaccinated individuals compared [...]
Silicon Transformed: A Breakthrough in Laser Nanofabrication
A new method enables precise nanofabrication inside silicon using spatial light modulation and laser pulses, creating advanced nanostructures for potential use in electronics and photonics. Silicon, the cornerstone of modern electronics, photovoltaics, and photonics, [...]
Caught in the actinium: New research could help design better cancer treatments
The element actinium was first discovered at the turn of the 20th century, but even now, nearly 125 years later, researchers still don't have a good grasp on the metal's chemistry. That's because actinium [...]
Innovative Light-Controlled Drugs Could Revolutionize Neuropathic Pain Treatment
A team of researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) has developed light-activated derivatives of the anti-epileptic drug carbamazepine to treat neuropathic pain. Light can be harnessed to target drugs to specific [...]
Green Gold: Turning E-Waste Into a Treasure Trove of Rare Earth Metals
Scientists are developing a process inspired by nature that efficiently recovers europium from old fluorescent lamps. The approach could lead to the long-awaited recycling of rare earth metals. A small molecule that naturally serves [...]
Cambridge Study: AI Chatbots Have an “Empathy Gap,” and It Could Be Dangerous
A new study suggests a framework for “Child Safe AI” in response to recent incidents showing that many children perceive chatbots as quasi-human and reliable. A study has indicated that AI chatbots often exhibit [...]
Nanoparticle-based delivery system could offer treatment for diabetics with rare insulin allergy
Up to 3% of people with diabetes have an allergic reaction to insulin. A team at Forschungszentrum Jülich has now studied a method that could be used to deliver the active substance into the [...]
Nanorobot kills cancer cells in mice with hidden weapon
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have developed nanorobots that kill cancer cells in mice. The robot's weapon is hidden in a nanostructure and is exposed only in the tumor microenvironment, sparing healthy cells. [...]