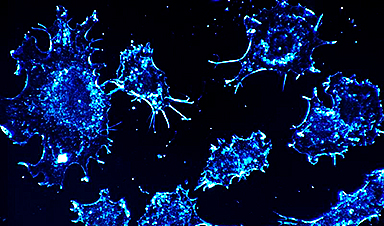
Researchers led by the University at Buffalo (UB) have devised a new method that could enhance the effectiveness of vaccines against the novel coronavirus, the virus that is responsible for causing COVID-19.
Jonathan F. Lovell, PhD, an associate professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at UB, is the principal investigator of the study titled “SARS-CoV-2 RBD Neutralizing Antibody Induction is Enhanced by Particulate Vaccination,” published online in the Advanced Materials journal on October 28th, 2020.
COVID-19 has resulted in an uncontrollable global pandemic, which has infected a minimum of 40 million people around the world and resulted in over 220,000 deaths in the United States alone. As the disease started spreading in early 2020, biomedical researchers have been working actively to develop an effective vaccine.
Lovell thinks that one solution could be to develop vaccines that partly imitate the virus structure. One of the proteins on the virus—situated on the characteristic COVID spike—includes a component known as the receptor-binding domain, or RBD, which is its “Achilles heel.” Lovell stated that antibodies against this part of the virus have the ability to neutralize the virus.
It would be appealing if a vaccine could induce high-levels of antibodies against the RBD. One way to achieve this goal is to use the RBD protein itself as an antigen, that is, the component of the vaccine that the immune response will be directed against.
Jonathan F. Lovell, Associate Professor, Department of Biomedical Engineering, University at Buffalo
The researchers speculated that if the RBD is transformed into a nanoparticle (similar in size to the virus itself) rather than retaining it in its natural form as a tiny protein, it would produce higher levels of neutralizing antibodies and its potential to produce an immune response would increase.
Earlier, Lovell’s group had designed a technology that enables the simple transformation of small, purified proteins into particles by using liposomes, or small nanoparticles developed from naturally occurring fatty components.
In the latest study, the team added a unique lipid known as cobalt-porphyrin-phospholipid or CoPoP inside the liposomes.
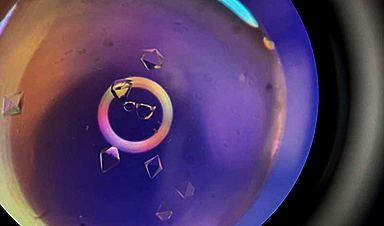
Image Credit: Facility for Electron Microscopy Research (FEMR) at McGill University.
Post by Amanda Scott, NA CEO. Follow her on twitter @tantriclens
Thanks to Heinz V. Hoenen. Follow him on twitter: @HeinzVHoenen
News
The Silent Battle Within: How Your Organs Choose Between Mom and Dad’s Genes
Research reveals that selective expression of maternal or paternal X chromosomes varies by organ, driven by cellular competition. A new study published today (July 26) in Nature Genetics by the Lymphoid Development Group at the MRC [...]
Study identifies genes increasing risk of severe COVID-19
Whether or not a person becomes seriously ill with COVID-19 depends, among other things, on genetic factors. With this in mind, researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn, in [...]
Small regions of the brain can take micro-naps while the rest of the brain is awake and vice versa
Sleep and wake: They're totally distinct states of being that define the boundaries of our daily lives. For years, scientists have measured the difference between these instinctual brain processes by observing brain waves, with [...]
Redefining Consciousness: Small Regions of the Brain Can Take Micro-Naps While the Rest of the Brain Is Awake
The study broadly reveals how fast brain waves, previously overlooked, establish fundamental patterns of sleep and wakefulness. Scientists have developed a new method to analyze sleep and wake states by detecting ultra-fast neuronal activity [...]
AI Reveals Health Secrets Through Facial Temperature Mapping
Researchers have found that different facial temperatures correlate with chronic illnesses like diabetes and high blood pressure, and these can be detected using AI with thermal cameras. They highlight the potential of this technology [...]
Breakthrough in aging research: Blocking IL-11 extends lifespan and improves health in mice
In a recent study published in the journal Nature, a team of researchers used murine models and various pharmacological and genetic approaches to examine whether pro-inflammatory signaling involving interleukin (IL)-11, which activates signaling molecules such [...]
Promise for a universal influenza vaccine: Scientists validate theory using 1918 flu virus
New research led by Oregon Health & Science University reveals a promising approach to developing a universal influenza vaccine—a so-called "one and done" vaccine that confers lifetime immunity against an evolving virus. The study, [...]
New Projects Aim To Pioneer the Future of Neuroscience
One study will investigate the alterations in brain activity at the cellular level caused by psilocybin, the psychoactive substance found in “magic mushrooms.” How do neurons respond to the effects of magic mushrooms? What [...]
Decoding the Decline: Scientific Insights Into Long COVID’s Retreat
Research indicates a significant reduction in long COVID risk, largely due to vaccination and the virus’s evolution. The study analyzes data from over 441,000 veterans, showing lower rates of long COVID among vaccinated individuals compared [...]
Silicon Transformed: A Breakthrough in Laser Nanofabrication
A new method enables precise nanofabrication inside silicon using spatial light modulation and laser pulses, creating advanced nanostructures for potential use in electronics and photonics. Silicon, the cornerstone of modern electronics, photovoltaics, and photonics, [...]
Caught in the actinium: New research could help design better cancer treatments
The element actinium was first discovered at the turn of the 20th century, but even now, nearly 125 years later, researchers still don't have a good grasp on the metal's chemistry. That's because actinium [...]
Innovative Light-Controlled Drugs Could Revolutionize Neuropathic Pain Treatment
A team of researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) has developed light-activated derivatives of the anti-epileptic drug carbamazepine to treat neuropathic pain. Light can be harnessed to target drugs to specific [...]
Green Gold: Turning E-Waste Into a Treasure Trove of Rare Earth Metals
Scientists are developing a process inspired by nature that efficiently recovers europium from old fluorescent lamps. The approach could lead to the long-awaited recycling of rare earth metals. A small molecule that naturally serves [...]
Cambridge Study: AI Chatbots Have an “Empathy Gap,” and It Could Be Dangerous
A new study suggests a framework for “Child Safe AI” in response to recent incidents showing that many children perceive chatbots as quasi-human and reliable. A study has indicated that AI chatbots often exhibit [...]
Nanoparticle-based delivery system could offer treatment for diabetics with rare insulin allergy
Up to 3% of people with diabetes have an allergic reaction to insulin. A team at Forschungszentrum Jülich has now studied a method that could be used to deliver the active substance into the [...]
Nanorobot kills cancer cells in mice with hidden weapon
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have developed nanorobots that kill cancer cells in mice. The robot's weapon is hidden in a nanostructure and is exposed only in the tumor microenvironment, sparing healthy cells. [...]