A new approach to brain tumor treatment using photodynamic therapy (PDT) with nanotechnology has been explored in a review published in the journal Biomedicines. Unlike radiotherapy and surgical resection, PDT can treat micro-invasive areas and protect critical brain tissue with a high probability of success.
Conventional Methods using PDT
Photodynamic therapy is a type of phototherapy that uses light and sensitizing chemical agents in combination with oxygen molecules to induce cell death. It is a two-stage remedy that incorporates light energy with a medicine (photosensitizer) designed to kill cancer cells and precancerous cells after they have been activated by light.
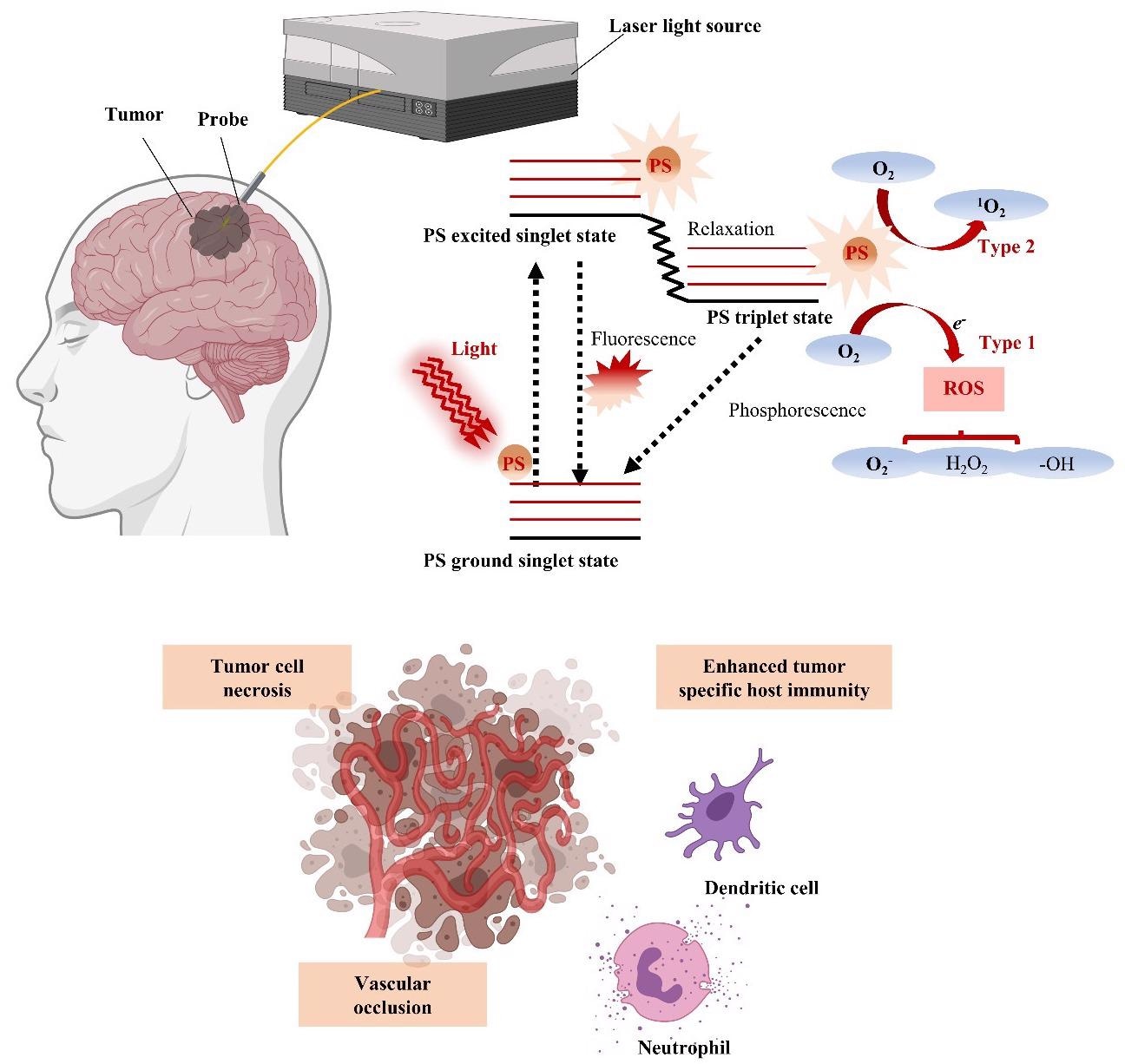
Schematic illustration of photodynamic therapy (PDT) for GBM treatment with energy diagram of the oxygen dependent response. If the photosensitizer (PS) in the ground singlet state is excited by the light wavelength, then the PS in the excited singlet state can convert to the excited triplet state via intersystem crossing. In the presence of molecular oxygen, the PS in the triplet state can undergo a Type 1 or Type 2 redox reaction, producing reactive oxygen species (ROS) that cause tumor cell necrosis, vascular occlusion, and tumor-specific host immunity. © Kim, H., and Lee, D. (2022).
Photosensitizers are initiated by a specific wavelength energy, which is typically generated by a laser. PDT has been shown to be effective in treating a variety of tumors, including melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and multidrug-resistant lung and mammary tumors.
PDT with Its Limited Efficacy
Following other oncology implementations, the interest in PDT as a high-grade glioma diagnosis stems from the essence of tumor growth and the limited efficacy of modern treatment options to this population of patients. Although surgical removal, partial radiation, and chemotherapy are important treatments for intracranial tumors, the obtrusive growth patterns, especially in the cerebrum’s central region, make total resection difficult.
As opposed to surgical resection and radiation, PDT can treat micro-invasive regions while preserving sensitive brain areas. These potential benefits over conventional therapies have been shown to improve results in clinical situations with low overall survival and a high incidence of iatrogenic damage.
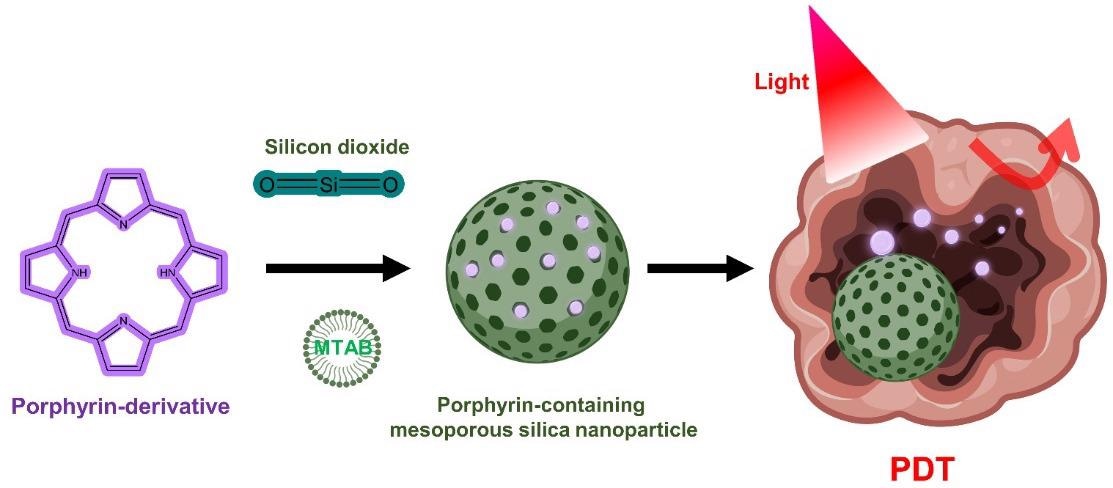
Porphyrin-containing mesoporous silica nanoparticles for PDT. © Kim, H., and Lee, D. (2022).
Nanomedicine as Opposed to Conventional Method
The rapidly growing areas of nanotechnology and nanomedicine are yielding nanostructured materials that may overcome the limitations of conventional clinical delivery methods. In fact, the existence of a functioning blood–brain barrier (BBB) inhibits therapeutic delivery to brain malignancies.
Many ways for temporarily opening the BBB by physical impact, including magnetic resonance (MR)-guided focussed ultrasound, have lately been researched to circumvent this barrier; however, this poses a technical problem.
One of the most promising solutions involves the utilization of multifunctional nanomedicines as drug delivery systems.
Advantages of Nanomedicine
The excellent physical and mechanical characteristics of nanocarriers vary based on their material, size, form (mesoporous microstructure, rod shape, particles), and ligand of choice. This enables enhanced brain-targeted administration of PS or therapeutic medicines.
Although many PS nanocapsules are still in the early phases of translation, major improvements in functional nanomedicines relying on BBB crossing have been accomplished in recent years.
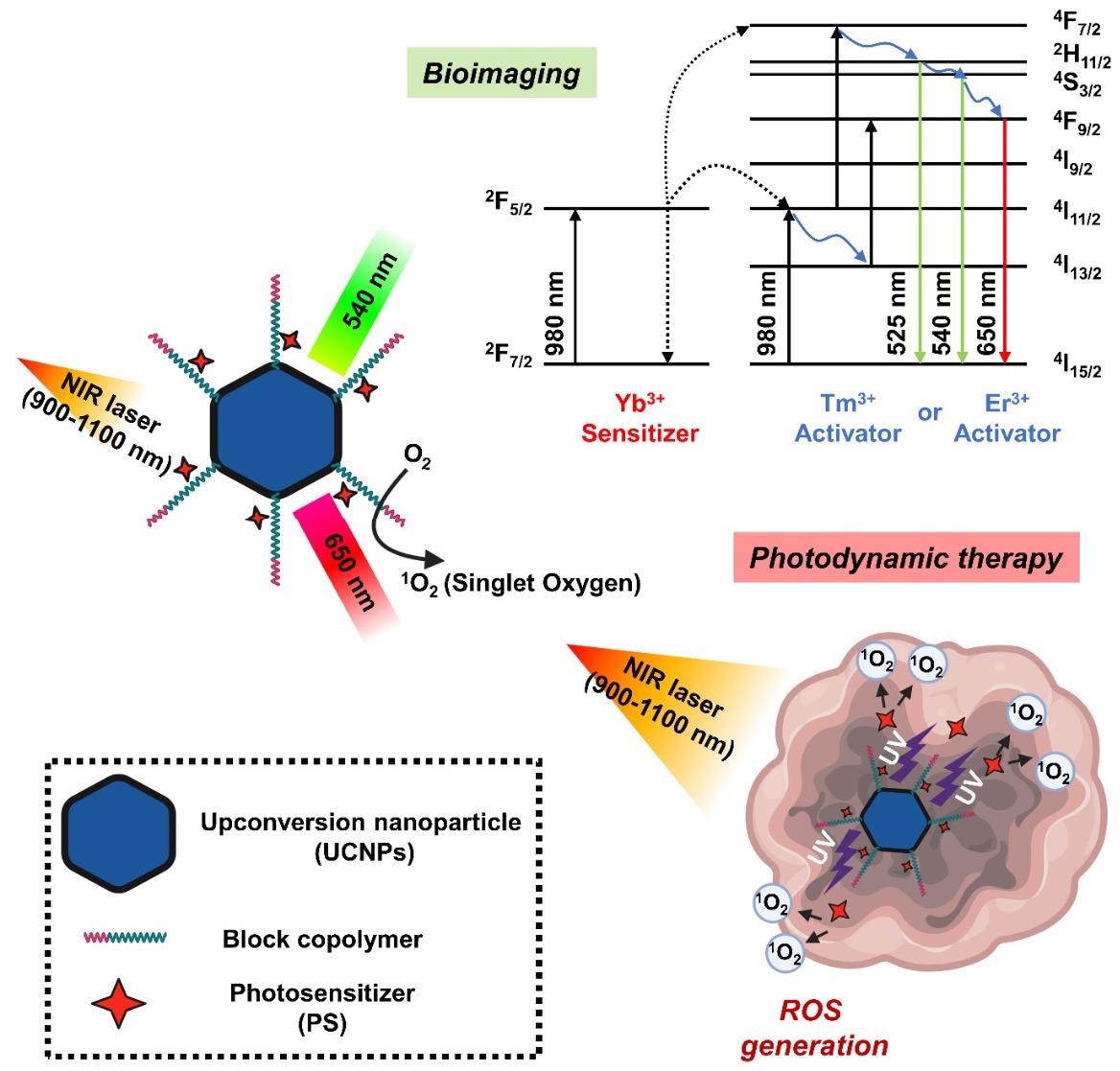
Schematic diagram showing the mechanism of photodynamic therapy and bioimaging through long-wavelength to short-wavelength conversion of upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs). © Kim, H., and Lee, D. (2022).
Another benefit of nanoparticles is that they may boost PS’s poor solubility, extend blood circulation, promote the targeted distribution and cellular absorption, and protect the medication from degradation.
Nanoparticles in PDT for Healing
Although contemporary PDT has considerably improved cancer patients’ quality of life and survival rates, it is critical to further enhance the therapeutic efficacy of nanocarriers to eliminate noticeable side effects.
In this respect, researchers have investigated a variety of nanocarriers, including polymers, liposomes, micelles, inorganic oxide, and new metal nanoparticles, to improve the therapeutic efficiency of photosensitizers.
First and foremost, nanocarriers must be used to effectively transport photosensitizers and singlet oxygen molecules to the target region in an ideal therapeutic range.
PDT is a dynamically evolving profession that is continually on the lookout for innovative technologies. To improve the efficacy and selectivity of PDT, molecular techniques based on nanotechnology are being explored. As a result, several novel organic and inorganic nanoparticles have already been discovered and produced for the targeted administration of photosensitizer medicines.
Nanoparticles may remedy the significant constraints of standard PS medication delivery.
Limitation of this Nanotechnology PDT
However, since intracranial brain tumors emerge from complex structures and distinct organs, such as those bordered by the blood–brain barrier, it is questionable if they can be completely removed using the same strategy as other cancers.
Further research is needed to determine if PDT may be utilized to treat malignant brain cancer that cannot be removed due to its location.
Ongoing research into the numerous PDTs described in this publication will decide whether breakthroughs in cancer research can reduce morbidity and mortality from intracranial malignancy and have the potential to change brain tumor therapy. As a result, although the development of new PDT technology is critical, establishing therapeutic guidelines via large-scale clinical practice should be prioritized.
Future Research in this Nanomedicine to Cure Brain Cancer
With the fast advancements in nanotechnology, researchers now have several synthetic approaches at their disposal to create gold nanoparticles with good shapes and characteristics for PDT applications.
In addition to the numerous physicochemical qualities listed above, the extra various synthesis potential should increase bioavailability and usefulness, indicating gold nanoparticles as a suitable choice for therapeutic cancer therapy.
News
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard it is for scientists to [...]
Are Pesticides Breeding the Next Pandemic? Experts Warn of Fungal Superbugs
Fungicides used in agriculture have been linked to an increase in resistance to antifungal drugs in both humans and animals. Fungal infections are on the rise, and two UC Davis infectious disease experts, Dr. George Thompson [...]
Scientists Crack the 500-Million-Year-Old Code That Controls Your Immune System
A collaborative team from Penn Medicine and Penn Engineering has uncovered the mathematical principles behind a 500-million-year-old protein network that determines whether foreign materials are recognized as friend or foe. How does your body [...]
Team discovers how tiny parts of cells stay organized, new insights for blocking cancer growth
A team of international researchers led by scientists at City of Hope provides the most thorough account yet of an elusive target for cancer treatment. Published in Science Advances, the study suggests a complex signaling [...]
Nanomaterials in Ophthalmology: A Review
Eye diseases are becoming more common. In 2020, over 250 million people had mild vision problems, and 295 million experienced moderate to severe ocular conditions. In response, researchers are turning to nanotechnology and nanomaterials—tools that are transforming [...]
Natural Plant Extract Removes up to 90% of Microplastics From Water
Researchers found that natural polymers derived from okra and fenugreek are highly effective at removing microplastics from water. The same sticky substances that make okra slimy and give fenugreek its gel-like texture could help [...]
Instant coffee may damage your eyes, genetic study finds
A new genetic study shows that just one extra cup of instant coffee a day could significantly increase your risk of developing dry AMD, shedding fresh light on how our daily beverage choices may [...]