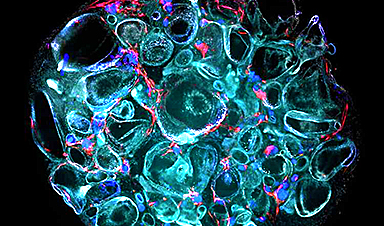
Scientists at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have successfully grown ‘mini kidneys’ in the lab and grafted them into live mice, revealing new insights into the metabolic defects and a potential therapy for polycystic kidney disease.
“Mini kidneys,” or kidney organoids, are kidney-like structures grown in the lab using stem cells. In the study led by NTU’s Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine (LKCMedicine), researchers grew the organoids using skin cells derived from patients with polycystic kidney disease (PKD), a prevalent form of genetic condition that affects 1 in 1,000 individuals across all ethnicities.
People with PKD often progress to end-stage kidney disease between their 50s and 60s, with the standard treatment options available being dialysis or a kidney transplant. However, dialysis significantly compromises a patient’s quality of life, while a transplanted kidney can be challenging to acquire. One other option is the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved drug Tolvaptan, which is very costly and has severe side effects on the liver.
To address the need for more effective treatment for PKD patients, the NTU research team sought to better understand the disease by engrafting their newly developed mini kidneys into mice.
Previous studies were conducted on mini kidneys grown in a dish, which could only partly mimic the kidney structure and function. The NTU scientists engrafted the mini kidneys into live mice to comprehensively replicate the pathological features of kidney disease, including blood flow, fluid movement (tubular fluid) and cellular communication with other organs.
Lead investigator Assistant Professor Xia Yun at LKCMedicine said, “Engrafting the kidney organoid in mice provided us with a physiologically sophisticated approach to studying polycystic kidney disease as we were able to successfully emulate critical disease characteristics similar to those observed in human kidney patients.”
Critical disease characteristics included abnormalities like the spontaneous formation of cysts in the kidneys and the subsequent damage to its tiny tubes.
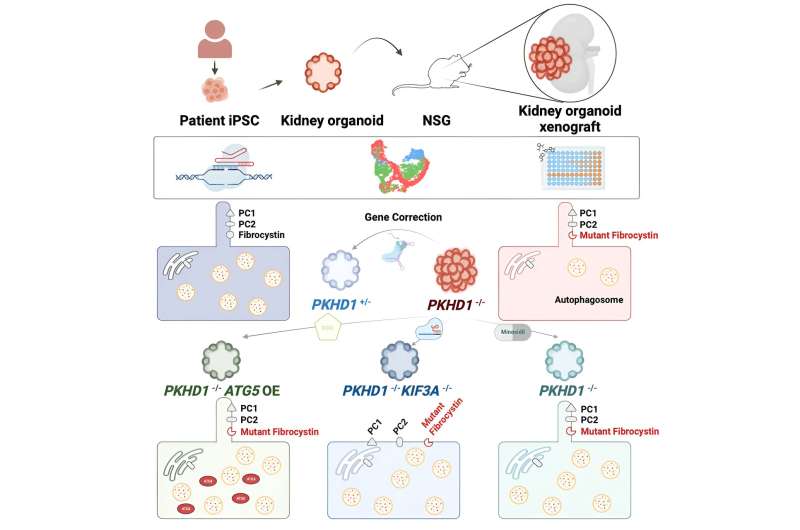
In their study, reported in the journal Cell Stem Cell, the NTU research team said that they believed their engrafted mini kidneys were high quality because cysts sustained without extra stress stimulation or chemicals, even after they were removed from the live mice for further investigations in a dish. In contrast, previous kidney organoids grown in a dish cannot form cysts without stress stimulation.
Co-investigator Assistant Professor Foo Jia Nee at LKCMedicine said, “The similarity between the disease manifestation observed in our engrafted mini kidney model and the real-life experiences of polycystic kidney disease patients suggest that growing kidney organoids and engrafting them into live mice could be beneficial in studying the disease and a useful tool to test new treatments.”
Metabolic defects in polycystic kidney disease
Scientists have long known that abnormalities in a structure on kidney cells, or the primary cilium, cause cysts to form in kidneys. However, tests to understand the regulatory mechanism and relationship between the primary cilium and cell metabolism (autophagy) in live mice with PKD, have not been possible until now.
By studying the development of PKD in live mice and testing cellular pathways, researchers found evidence that boosting autophagy could reduce the severity of cysts in the mini kidney.
After establishing that boosting autophagy could reduce cysts, the NTU scientists shortlisted 22 drugs known for their effects on cell metabolism and tested them in the lab. Results showed that minoxidil, a clinical drug widely used to cure hypertension and hair loss, effectively reduced cyst formation in the novel mouse model.
Asst Prof Xia Yun said, “Our study has demonstrated how cysts in polycystic diseased kidneys can be reduced by boosting autophagy, suggesting that this could be a promising treatment for PKD. Moreover, the proven clinical safety of minoxidil may allow it to be quickly re-purposed to treat PKD patients in clinic. However, more research will be needed to establish this potential.”
Commenting as an independent expert, Associate Professor Ng Kar Hui, Senior Consultant, Division of Paediatric Nephrology, Dialysis and Renal Transplantation, Department of Paediatrics, Khoo Teck Puat—National University Children’s Medical Institute, National University Hospital, said, “Polycystic kidney disease is one of the biggest causes of chronic kidney diseases among adults. An effective treatment may potentially ameliorate the rising numbers of people with kidney failure in Singapore. The establishment of such models in live organisms brings us one step closer to finding more treatment options.”
In future studies, the NTU team will test the efficacy of minoxidil and adapt the mini kidney models to investigate other burgeoning kidney diseases without a strong genetic underpinning, such as diabetic kidney disease.
More information: Meng Liu et al, Kidney organoid models reveal cilium-autophagy metabolic axis as a therapeutic target for PKD both in vitro and in vivo, Cell Stem Cell (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.12.003
News
The Silent Battle Within: How Your Organs Choose Between Mom and Dad’s Genes
Research reveals that selective expression of maternal or paternal X chromosomes varies by organ, driven by cellular competition. A new study published today (July 26) in Nature Genetics by the Lymphoid Development Group at the MRC [...]
Study identifies genes increasing risk of severe COVID-19
Whether or not a person becomes seriously ill with COVID-19 depends, among other things, on genetic factors. With this in mind, researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn, in [...]
Small regions of the brain can take micro-naps while the rest of the brain is awake and vice versa
Sleep and wake: They're totally distinct states of being that define the boundaries of our daily lives. For years, scientists have measured the difference between these instinctual brain processes by observing brain waves, with [...]
Redefining Consciousness: Small Regions of the Brain Can Take Micro-Naps While the Rest of the Brain Is Awake
The study broadly reveals how fast brain waves, previously overlooked, establish fundamental patterns of sleep and wakefulness. Scientists have developed a new method to analyze sleep and wake states by detecting ultra-fast neuronal activity [...]
AI Reveals Health Secrets Through Facial Temperature Mapping
Researchers have found that different facial temperatures correlate with chronic illnesses like diabetes and high blood pressure, and these can be detected using AI with thermal cameras. They highlight the potential of this technology [...]
Breakthrough in aging research: Blocking IL-11 extends lifespan and improves health in mice
In a recent study published in the journal Nature, a team of researchers used murine models and various pharmacological and genetic approaches to examine whether pro-inflammatory signaling involving interleukin (IL)-11, which activates signaling molecules such [...]
Promise for a universal influenza vaccine: Scientists validate theory using 1918 flu virus
New research led by Oregon Health & Science University reveals a promising approach to developing a universal influenza vaccine—a so-called "one and done" vaccine that confers lifetime immunity against an evolving virus. The study, [...]
New Projects Aim To Pioneer the Future of Neuroscience
One study will investigate the alterations in brain activity at the cellular level caused by psilocybin, the psychoactive substance found in “magic mushrooms.” How do neurons respond to the effects of magic mushrooms? What [...]
Decoding the Decline: Scientific Insights Into Long COVID’s Retreat
Research indicates a significant reduction in long COVID risk, largely due to vaccination and the virus’s evolution. The study analyzes data from over 441,000 veterans, showing lower rates of long COVID among vaccinated individuals compared [...]
Silicon Transformed: A Breakthrough in Laser Nanofabrication
A new method enables precise nanofabrication inside silicon using spatial light modulation and laser pulses, creating advanced nanostructures for potential use in electronics and photonics. Silicon, the cornerstone of modern electronics, photovoltaics, and photonics, [...]
Caught in the actinium: New research could help design better cancer treatments
The element actinium was first discovered at the turn of the 20th century, but even now, nearly 125 years later, researchers still don't have a good grasp on the metal's chemistry. That's because actinium [...]
Innovative Light-Controlled Drugs Could Revolutionize Neuropathic Pain Treatment
A team of researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) has developed light-activated derivatives of the anti-epileptic drug carbamazepine to treat neuropathic pain. Light can be harnessed to target drugs to specific [...]
Green Gold: Turning E-Waste Into a Treasure Trove of Rare Earth Metals
Scientists are developing a process inspired by nature that efficiently recovers europium from old fluorescent lamps. The approach could lead to the long-awaited recycling of rare earth metals. A small molecule that naturally serves [...]
Cambridge Study: AI Chatbots Have an “Empathy Gap,” and It Could Be Dangerous
A new study suggests a framework for “Child Safe AI” in response to recent incidents showing that many children perceive chatbots as quasi-human and reliable. A study has indicated that AI chatbots often exhibit [...]
Nanoparticle-based delivery system could offer treatment for diabetics with rare insulin allergy
Up to 3% of people with diabetes have an allergic reaction to insulin. A team at Forschungszentrum Jülich has now studied a method that could be used to deliver the active substance into the [...]
Nanorobot kills cancer cells in mice with hidden weapon
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have developed nanorobots that kill cancer cells in mice. The robot's weapon is hidden in a nanostructure and is exposed only in the tumor microenvironment, sparing healthy cells. [...]