Viruses need hosts. Whether it’s measles, the flu or coronavirus, viral pathogens cannot multiply or infect other organisms without the assistance of their hosts’ cellular infrastructure. However, humans are not the only ones affected by viruses: animals, plants and even microorganisms can all serve as hosts.
Viruses that use bacteria as host cells are called bacteriophages (or simply “phages” for short) and are thought to be the most abundant biological entities of all. Just as the human immune system springs into action to resist a flu or coronavirus infection, bacteria do not simply allow phages to infiltrate their cellular machinery without a fight.
A research team at the University of Jena and its Cluster of Excellence “Balance of the Microverse” has examined in detail the complex interaction of attack and defense strategies when cholera-causing bacteria (Vibrio cholerae) are infected with a bacteriophage known as VP882—and discovered that tiny RNA molecules play a decisive role. The researchers’ findings have been published in the latest issue of the journal Cell Host & Microbe.
From harmless housemate to cunning kidnapper
There are two ways in which phages can multiply after infecting bacteria: either as invisible passengers, hidden in the bacteria’s genetic material, or as cunning kidnappers, multiplying in vast numbers in bacterial cells without regard for potential losses and, ultimately, destroying the cells. Which method a phage adopts depends on whether sufficient numbers of other host cells are available in the immediate environment to provide shelter.
But how do phages determine this? “They rely on a chemical counting mechanism that bacteria use to identify other members of their species,” explains Prof. Dr. Kai Papenfort of the University of Jena, who headed up the project.
Known as “quorum sensing,” this method uses signal molecules that are produced by bacteria and released into their surroundings. At the same time, the bacteria monitor the concentration of these molecules using specific receptors, thereby gaining information about the size of their current population.
“The phages’ trick essentially involves ‘listening in’ to this chemical communication between bacteria,” says Papenfort.
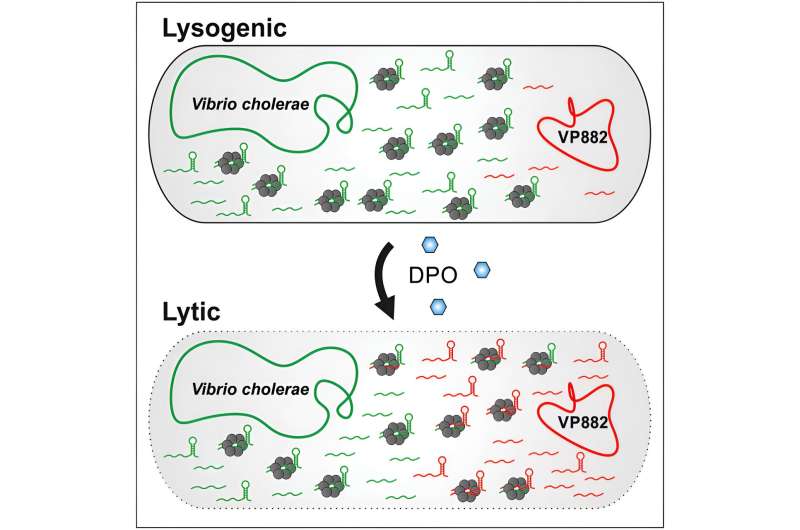
In their experiments, the Jena researchers examined what happens to the phages and bacteria once the bacteria emit their quorum sensing signals. “We have observed that 99% of bacteria are destroyed within 60 minutes, in which time the phages take control,” reports Dr. Marcel Sprenger, the lead author of the article.
The team discovered that this switchover is controlled by tiny RNA molecules, one of which is called “VpdS” (VP882 phage-derived sRNA). “As soon as the phages receive the chemical signal from the bacteria, this RNA is produced in high quantities,” says Sprenger.
How bacteria fight back against viruses
In order to find out precisely which genes are regulated by VpdS, the team adopted a comprehensive, technological approach and infected bacteria cultures with both VP882 phages and genetically modified phages unable to produce VpdS.
Applying a method known as “RNA interaction by ligation and sequencing,” the researchers were able to identify the interactions between all RNA molecules in the bacteria cultures at different times. “This not only gave us insights into which genes are active, it also showed how they interact,” says Papenfort.
This method enabled the researchers to examine the genes of the phages as well as those of the host bacteria. As a result, the researchers gained extensive insights into the changes that occurred both during and after quorum sensing. “We were able to demonstrate that VpdS regulates phage genes as well as genes of the host, which effectively explains the destruction of bacterial cells,” says Papenfort.
However, the researchers have been able to deduce further relationships from the data they collected. For example, bacteria also have genes that, when activated by a chemical signal, fight back against the phages’ propagation and thereby counteract their own destruction.
According to Papenfort, this aspect is particularly interesting. “We can see these as the precursors to the immune systems in higher organisms. Bacteria have many genes that protect them against viruses.” Given that these genes are also present in higher organisms, the researchers surmise that RNA molecules could also play an important role in their regulation.
More information: Small RNAs direct attack and defence mechanisms in a quorum sensing phage and its host, Cell Host & Microbe (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2024.03.010. www.cell.com/cell-host-microbe … 1931-3128(24)00090-8
Journal information: Cell Host & Microbe
News
The Silent Battle Within: How Your Organs Choose Between Mom and Dad’s Genes
Research reveals that selective expression of maternal or paternal X chromosomes varies by organ, driven by cellular competition. A new study published today (July 26) in Nature Genetics by the Lymphoid Development Group at the MRC [...]
Study identifies genes increasing risk of severe COVID-19
Whether or not a person becomes seriously ill with COVID-19 depends, among other things, on genetic factors. With this in mind, researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn, in [...]
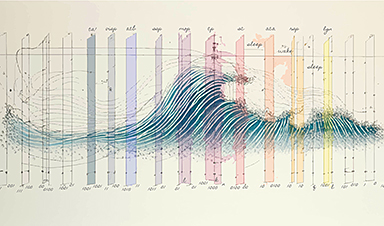
Small regions of the brain can take micro-naps while the rest of the brain is awake and vice versa
Sleep and wake: They're totally distinct states of being that define the boundaries of our daily lives. For years, scientists have measured the difference between these instinctual brain processes by observing brain waves, with [...]
Redefining Consciousness: Small Regions of the Brain Can Take Micro-Naps While the Rest of the Brain Is Awake
The study broadly reveals how fast brain waves, previously overlooked, establish fundamental patterns of sleep and wakefulness. Scientists have developed a new method to analyze sleep and wake states by detecting ultra-fast neuronal activity [...]
AI Reveals Health Secrets Through Facial Temperature Mapping
Researchers have found that different facial temperatures correlate with chronic illnesses like diabetes and high blood pressure, and these can be detected using AI with thermal cameras. They highlight the potential of this technology [...]
Breakthrough in aging research: Blocking IL-11 extends lifespan and improves health in mice
In a recent study published in the journal Nature, a team of researchers used murine models and various pharmacological and genetic approaches to examine whether pro-inflammatory signaling involving interleukin (IL)-11, which activates signaling molecules such [...]
Promise for a universal influenza vaccine: Scientists validate theory using 1918 flu virus
New research led by Oregon Health & Science University reveals a promising approach to developing a universal influenza vaccine—a so-called "one and done" vaccine that confers lifetime immunity against an evolving virus. The study, [...]
New Projects Aim To Pioneer the Future of Neuroscience
One study will investigate the alterations in brain activity at the cellular level caused by psilocybin, the psychoactive substance found in “magic mushrooms.” How do neurons respond to the effects of magic mushrooms? What [...]
Decoding the Decline: Scientific Insights Into Long COVID’s Retreat
Research indicates a significant reduction in long COVID risk, largely due to vaccination and the virus’s evolution. The study analyzes data from over 441,000 veterans, showing lower rates of long COVID among vaccinated individuals compared [...]
Silicon Transformed: A Breakthrough in Laser Nanofabrication
A new method enables precise nanofabrication inside silicon using spatial light modulation and laser pulses, creating advanced nanostructures for potential use in electronics and photonics. Silicon, the cornerstone of modern electronics, photovoltaics, and photonics, [...]
Caught in the actinium: New research could help design better cancer treatments
The element actinium was first discovered at the turn of the 20th century, but even now, nearly 125 years later, researchers still don't have a good grasp on the metal's chemistry. That's because actinium [...]
Innovative Light-Controlled Drugs Could Revolutionize Neuropathic Pain Treatment
A team of researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) has developed light-activated derivatives of the anti-epileptic drug carbamazepine to treat neuropathic pain. Light can be harnessed to target drugs to specific [...]
Green Gold: Turning E-Waste Into a Treasure Trove of Rare Earth Metals
Scientists are developing a process inspired by nature that efficiently recovers europium from old fluorescent lamps. The approach could lead to the long-awaited recycling of rare earth metals. A small molecule that naturally serves [...]
Cambridge Study: AI Chatbots Have an “Empathy Gap,” and It Could Be Dangerous
A new study suggests a framework for “Child Safe AI” in response to recent incidents showing that many children perceive chatbots as quasi-human and reliable. A study has indicated that AI chatbots often exhibit [...]
Nanoparticle-based delivery system could offer treatment for diabetics with rare insulin allergy
Up to 3% of people with diabetes have an allergic reaction to insulin. A team at Forschungszentrum Jülich has now studied a method that could be used to deliver the active substance into the [...]
Nanorobot kills cancer cells in mice with hidden weapon
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have developed nanorobots that kill cancer cells in mice. The robot's weapon is hidden in a nanostructure and is exposed only in the tumor microenvironment, sparing healthy cells. [...]