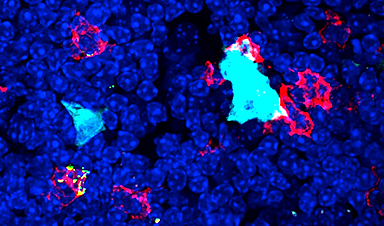
Biomedical scientists from UC Riverside state that the cells resemble M cells found in the gut and airways.
It came as a surprise to Professor David Lo and his graduate student Diana Del Castillo when they were recently consulted by researchers in Israel for their expertise on specialized cells called Microfold cells, or M cells, which are mostly known for their presence in the intestinal epithelium. The Israeli group had identified similar cells in the thymus, an organ located just above the heart that makes lymphocytes — white blood cells that play an important role in the immune system and protect the body against infection.
Lo, a distinguished professor of biomedical sciences in the UC Riverside School of Medicine, and Del Castillo, who are co-authors on the research paper published in Nature, confirmed the newly discovered cells in the thymus are just like M cells. Acting like gatekeepers, M cells are specialized antigen-delivery cells for the immune system in organs like the intestine and lungs. They play a key role in the development of the body’s immune system.
The researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel, led by Jakub Abramson, initiated the mouse study on the thymic epithelium before contacting Lo, whose research interests include understanding how M cells in the gut and airways work to build our immune system.
“I have been working on these cells for several years, so when the Israeli team contacted me, I was intrigued,” Lo said. “I learned this group had been doing studies on the cellular architecture of stromal cells — cells that make up certain types of connective tissue — in the thymus and, using a new advanced method, had discovered a population of cells much like the M cells we see in the gut and airways. In my own research, I had simply never thought to look for M cells in the thymus.”
Fortuitously for the Israeli scientists, Del Castillo, under Lo’s guidance, had been studying mucosal tissues — tissues that line some of the body’s canals and organs — in mice in the lab and was able to answer several questions, such as where in the thymus the newly discovered cells are located and what they are doing there.
The Unique Nature of Thymic M Cells
“These particular M cells are limited to a specific region in the thymus and have unique associations with different cell types and functions,” Del Castillo said. “Questions these cells have already prompted include how similar are they to M cells elsewhere in the body and what is different about where they have been found.”
Lo explained that for many years the thymus has been a tissue of interest to immunologists because most of the immune system’s development is centered and dependent on the thymus.
“It’s still an ongoing deep puzzle that continues to attract interest,” he said. “The thymus offers clues to how the immune system got its start. This complicated organ, with so many different stromal cell types and interactions, is responsible for producing lymphocytes that protect us from infection.”
According to Lo, the newly discovered M cells are extremely similar to the M cells seen in the gut and airways.
“But the thymic M cells have different developmental origins, which is an interesting puzzle in itself,” he said. “After they develop, they look very much like the ones we have been studying in the gut. As we know, M cells capture viruses and bugs that enter the airways and hand them off to the immune system, which then responds to the infectious agents. Are the M cells doing the same thing in the thymus in terms of organization and function? That’s what we would like to know.”
Exploring the Function of Thymic M Cells
Del Castillo, who is working toward her doctoral degree in biomedical sciences, used genetically engineered mice to tackle the questions from the Israeli researchers.
“We found the new cells were scattered in the medullary region of the thymus,” she said. “This has interesting implications in terms of the role and compartmentalization of the thymus, such as how these cells may function to regulate lymphocyte training within this organ.”
Lo and Del Castillo were surprised to find that many steps involved in shaping an immune response in various parts of the body seem to be echoed in the thymus.
“It is fascinating to see that many of these early cell interactions and development we have studied closely in the peripheral immune system take place in the thymus,” Lo said. “We had not anticipated to see these interactions here. It’s like watching a short video in the thymus about what is happening big-scale out in the periphery.”
The thymus also ensures that lymphocytes do not accidentally attack our own tissues; the thymic medulla is where these decisions are made, the UCR scientists said.
“The newly discovered M cells are part of this decision-making process,” Del Castillo said. “The production of antibodies in the peripheral immune system to fight off infectious organisms involves several steps and many cells interacting with each other. What is fascinating is that some of these interactions are recapitulated in the early stages of the development of the thymic M cells.”
According to Lo, the thymic M cells could be seen as being trained to function later, when needed, in the periphery in such a way that they are ready to communicate and interact with other cells.
“The thymus is complicated because it creates a whole functional immune system and repertoire, and we know many component parts play a role in its performance,” he said. “We didn’t expect M cells to even show up in the thymus. This is, therefore, a satisfying discovery because it is so clearly connected to similar processes happening in the gut and airways, which is where 60-70% of our infectious agents enter our bodies.”
Reference: “Thymic mimetic cells function beyond self-tolerance” by Tal Givony, Dena Leshkowitz, Diana Del Castillo, Shir Nevo, Noam Kadouri, Bareket Dassa, Yael Gruper, Razi Khalaila, Osher Ben-Nun, Tom Gome, Jan Dobeš, Shifra Ben-Dor, Merav Kedmi, Hadas Keren-Shaul, Rebecca Heffner-Krausz, Ziv Porat, Ofra Golani, Yoseph Addadi, Ori Brenner, David D. Lo, Yael Goldfarb and Jakub Abramson, 6 September 2023, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06512-8
News
Team finds flawed data in recent study relevant to coronavirus antiviral development
The COVID pandemic illustrated how urgently we need antiviral medications capable of treating coronavirus infections. To aid this effort, researchers quickly homed in on part of SARS-CoV-2's molecular structure known as the NiRAN domain—an [...]
Drug-Coated Neural Implants Reduce Immune Rejection
Summary: A new study shows that coating neural prosthetic implants with the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone helps reduce the body’s immune response and scar tissue formation. This strategy enhances the long-term performance and stability of electrodes [...]
Scientists discover cancer-fighting bacteria that ‘soak up’ forever chemicals in the body
A family of healthy bacteria may help 'soak up' toxic forever chemicals in the body, warding off their cancerous effects. Forever chemicals, also known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), are toxic chemicals that [...]
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard it is for scientists to [...]
Are Pesticides Breeding the Next Pandemic? Experts Warn of Fungal Superbugs
Fungicides used in agriculture have been linked to an increase in resistance to antifungal drugs in both humans and animals. Fungal infections are on the rise, and two UC Davis infectious disease experts, Dr. George Thompson [...]
Scientists Crack the 500-Million-Year-Old Code That Controls Your Immune System
A collaborative team from Penn Medicine and Penn Engineering has uncovered the mathematical principles behind a 500-million-year-old protein network that determines whether foreign materials are recognized as friend or foe. How does your body [...]
Team discovers how tiny parts of cells stay organized, new insights for blocking cancer growth
A team of international researchers led by scientists at City of Hope provides the most thorough account yet of an elusive target for cancer treatment. Published in Science Advances, the study suggests a complex signaling [...]
Nanomaterials in Ophthalmology: A Review
Eye diseases are becoming more common. In 2020, over 250 million people had mild vision problems, and 295 million experienced moderate to severe ocular conditions. In response, researchers are turning to nanotechnology and nanomaterials—tools that are transforming [...]
Natural Plant Extract Removes up to 90% of Microplastics From Water
Researchers found that natural polymers derived from okra and fenugreek are highly effective at removing microplastics from water. The same sticky substances that make okra slimy and give fenugreek its gel-like texture could help [...]
Instant coffee may damage your eyes, genetic study finds
A new genetic study shows that just one extra cup of instant coffee a day could significantly increase your risk of developing dry AMD, shedding fresh light on how our daily beverage choices may [...]