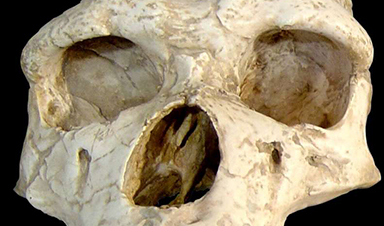
Everybody loves Neandertals, those big-brained brutes we supposedly outcompeted and ultimately replaced using our sharp tongues and quick, delicate minds. But did we really, though? Is it mathematically possible that we could yet be them, and they us?
By the same token, could not the impossibly singular Mitochondrial Eve, her contemporary Y-chromosome Adam, and even the “Out of Africa” hypothesis simply be convenient fictions paleogeneticists tell each other at conferences to give their largely arbitrary haplotype designations and subsequently derived evolutionary trees more credence?
Perhaps one of the best ways to try to answer this question is to ask what the coronavirus has to say about the issue. Svante Pääbo, director of the genetics department at the Max Planck Institute certainly believes that Homo sapiens Neanderthalensis, or just Homo Neanderthalensis, if you prefer, is extinct. Pääbo, the son of 1982 Noble laureate Sune Bergström, has made a nice living off of Neandertal bones, finding gene after gene that is distinctly “Neandertal.” In 1997, Pääbo successfully sequenced mitochondrial DNA from a specimen found in Feldhofer grotto in the Neander valley. Fast-forwarding past a few recent PR disasters, the Germans were able to capture the productive Swede and set him upon the task of dealing with these inconvenient heirloom skeletons that kept showing up.
This September, Pääbo and colleague Hugo Zeberg announced that the major genetic risk factor for severe COVID-19 is inherited from Neanderthals. (We note that Nature publications prefer to include the h.) By any measure, this is a bold statement. The team found that severe COVID-19 disease is associated with specific genetic variants in six genes within a 50K-base-pair-long region of chromosome 3 that derived directly from a Neanderthal heritage. Similar investigations have also identified a protective Neanderthal haplotype on chromosome (chr) 12 that reduces the risk of severe COVID-9, and a protective region on chromosome 9 that is associated with the ABO blood groups.
Not content to rest on their laurels, Pääbo and Zeberg have just kicked things up a notch. The pair recently reported on the bioRxiv preprint server that another exclusively Neandertal variant, this time in the promoter region of the DPP4 gene at chr2q24.2, is really pulling the strings on COVID susceptibility. DPP4 is a widely expressed extracellular dipeptidyl peptidase involved in immune function and glucose metabolism. As it happens, DPP4 is also the receptor gene for the MERS coronavirus. Now we are getting somewhere.
Image Credit: Wikipedia
Post by Amanda Scott, NA CEO. Follow her on twitter @tantriclens
Thanks to Heinz V. Hoenen. Follow him on twitter: @HeinzVHoenen
News
The Silent Battle Within: How Your Organs Choose Between Mom and Dad’s Genes
Research reveals that selective expression of maternal or paternal X chromosomes varies by organ, driven by cellular competition. A new study published today (July 26) in Nature Genetics by the Lymphoid Development Group at the MRC [...]
Study identifies genes increasing risk of severe COVID-19
Whether or not a person becomes seriously ill with COVID-19 depends, among other things, on genetic factors. With this in mind, researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn, in [...]
Small regions of the brain can take micro-naps while the rest of the brain is awake and vice versa
Sleep and wake: They're totally distinct states of being that define the boundaries of our daily lives. For years, scientists have measured the difference between these instinctual brain processes by observing brain waves, with [...]
Redefining Consciousness: Small Regions of the Brain Can Take Micro-Naps While the Rest of the Brain Is Awake
The study broadly reveals how fast brain waves, previously overlooked, establish fundamental patterns of sleep and wakefulness. Scientists have developed a new method to analyze sleep and wake states by detecting ultra-fast neuronal activity [...]
AI Reveals Health Secrets Through Facial Temperature Mapping
Researchers have found that different facial temperatures correlate with chronic illnesses like diabetes and high blood pressure, and these can be detected using AI with thermal cameras. They highlight the potential of this technology [...]
Breakthrough in aging research: Blocking IL-11 extends lifespan and improves health in mice
In a recent study published in the journal Nature, a team of researchers used murine models and various pharmacological and genetic approaches to examine whether pro-inflammatory signaling involving interleukin (IL)-11, which activates signaling molecules such [...]
Promise for a universal influenza vaccine: Scientists validate theory using 1918 flu virus
New research led by Oregon Health & Science University reveals a promising approach to developing a universal influenza vaccine—a so-called "one and done" vaccine that confers lifetime immunity against an evolving virus. The study, [...]
New Projects Aim To Pioneer the Future of Neuroscience
One study will investigate the alterations in brain activity at the cellular level caused by psilocybin, the psychoactive substance found in “magic mushrooms.” How do neurons respond to the effects of magic mushrooms? What [...]
Decoding the Decline: Scientific Insights Into Long COVID’s Retreat
Research indicates a significant reduction in long COVID risk, largely due to vaccination and the virus’s evolution. The study analyzes data from over 441,000 veterans, showing lower rates of long COVID among vaccinated individuals compared [...]
Silicon Transformed: A Breakthrough in Laser Nanofabrication
A new method enables precise nanofabrication inside silicon using spatial light modulation and laser pulses, creating advanced nanostructures for potential use in electronics and photonics. Silicon, the cornerstone of modern electronics, photovoltaics, and photonics, [...]
Caught in the actinium: New research could help design better cancer treatments
The element actinium was first discovered at the turn of the 20th century, but even now, nearly 125 years later, researchers still don't have a good grasp on the metal's chemistry. That's because actinium [...]
Innovative Light-Controlled Drugs Could Revolutionize Neuropathic Pain Treatment
A team of researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) has developed light-activated derivatives of the anti-epileptic drug carbamazepine to treat neuropathic pain. Light can be harnessed to target drugs to specific [...]
Green Gold: Turning E-Waste Into a Treasure Trove of Rare Earth Metals
Scientists are developing a process inspired by nature that efficiently recovers europium from old fluorescent lamps. The approach could lead to the long-awaited recycling of rare earth metals. A small molecule that naturally serves [...]
Cambridge Study: AI Chatbots Have an “Empathy Gap,” and It Could Be Dangerous
A new study suggests a framework for “Child Safe AI” in response to recent incidents showing that many children perceive chatbots as quasi-human and reliable. A study has indicated that AI chatbots often exhibit [...]
Nanoparticle-based delivery system could offer treatment for diabetics with rare insulin allergy
Up to 3% of people with diabetes have an allergic reaction to insulin. A team at Forschungszentrum Jülich has now studied a method that could be used to deliver the active substance into the [...]
Nanorobot kills cancer cells in mice with hidden weapon
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have developed nanorobots that kill cancer cells in mice. The robot's weapon is hidden in a nanostructure and is exposed only in the tumor microenvironment, sparing healthy cells. [...]