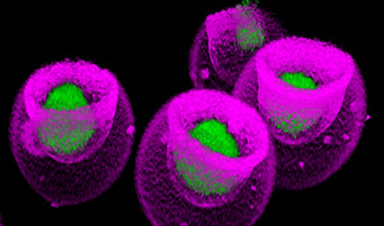
A team of researchers from the University of Cambridge has developed a chemical ‘camera’ using a molecular glue that allows chemical reactions to be observed in real-time. The device is made up of semiconductor nanocrystals, referred to as quantum dots, and gold nanoparticles held together with a molecular glue called cucurbituril, with potential applications for a wide range of sectors due to its ease of use.
The research was published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, and shows that once added to water, these components self-assemble to produce a tool that allows monitoring of chemical reactions as they happen. As well as being a powerful device, it is stable and assembles in seconds.
Using the light within the semiconductor nanocrystals, the camera causes an electron transfer process to take place, enabling the researchers to use spectroscopy to observe chemical species directly. Previously, this ability had only been theorized.
What is the Nano Camera?
The nano camera is produced by combining semiconductor nanocrystals, gold nanoparticles, and cucurbituril to produce a stable, hybrid material that interacts with light and allows for real-time monitoring of chemical reactions. Professor Oren Scherman and his team at Cambridge’s Cavendish Laboratory and University College London developed this new method.
The semiconductor nanocrystals act as assembly modulators, controlling the assembly of the larger gold nanoparticles through a process which the team named ‘interfacial self-limiting aggregation’. Doing so enabled the production of a stable hybrid material that can interact with light, composing the nano camera.
In the laboratory, the team combined the individual components of their camera along with the molecule they wished to observe in water at room temperature. Past attempts to mix gold nanoparticles with cucurbituril led to items undergoing unlimited aggregation. However, the addition of semiconductor nanocrystals to the mixture produced a stable semiconductor-metal hybrid.
Key Findings
The researchers used spectroscopy to observe the chemical reactions once the components were mixed together. With the camera’s presence, they observed the formation of a radical species and products of the assembly, including a sigma violgen dimeric species, the product of two radicals forming a reversible carbon-carbon bond.
All the components used are readily available, and the camera can be formed without the need for extreme conditions.
We were surprised how powerful this new tool is, considering how straightforward it is to assemble.
Dr. Kamil Sokolowksi, first author
Individually, each component’s properties and uses are well known, but their unique combination makes this research an innovation.
For example, cucurbituril is a macrocyclic molecule made up of glycoluril monomers linked by a methylene bridge. It has a high affinity, highly selective, and its binding properties have led to use as a molecular ‘glue’ in the aggregation of nanoparticles in the past.
Both the aggregation of semiconductor nanocrystals and old nanoparticles are well documented; however, their use with cucurbituril to produce a nano camera is a novelty that could be pivotal in understanding other significant reactions in nanotechnology.
The Future of the Nano Camera in Nanotechnology Research
The nano camera has vast potential to be used in research and industry. It is inexpensive and straightforward to produce, meaning that it can replace more expensive, complicated methods which were not accessible in the past.
The type of complex hybrid produced can be formed in nature thanks to a self-limiting process, but this is not easy to replicate under lab conditions and is often a costly and lengthy process.
This innovative, simple process can be applied to many different combinations of metal nanoparticles and semiconductor nanocrystals that could not form hybrids in a laboratory previously, therefore providing new opportunities for imaging chemical reactions.
In a press release from the University of Cambridge, Dr. Sokolowski explained “This platform is a really big toolbox considering the number of metal and semiconductor building blocks that can be now coupled together using this chemistry– it opens up lots of new possibilities for imaging chemical reactions and sensing through taking snapshots of monitored chemical systems.”
One of the industries that may benefit from the use of the nano camera is renewable energies. The Scherman lab in Cambridge team is already working on developing a hybrid that will allow the observation of electron-transfer processes in artificial photosynthetic systems and photocatalysis.
Understanding and harnessing an artificial photosynthetic system would greatly advance the renewable energy sector. Current solar panels using photovoltaic cells are not efficient and are unable to store energy. Artificial photosynthesis could produce clean, storable fuels, and the ability to observe a chemical reaction in real-time could allow it to be replicated on a large scale.
The research team is also exploring how the process can be used to observe the formation of carbon-carbon bonds. Experiments exploring electrode interfaces for battery applications are also being conducted.
It is clear the knowledge that could be gleaned from observing real-time reactions could improve existing nanotechnology and produce new innovations, making this device an appealing addition to the future of the sector.
News
Scientists study lipids cell by cell, making new cancer research possible
Imagine being able to look inside a single cancer cell and see how it communicates with its neighbors. Scientists are celebrating a new technique that lets them study the fatty contents of cancer cells, [...]
Antibiotic Breakthrough: Revolutionary Chinese Study Paves Way for Superbug Defeating Drugs
New research reveals that fluorous lipopetides act as highly effective antibiotics. Bacterial infections resistant to multiple drugs, which no existing antibiotics can treat, represent a significant worldwide challenge. A research group from China has [...]
Signs of Multiple Sclerosis Show Up in Blood Years Before Symptoms Appear
UCSF scientists clear a potential path toward earlier treatment for a disease that affects nearly 1,000,000 people in the United States. By Levi Gadye In a discovery that could hasten treatment for patients with multiple [...]
Advanced RNA Sequencing Reveals the Drivers of New COVID Variants
A study reveals that a new sequencing technique, tARC-seq, can accurately track mutations in SARS-CoV-2, providing insights into the rapid evolution and variant development of the virus. The SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID has the unsettling [...]
No More Endless Boosters? Scientists Develop One-for-All Virus Vaccine
End of the line for endless boosters? Researchers at UC Riverside have developed a new vaccine approach using RNA that is effective against any strain of a virus and can be used safely even by babies or the immunocompromised. Every [...]
How Are Hydrogels Shaping the Future of Biomedicine?
Hydrogels have gained widespread recognition and utilization in biomedical engineering, with their applications dating back to the 1960s when they were first used in contact lens production. Hydrogels are distinguished from other biomaterials in [...]
Nanovials method for immune cell screening uncovers receptors that target prostate cancer
A recent UCLA study demonstrates a new process for screening T cells, part of the body's natural defenses, for characteristics vital to the success of cell-based treatments. The method filters T cells based on [...]
New Research Reveals That Your Sense of Smell May Be Smarter Than You Think
A new study published in the Journal of Neuroscience indicates that the sense of smell is significantly influenced by cues from other senses, whereas the senses of sight and hearing are much less affected. A popular [...]
Deadly bacteria show thirst for human blood: the phenomenon of bacterial vampirism
Some of the world's deadliest bacteria seek out and feed on human blood, a newly-discovered phenomenon researchers are calling "bacterial vampirism." A team led by Washington State University researchers has found the bacteria are [...]
Organ Architects: The Remarkable Cells Shaping Our Development
Finding your way through the winding streets of certain cities can be a real challenge without a map. To orient ourselves, we rely on a variety of information, including digital maps on our phones, [...]
Novel hydrogel removes microplastics from water
Microplastics pose a great threat to human health. These tiny plastic debris can enter our bodies through the water we drink and increase the risk of illnesses. They are also an environmental hazard; found [...]
Researchers Discover New Origin of Deep Brain Waves
Understanding hippocampal activity could improve sleep and cognition therapies. Researchers from the University of California, Irvine’s biomedical engineering department have discovered a new origin for two essential brain waves—slow waves and sleep spindles—that are critical for [...]
The Lifelong Cost of Surviving COVID: Scientists Uncover Long-Term Effects
Many of the individuals released to long-term acute care facilities suffered from conditions that lasted for over a year. Researchers at UC San Francisco studied COVID-19 patients in the United States who survived some of the longest and [...]
Previously Unknown Rogue Immune Key to Chronic Viral Infections Discovered
Scientists discovered a previously unidentified rogue immune cell linked to poor antibody responses in chronic viral infections. Australian researchers have discovered a previously unknown rogue immune cell that can cause poor antibody responses in [...]
Nature’s Betrayal: Unmasking Lead Lurking in Herbal Medicine
A case of lead poisoning due to Ayurvedic medicine use demonstrates the importance of patient history in diagnosis and the need for public health collaboration to prevent similar risks. An article in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association [...]
Frozen in Time: How a DNA Anomaly Misled Scientists for Centuries
An enormous meteor spelled doom for most dinosaurs 65 million years ago. But not all. In the aftermath of the extinction event, birds — technically dinosaurs themselves — flourished. Scientists have spent centuries trying [...]