Tiny particles called quantum dots reduce symptoms in mice primed to develop a type of Parkinson’s disease, and also block formation of the toxic protein clumps in Alzheimer’s. They could one day be a novel treatment for these brain disorders, although tests in people are some years away.
Quantum dots are just a few nanometres in size – so small they become subject to some of the strange effects of quantum physics. They have useful electronic and fluorescent properties and are found in some TV screens and LED lights.
Unlike most medicines, their tiny size means they can pass from bloodstream into the brain. Byung Hee Hong of Seoul National University in the South Korea and his colleagues wondered if they would affect the molecules involved in Parkinson’s or other brain disorders.
Parkinson’s disease involves gradually worsening tremors and movement problems. It is thought to be caused by a protein called synuclein found in nerve cells folding into the wrong shape, which triggers a chain reaction of misfolding in nearby synuclein molecules. This leads to a build-up of long strands or “fibrils” of the protein, killing neurons.
Quantum surprise
Hong’s team found that in a dish, quantum dots made from graphene – a form of carbon – bind to synuclein, and not only stop it from clumping into fibres, but also cause existing fibres to break up into individual molecules. “We didn’t expect the quantum dots to induce disaggregation of fibrils,” says Hong.
If the treatment affects people the same way, Hong says it is unclear how much benefit this would bring. “It’s hard to translate the results in mice to actual patients, whose systems are way more complicated. But we do believe quantum dots can make positive impacts to some extent.”
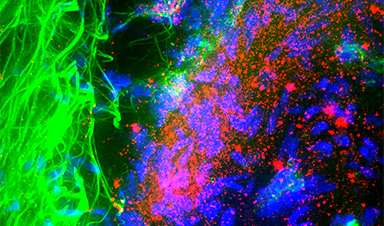
Image Credit: May C. Schiess, Roger Back, UT Medical School/Science Photo Library
News This Week
Scientists Discover Simple Saliva Test That Reveals Hidden Diabetes Risk
Researchers have identified a potential new way to assess metabolic health using saliva instead of blood. High insulin levels in the blood, known as hyperinsulinemia, can reveal metabolic problems long before obvious symptoms appear. It is [...]
One Nasal Spray Could Protect Against COVID, Flu, Pneumonia, and More
A single nasal spray vaccine may one day protect against viruses, pneumonia, and even allergies. For decades, scientists have dreamed of creating a universal vaccine capable of protecting against many different pathogens. The idea [...]
New AI Model Predicts Cancer Spread With Incredible Accuracy
Scientists have developed an AI system that analyzes complex gene-expression signatures to estimate the likelihood that a tumor will spread. Why do some tumors spread throughout the body while others remain confined to their [...]
Scientists Discover DNA “Flips” That Supercharge Evolution
In Lake Malawi, hundreds of species of cichlid fish have evolved with astonishing speed, offering scientists a rare opportunity to study how biodiversity arises. Researchers have identified segments of “flipped” DNA that may allow fish to adapt rapidly [...]
Our books now available worldwide!
Online Sellers other than Amazon, Routledge, and IOPP Indigo Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artifcial Intelligence Global Health Care Equivalency In The Age Of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine And Artificial [...]
Scientists Discover Why Some COVID Survivors Still Can’t Taste Food Years Later
A new study provides the first direct biological evidence explaining why some people continue to experience taste loss long after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers have uncovered specific biological changes in taste buds that could help [...]
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]













Leave A Comment