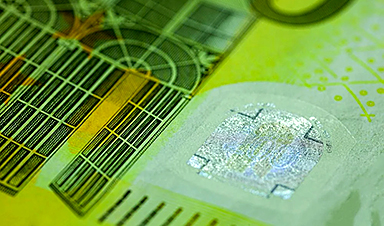
In a study published in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, a mix of chemistry, nanomaterials, and artificial intelligence (AI) was used to produce a straightforward yet cryptographic anticounterfeiting measure.
The Need for Effective Anticounterfeiting Techniques
The requirement for robust anti-counterfeit solutions is driving scholarly and corporate research to enhance the authenticity and safety of products. The spread of counterfeit commodities is a huge nuisance all over the globe, particularly in the retail and pharmaceutical industries. Fake pharma goods endanger patients and compromise public health, resulting in high economic and social costs for developed as well as developing nations.
To put the magnitude of the issue into perspective, counterfeit medications for treatments of pneumonia and malaria kill roughly 250,000 children annually. Such a significant problem necessitates a serious technical effort to develop powerful anti-counterfeit technologies that are also consistent with market constraints.
Numerous substances and chemical procedures have been suggested as biometric markers. These vary from intricate ink compositions utilized in currency notes to luminous upconverting nano-phosphorous tags, inkjet printable conjugate polymeric platforms, or molecular identifiers like peptides, DNA, and polymers that promise large encoding potentials and secrecy.
These technologies, however, may be cloneable. Moreover, they often need costly hardware and highly skilled workers, restricting their practical uses.
Nanotechnology can Improve PUFs
A highly sophisticated anti-counterfeit technique was provided in this system using physically unclonable functions (PUFs) that are predicated on distinct markers created by chemical procedures in a stochastic mechanism. The unpredictability created by the non-deterministic technique assures that replicating the PUF key is just about impossible whenever the PUF sequence is digitized and saved.
If there are not enough distinct markers to secure a significant number of objects, PUFs’ encoding capability may be restricted. Owing to the unpredictability and huge parametric space provided by nanostructures paired with physiochemical procedures, this problem may be solved if PUFs are created using methods based on nanotechnology that provide a significant encoding potential which translates to a large quantity of distinct markers.
Critical Aspects of PUFs
The distinguishing physical trait is often a randomized two-dimensional or three-dimensional pattern, leading to various visual readings. Certain nanotechnology-based PUFs, like glass microbead randomized speckle patterning, inkjet-printed unclonable quantum dot (QD) fluorescent tags, and Au nanoparticle (NP) or Ag nanowire (NW) randomized patterns have lately been described.
Tag reading is crucial because several approaches depend on intricate hardware for verification, like dark-field, fluorescent, or electron microscopy, limiting their applicability for the overall supply chain needs, like mobility, quickness, repeatability, and reduced price of the procedure.
Salient Features of the Study
The technique suggested in this study aimed to achieve all of the aforementioned desirable characteristics, delivering an adequate anti-counterfeit approach via a rapid (1 minute), reversible, and equipment-free colorimetry reading facilitated by nanoscale Pt catalysts, which would be usable at any juncture of the supply network, even the end user.
Owing to the creation of a dependable AI method for quick and reliable visual marker authentication on the basis of Deep Learning and Computer Vision approaches, this nanotechnology-facilitated system may be readily encoded and then authorized via a cellphone.
Key Takeaways
In this study, the team demonstrated the possibility of merging chemistry, nanotechnology, and artificial intelligence to build novel cross-discipline techniques aimed at addressing critical sustainability and security challenges.
A sophisticated reversible PUF marker was presented that combined the achievement of distinct patterning with substantial encryption capabilities with a visual colorimetry reading perceptible by the human eye and analyzable using a cellphone.
The approach adopted by the team provided great ease in authenticating (i.e., equipment-free visual reading) as well as cutting-edge encryption capabilities by using the catalytic characteristics of nanoparticles. The suggested technique may be improved by creating various stochastic patterns and platforms, resulting in even greater security levels.
The ability to achieve repeated verification cycles in ambient settings, owing to the rapid (ON/OFF) color emergence/fading system evoked by the nanoscale platinum catalysts, opens up fresh avenues for in-situ analyses of potential counterfeits of high-quality goods throughout the entire supply network, from quality control after production to individual evaluation by the end-user.
News
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]
Scientists Develop Spray-On Powder That Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds
KAIST scientists have created a fast-acting, stable powder hemostat that stops bleeding in one second and could significantly improve survival in combat and emergency medicine. Severe blood loss remains the primary cause of death from [...]
Oceans Are Struggling To Absorb Carbon As Microplastics Flood Their Waters
New research points to an unexpected way plastic pollution may be influencing Earth’s climate system. A recent study suggests that microscopic plastic pollution is reducing the ocean’s capacity to take in carbon dioxide, a [...]
Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine – New book from Frank Boehm
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
New Book! NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artificial Intelligence
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
Miller School Researchers Pioneer Nanovanilloid-Based Brain Cooling for Traumatic Injury
A multidisciplinary team at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine has developed a breakthrough nanodrug platform that may prove beneficial for rapid, targeted therapeutic hypothermia after traumatic brain injury (TBI). Their work, published in ACS [...]
COVID-19 still claims more than 100,000 US lives each year
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers report national estimates of 43.6 million COVID-19-associated illnesses and 101,300 deaths in the US during October 2022 to September 2023, plus 33.0 million illnesses and 100,800 deaths [...]
Nanomedicine in 2026: Experts Predict the Year Ahead
Progress in nanomedicine is almost as fast as the science is small. Over the last year, we've seen an abundance of headlines covering medical R&D at the nanoscale: polymer-coated nanoparticles targeting ovarian cancer, Albumin recruiting nanoparticles for [...]
Lipid nanoparticles could unlock access for millions of autoimmune patients
Capstan Therapeutics scientists demonstrate that lipid nanoparticles can engineer CAR T cells within the body without laboratory cell manufacturing and ex vivo expansion. The method using targeted lipid nanoparticles (tLNPs) is designed to deliver [...]
The Brain’s Strange Way of Computing Could Explain Consciousness
Consciousness may emerge not from code, but from the way living brains physically compute. Discussions about consciousness often stall between two deeply rooted viewpoints. One is computational functionalism, which holds that cognition can be [...]
First breathing ‘lung-on-chip’ developed using genetically identical cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and AlveoliX have developed the first human lung-on-chip model using stem cells taken from only one person. These chips simulate breathing motions and lung disease in an individual, [...]
Cell Membranes May Act Like Tiny Power Generators
Living cells may generate electricity through the natural motion of their membranes. These fast electrical signals could play a role in how cells communicate and sense their surroundings. Scientists have proposed a new theoretical [...]
This Viral RNA Structure Could Lead to a Universal Antiviral Drug
Researchers identify a shared RNA-protein interaction that could lead to broad-spectrum antiviral treatments for enteroviruses. A new study from the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC), published in Nature Communications, explains how enteroviruses begin reproducing [...]
New study suggests a way to rejuvenate the immune system
Stimulating the liver to produce some of the signals of the thymus can reverse age-related declines in T-cell populations and enhance response to vaccination. As people age, their immune system function declines. T cell [...]