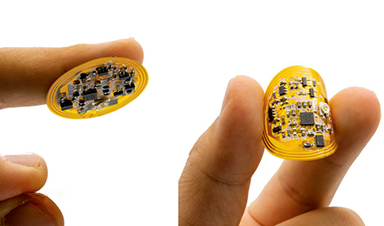
| Some wounds just won’t heal. Infections, diseases like diabetes, and suppressed immune systems often stack up to slow healing. Chronic wounds can last months and lead to anxiety and depression. In the worst cases, they are life threatening. Cost of treatment has soared to $25 billion each year. | |
| So far, however, solutions for treating chronic wounds have been few and far between, but researchers at Stanford University now report that they have developed a wireless smart bandage that has shown promise in speeding up tissue repair by monitoring the wound healing process and treating the wound simultaneously. The researchers say in a paper published in Nature Biotechnology (“Wireless, closed-loop, smart bandage with integrated sensors and stimulators for advanced wound care and accelerated healing”) that their device promotes faster closure of wounds, increases new blood flow to injured tissue, and enhances skin recovery by significantly reducing scar formation. | |
| The smart bandage is composed of wireless circuitry that uses impedance/temperature sensors to monitor the progression of wound healing. If the wound is less healed or an infection is detected, the sensors inform a central processing unit to apply more electrical stimulation across the wound bed to accelerate tissue closure and reduce infection. The researchers were able to track the sensor data in real time on a smart phone, all without the need for wires. |
Engineering marvel |
|
| The electronic layer, including a microcontroller unit (MCU), radio antenna, memory, electrical stimulator, biosensors, and other components, is just 100 microns thick—about the thickness of a single coat of latex paint. | |
| All that circuitry rides atop a cleverly engineered hydrogel – a rubbery, skin-like polymer – that is integrated to both deliver healing electrical stimulation to the injured tissue and collect real-time biosensor data. | |
| The polymer in the hydrogel is carefully designed to adhere securely to the wound surface when needed, yet to pull away cleanly and gently without harm to the wound when warmed to just a few degrees above body temperature (40°C/104°F). | |
| “In sealing the wound, the smart bandage protects as it heals,” says Yuanwen Jiang, co-first author of the study and a post-doctoral scholar in the lab of Zhenan Bao, the K.K. Lee Professor in Chemical Engineering in the Stanford School of Engineering. “But it is not a passive tool. It is an active healing device that could transform the standard of care in the treatment of chronic wounds.” | |
| Electrical stimulation, also known as galvanotaxis, has been previously reported to accelerate the migration of keratinocytes to the wound site, limit bacterial infections and prevent the development of biofilms on wound surfaces, to proactively promote tissue growth and help with tissue repair. The researchers were able to take this well-studied technology and integrate it with real-time biosensor data to provide a novel automated treatment modality that is informed by biosensors. | |
| The smart bandage’s biosensing capabilities monitor biophysical changes in the local environment, providing a real-time, rapid, robust, and extremely accurate way to measure wound condition. Technically speaking, the smart bandage senses conductivity and temperature changes in the skin as the wound heals—electrical impedance increases as wounds heal and local temperatures decline as inflammation subsides. | |
| “With stimulation and sensing in one device, the smart bandage speeds healing, but it also keeps track as the wound is improving,” says Artem Trotsyuk, likewise a co-first author of the study who completed his graduate work in the lab of Geoffrey Gurtner, MD, formerly the Johnson & Johnson Distinguished Professor of Surgery (Emeritus) in the Stanford School of Medicine, and currently the Chair of the Department of Surgery and Professor of Biomedical Engineering at the University of Arizona in Tucson. “We think it represents a new modality that will enable new biological discovery and the exploration of previously difficult-to-test hypotheses on the human healing process.” |
Welcome results, new directions
The researchers took their study a step further, venturing to understand why and how electrical stimulation heals the wound faster. They now believe that electrical stimulation promotes the activation of pro-regenerative genes such as Selenop, an anti-inflammatory gene that has been found to help with pathogen clearance and wound repair, and Apoe, which has been shown to increase muscle and soft tissue growth. Likewise, electrical stimulation increased the amount of white blood cell populations, namely monocytes and macrophages, through the recruitment of greater amounts of M2 anti-inflammatory macrophages, which have been previously reported as pro-regenerative and playing a key role in the extracellular matrix formation that is required during the proliferative phases of wound healing.
The researchers caution that the smart bandage is, as yet, a proof of concept, albeit a promising one. Many challenges remain, however. These include increasing the size of the device to human scale, reducing cost, and solving long-term data storage issues – all necessary to scale up to mass production should need and opportunity arise. Likewise, there are potentially new sensors not currently integrated that might be added, such as those that measure metabolites, biomarkers, and pH. And there are some potential roadblocks to clinical use, such as hydrogel rejection, in which the skin may react to the device and create a bad gel-to-skin combination, or biofouling of the sensors, which can cause irritation.
Despite these hurdles, the researchers are pushing ahead and remain optimistic about the potential of their smart bandage to provide hope for patients suffering with chronic wounds.
Stanford co-first authors: Yuanwen Jiang is a postdoctoral fellow in the Bao Group; Artem Trotsyuk is a former graduate student in the Gurtner Lab; Simiao Niu is a former postdoctoral scholar in the Bao Group.
News
Johns Hopkins Researchers Uncover a New Way To Kill Cancer Cells
A new study reveals that blocking ribosomal RNA production rewires cancer cell behavior and could help treat genetically unstable tumors. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular [...]
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard it is for scientists to [...]
Are Pesticides Breeding the Next Pandemic? Experts Warn of Fungal Superbugs
Fungicides used in agriculture have been linked to an increase in resistance to antifungal drugs in both humans and animals. Fungal infections are on the rise, and two UC Davis infectious disease experts, Dr. George Thompson [...]
Scientists Crack the 500-Million-Year-Old Code That Controls Your Immune System
A collaborative team from Penn Medicine and Penn Engineering has uncovered the mathematical principles behind a 500-million-year-old protein network that determines whether foreign materials are recognized as friend or foe. How does your body [...]
Team discovers how tiny parts of cells stay organized, new insights for blocking cancer growth
A team of international researchers led by scientists at City of Hope provides the most thorough account yet of an elusive target for cancer treatment. Published in Science Advances, the study suggests a complex signaling [...]
Nanomaterials in Ophthalmology: A Review
Eye diseases are becoming more common. In 2020, over 250 million people had mild vision problems, and 295 million experienced moderate to severe ocular conditions. In response, researchers are turning to nanotechnology and nanomaterials—tools that are transforming [...]
Natural Plant Extract Removes up to 90% of Microplastics From Water
Researchers found that natural polymers derived from okra and fenugreek are highly effective at removing microplastics from water. The same sticky substances that make okra slimy and give fenugreek its gel-like texture could help [...]
Instant coffee may damage your eyes, genetic study finds
A new genetic study shows that just one extra cup of instant coffee a day could significantly increase your risk of developing dry AMD, shedding fresh light on how our daily beverage choices may [...]
Nanoneedle patch offers painless alternative to traditional cancer biopsies
A patch containing tens of millions of microscopic nanoneedles could soon replace traditional biopsies, scientists have found. The patch offers a painless and less invasive alternative for millions of patients worldwide who undergo biopsies [...]
Small antibodies provide broad protection against SARS coronaviruses
Scientists have discovered a unique class of small antibodies that are strongly protective against a wide range of SARS coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-1 and numerous early and recent SARS-CoV-2 variants. The unique antibodies target an [...]
Controlling This One Molecule Could Halt Alzheimer’s in Its Tracks
New research identifies the immune molecule STING as a driver of brain damage in Alzheimer’s. A new approach to Alzheimer’s disease has led to an exciting discovery that could help stop the devastating cognitive decline [...]