A new study led by the University of Kansas might resolve a mystery in the "aging process" in species — or, how a species' risk of going extinct changes after that species appears on the scene.
For years, evolutionary biologists believed older species lacked any real advantage over younger ones in avoiding extinction — an idea known as "Red Queen theory" among researchers.
Revisiting the Red Queen Theory
"The Red Queen theory is that species have to keep running just to stay still, like the character in Lewis Carroll's book 'Through the Looking-Glass,'" said lead author James Saulsbury, a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Ecology & Evolutionary Biology at KU. "This idea was turned into a kind of ecological theory in the 1970s in an attempt to explain an observation that extinction risk didn't seem to change over the lifespan of species."
Yet the years have not been kind to this theory.
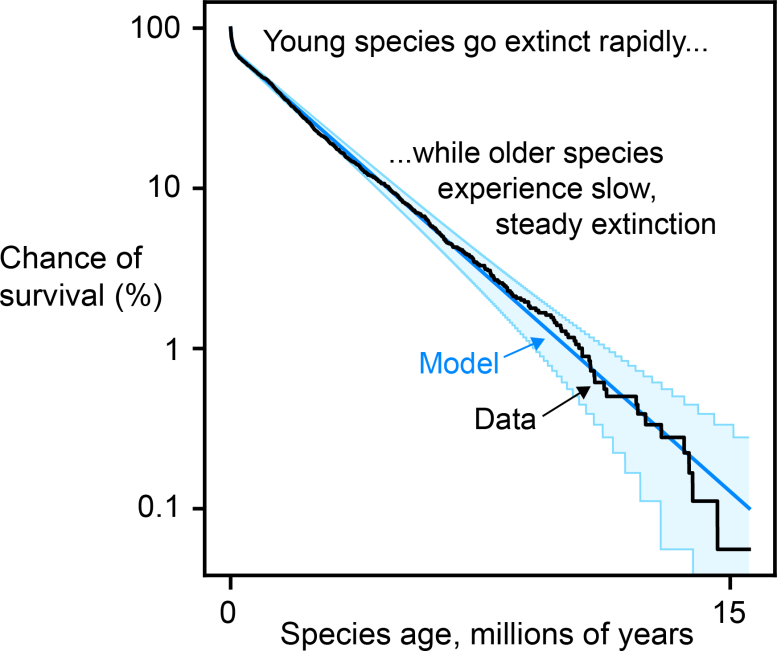
"In the earliest investigations of this phenomenon, species of all ages seemed to go extinct at about the same rate, perhaps just because of the relative crudeness of the evidence available at the time," Saulsbury said. "This made sense under this Red Queen model, where species are constantly competing with other species that are also adapting alongside them."
Questioning and Beyond the Red Queen
But as more data was collected and analyzed in more sophisticated ways, scientists increasingly found refutations of Red Queen theory.
Younger species are generally at greater risk of extinction. A new model from the University of Kansas shows this newer finding of age-dependent extinction while also emphasizing the importance of zero-sum competition in explaining extinction, as in the older Red Queen theory. Credit: Saulsbury et al
"Scientists kept finding instances where young species are especially at risk of extinction," Saulsbury said. "So we had a theory vacuum – a bunch of anomalous observations and no unified way of understanding them."
But now, Saulsbury has led research appearing in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences that may resolve this mystery. Saulsbury and his co-authors showed the relationship between a species' age and its risk of going extinct could be accurately predicted by an ecological model called the "neutral theory of biodiversity."
Neutral Theory's Insights
Neutral theory is a simple model of ecologically similar species competing for limited resources, where the outcome for each species is more or less random.
In the theory, "Species either go extinct or expand from small initial population size to become less vulnerable to extinction, but they are always susceptible to being replaced by their competitors," according to a lay summary of the PNAS paper. By extending this theory to make predictions for the fossil record, Saulsbury and colleagues found that neutral theory "predicts survivorship among fossil zooplankton with surprising accuracy and accounts for empirical deviations from the predictions of Red Queen more generally."
Saulsbury's co-authors were C. Tomomi Parins-Fukuchi of the University of Toronto, Connor Wilson of the University of Oxford and the University of Arizona, and Trond Reitan and Lee Hsiang Liow of the University of Oslo.
While neutral theory might seem to spell curtains for the Red Queen theory, the KU researcher said the Red Queen still has value. Mainly, it proposes the still valid idea that species compete in a zero-sum game against one another for finite resources, always battling for a bigger slice of nature's pie.
"Red Queen theory has been a compelling and important idea in the evolutionary biological community, but the data from the fossil record no longer seems to support that theory," Saulsbury said. "But I don't think our paper really refutes this idea because, in fact, the Red Queen theory and the neutral theory are, in a deep way, pretty similar. They both present a picture of extinction happening as a result of competition between species for resources and of constant turnover in communities resulting from biological interactions."
Relevance and Implications for Conservation
Ultimately, the findings not only help make sense of the forces that shape the natural world but may be relevant for conservation efforts as species face increasing threats from climate change and habitat loss around the globe.
"What makes a species vulnerable to extinction?" Saulsbury asked. "People are interested in learning from the fossil record whether it can tell us anything to help conserve species. The pessimistic side of our study is that there are ecological situations where there isn't a whole lot of predictability in the fates of species; there's some limit to how much we can predict extinction. To some extent, extinction will be decided by seemingly random forces — accidents of history. There's some support for this in paleobiological studies."
He said there has been effort to understand predictors of extinction in the fossil record, but not many generalities have emerged so far.
"There's no trait that makes you immortal or not susceptible to extinction," Saulsbury said. "But the optimistic side of our study is that entire communities can have patterns of extinction that are quite predictable and understandable. We can get a pretty good grasp on features of the biota, like how the extinction risk of species changes as they age. Even if the fate of a single species can be hard to predict, the fate of a whole community can be quite understandable."
Saulsbury added a caveat: It remains to be seen how broadly the neutral explanation for extinction succeeds across different parts of the tree of life.
"Our study is also working on the geological timescale in millions of years," he said. "Things may look very different on the timescale of our own lifetimes."
Reference: "Age-dependent extinction and the neutral theory of biodiversity" by James G. Saulsbury, C. Tomomi Parins-Fukuchi, Connor J. Wilson, Trond Reitan and Lee Hsiang Liow, 27 December 2023, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2307629121
News
Catching COVID significantly raises the risk of developing kidney disease, researchers find
Catching Covid significantly raises the risk of developing deadly kidney disease, research has shown. The virus was found to increase the chances that patients will develop the incurable condition by around 50 per cent. [...]
New Toothpaste Stops Gum Disease Without Harming Healthy Bacteria
Researchers have developed a targeted approach to combat periodontitis without disrupting the natural balance of the oral microbiome. The innovation could reshape how gum disease is treated while preserving beneficial bacteria. The human mouth [...]
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]