Research teams have successfully regenerated mouse brain circuits using rat stem cells, showcasing a new method for restoring brain function and studying interspecies brain development.
These findings open up possibilities for treating neurological diseases and understanding brain evolution, while also hinting at future clinical applications and ethical challenges in using similar techniques for human organ transplantation.
Scientists Regenerate Neural Pathways in Mice With Cells From Rats
Two independent research groups have successfully restored brain circuits in mice using neurons derived from rat stem cells. Recently published in the journal Cell, these studies provide important insights into brain tissue development and open up new possibilities for rejuvenating brain functions lost to diseases and aging.
"This research helps to show the brain's potential flexibility in using synthetic neural circuits to restore brain functions," says Kristin Baldwin, a professor at Columbia University in New York and corresponding author of one of the two papers. Baldwin's team restored mouse olfactory neural circuits, the interconnected neurons in the brain responsible for the sense of smell, and their function using stem cells from rats.
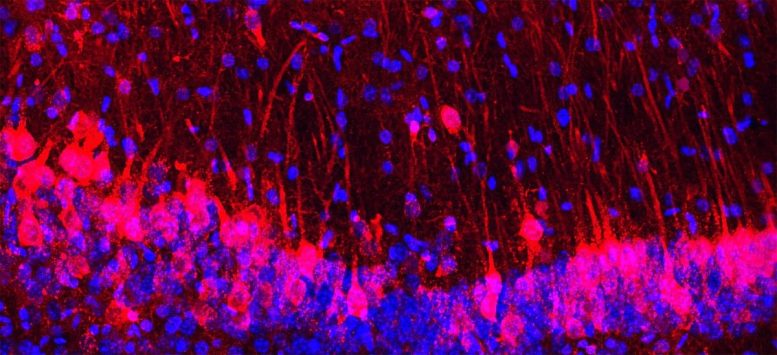
Mouse hippocampus with rat cells (red) and nuclei of both mouse and rat cells (blue). Credit: M. Khadeesh Imtiaz, Columbia University Irving Medical Center
Interspecies Genetic Engineering and Its Implications
"Being able to generate brain tissues from one species inside another can help us understand brain development and evolution in different species," says Jun Wu, an associate professor at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas and corresponding author of the other paper. Wu's team developed a CRISPR-based platform that could efficiently identify specific genes that drive the development of specific tissues. They tested the platform by silencing a gene needed for forebrain development in mice and then restoring the tissue using rat stem cells.
Mice and rats are two distinct species that evolved independently for approximately 20 to 30 million years. In previous experiments, scientists were able to replace pancreases in mice using rat stem cells through a process called blastocyst complementation. For this process to work, researchers inject rat stem cells into mice blastocysts—early-stage embryos—that lack the ability to develop a pancreas due to genetic mutations. The rat stem cells then developed into the missing pancreas and complemented its function.
Breakthroughs in Brain Tissue Regeneration
But, to date, generating brain tissues using stem cells from a different species through blastocyst complementation has not been reported. Now, using CRISPR, Wu's team tested seven different genes and found that knocking out Hesx1 could reliably generate mice that had no forebrain. The team then injected rat stem cells in blastocysts of Hesx1 knockout mice, and the rat cells filled in the niche to form a forebrain in mice. Rats have bigger brains than mice, but the rat-origin forebrains developed at the same pace and size as that of mice. In addition, rat neurons were able to transmit signals to the neighboring mouse neurons and vice versa.
The researchers didn't test whether the forebrain from rat stem cells changed mice's behaviors. "There's a lack of good behavioral tests to distinguish rats from mice," Wu says. "But from our experiment, it seems like these mice with rat forebrain don't behave out of the ordinary."
Advanced Applications and Future Prospects
In the other study, Baldwin's team used specific genes to either kill or silence mouse olfactory sensory neurons used for the sense of smell and injected rat stem cells into the mice embryos. The silencing model mimics what is seen in neurodevelopmental disorders, where certain neurons cannot communicate well with the brain. The killing model removed the neurons entirely, simulating degenerative diseases.
They found blastocyst complementation restored mouse olfactory neural circuits differently depending on the model. When mouse neurons were present but silent, the rat neurons helped form better-organized brain regions compared to the killing model. However, when the team tested these rat-mouse chimeras by training them to find a hidden cookie buried in a cage, rat neurons were best at rescuing behaviors in the killing model.
"This really surprising result allows us to look at what's different between those two disease models and try to identify mechanisms that could help restore functions in either type of brain disease," Baldwin says. Her team also tested blastocyst complementation in disease-model mice using cells from mice with normal olfactory systems. They showed that intraspecies complementation rescued cookie finding in both models.
Exploring the Frontiers of Medical Science
"Right now, people are being transplanted with stem cell-derived neurons for Parkinson's disease and epilepsy in clinical trials. How well will that work? And will different genetic backgrounds between the patient and the transplanted cells pose a barrier? This study provides a system in which we can evaluate the possibilities for same species brain complementation at a much larger scale than a clinical trial," Baldwin says.
Blastocyst complementation is still far from clinical application in humans, but both studies suggest stem cells from different species can synchronize their development with the host's brain.
Scientists have also been experimenting with growing human organs in other species like pigs using blastocyst complementation. Last year, scientists generated embryonic kidneys using human stem cells in pigs, offering a potential solution for the many people on waitlists for transplants.
"Our aspiration is to enrich pig organs with a certain percentage of human cells, with the aim of improving outcomes for organ recipients. But currently, there are still many technical and ethical challenges that we need to overcome before we can test this in clinical trials," says Wu.
Besides the studies' implications in medicine, the teams are also interested in using this approach to study the brains of many wild rodents that were not accessible in the laboratory setting.
"There are over 2,000 living rodent species in the world. Many of them behave differently from the rodents we commonly study in the lab. Interspecies neural blastocyst complementation can potentially open the door to study how the brains from those species develop, evolve, and function," Wu says.
For more on this research, see Mice Engineered With Rat Neurons Show Advanced Sensory Skills.
References:
"Functional sensory circuits built from neurons of two species" by Benjamin T. Throesch, Muhammad Khadeesh bin Imtiaz, Rodrigo Muñoz-Castañeda, Masahiro Sakurai, Andrea L. Hartzell, Kiely N. James, Alberto R. Rodriguez, Greg Martin, Giordano Lippi, Sergey Kupriyanov, Zhuhao Wu, Pavel Osten, Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte, Jun Wu and Kristin K. Baldwin, 25 April 2024, Cell.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.03.042
News
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]