Boron nitride nanotubes are primed to become effective building blocks for next-generation composite and polymer materials based on a new discovery at Rice University – and a previous one.
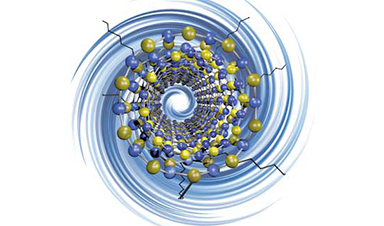
Scientists at known-for-nano Rice have found a way to enhance a unique class of nanotubes using a chemical process pioneered at the university. The Rice lab of chemist Angel Martí took advantage of the Billups-Birch reaction process to enhance boron nitride nanotubes.
The work is described in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Applied Nano Materials (“Chemical Decoration of Boron Nitride Nanotubes Using the Billups-Birch Reaction: Toward Enhanced Thermostable Reinforced Polymer and Ceramic Nanocomposites”).
Boron nitride nanotubes, like their carbon cousins, are rolled sheets of hexagonal arrays. Unlike carbon nanotubes, they’re electrically insulating hybrids made of alternating boron and nitrogen atoms.
Insulating nanotubes that can be functionalized will be a valuable building block for nanoengineering projects, Martí said. “Carbon nanotubes have outstanding properties, but you can only get them in semiconducting or metallic conducting types,” he said. “Boron nitride nanotubes are complementary materials that can fill that gap.”
Until now, these nanotubes have steadfastly resisted functionalization, the “decorating” of structures with chemical additives that allows them to be customized for applications. The very properties that give boron nitride nanotubes strength and stability, especially at high temperatures, also make them hard to modify for their use in the production of advanced materials.
But the Billups-Birch reaction developed by Rice Professor Emeritus of Chemistry Edward Billups, which frees electrons to bind with other atoms, allowed Martí and lead author Carlos de los Reyes to give the electrically inert boron nitride nanotubes a negative charge.
That, in turn, opened them up to functionalization with other small molecules, including aliphatic carbon chains.
“Functionalizing the nanotubes modifies or tunes their properties,” Martí said. “When they’re pristine they are dispersible in water, but once we attach these alkyl chains, they are extremely hydrophobic (water-avoiding). Then, if you put them in very hydrophobic solvents like those with long-chain hydrocarbons, they are more dispersible than their pristine form.
Image Credit: Martí Research Group
News This Week
New study suggests a way to rejuvenate the immune system
Stimulating the liver to produce some of the signals of the thymus can reverse age-related declines in T-cell populations and enhance response to vaccination. As people age, their immune system function declines. T cell [...]
Nerve Damage Can Disrupt Immunity Across the Entire Body
A single nerve injury can quietly reshape the immune system across the entire body. Preclinical research from McGill University suggests that nerve injuries may lead to long-lasting changes in the immune system, and these [...]
Fake Science Is Growing Faster Than Legitimate Research, New Study Warns
New research reveals organized networks linking paper mills, intermediaries, and compromised academic journals Organized scientific fraud is becoming increasingly common, ranging from fabricated research to the buying and selling of authorship and citations, according [...]
Scientists Unlock a New Way to Hear the Brain’s Hidden Language
Scientists can finally hear the brain’s quietest messages—unlocking the hidden code behind how neurons think, decide, and remember. Scientists have created a new protein that can capture the incoming chemical signals received by brain [...]
Does being infected or vaccinated first influence COVID-19 immunity?
A new study analyzing the immune response to COVID-19 in a Catalan cohort of health workers sheds light on an important question: does it matter whether a person was first infected or first vaccinated? [...]
We May Never Know if AI Is Conscious, Says Cambridge Philosopher
As claims about conscious AI grow louder, a Cambridge philosopher argues that we lack the evidence to know whether machines can truly be conscious, let alone morally significant. A philosopher at the University of [...]
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]











Leave A Comment