A study from Weill Cornell Medicine has shed light on a survival mechanism employed by cancers, which often emit molecules into the bloodstream that cause detrimental changes to the liver. These modifications shift the liver into a state of inflammation, leading to a buildup of fat and hindering its regular detoxifying abilities. The research reveals potential avenues for developing new diagnostic tests and treatments to detect and reverse this process.
The study, which was recently published in the journal Nature, discovered that various types of tumors located outside the liver can remotely induce alterations to the liver that mimic fatty liver disease. This transformation is brought about by the secretion of extracellular vesicles and particles (EVPs) loaded with fatty acids. Evidence of this mechanism was discovered in both animal cancer models and the livers of human cancer patients.
"Our findings show that tumors can lead to significant systemic complications including liver disease, but also suggest that these complications can be addressed with future treatments," said study co-senior author Dr. David Lyden, the Stavros S. Niarchos Professor in Pediatric Cardiology and a professor of pediatrics and of cell and developmental biology at Weill Cornell Medicine.
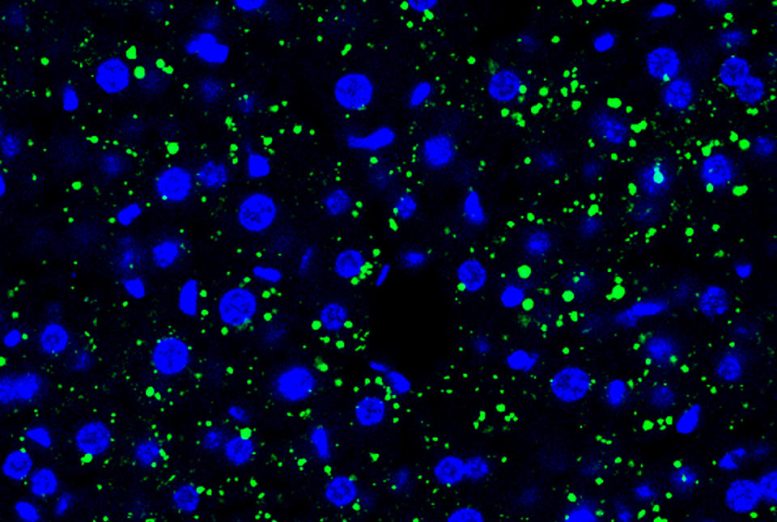
Tumor cell-derived EVPs induced accumulation of lipid droplets in the mouse liver. Green, lipid droplet. Blue, DAPI. Credit: Gang Wang, Jianlong Li, David Lyden
For the past two decades, Dr. Lyden, who is also a member of the Gale and Ira Drukier Institute for Children's Health and the Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center at Weill Cornell Medicine, and his research group have been studying the systemic effects of cancers. These effects reflect specific strategies cancers use to secure their survival and speed their progression. In their work published in 2015, for example, the team discovered that pancreatic cancers secrete molecules encapsulated in extracellular vesicles, that travel through the bloodstream, are taken up by the liver, and prepare the organ to support the outgrowth of new, metastatic tumors.
In the new study, the researchers uncovered a different set of liver changes caused by distant cancer cells which they observed in animal models of bone, skin, and breast cancer that metastasize to other organs but not to the liver. The study's key finding is that these tumors induce the accumulation of fat molecules in liver cells, consequently reprogramming the liver in a way that resembles the obesity- and alcohol-related condition known as fatty liver disease.
The team also observed that reprogrammed livers have high levels of inflammation, marked by elevated levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and low levels of drug-metabolizing enzymes called cytochrome P450, which break down potentially toxic molecules, including many drug molecules. The observed reduction in cytochrome P450 levels could explain why cancer patients often become less tolerant of chemotherapy and other drugs as their illness progresses.
The researchers traced this liver reprogramming to EVPs that are released by the distant tumors and carry fatty acids, especially palmitic acid. When taken up by liver-resident immune cells called Kupffer cells, the fatty acid cargo triggers the production of TNF-α, which consequently drives fatty liver formation.
Although the researchers principally used animal models of cancers in the study, they observed similar changes in the livers of newly diagnosed pancreatic cancer patients who later developed non-liver metastases.
"One of our more striking observations was that this EVP-induced fatty liver condition did not co-occur with liver metastases, suggesting that causing fatty liver and preparing the liver for metastasis are distinct strategies that cancers use to manipulate liver function," said co-first author Dr. Gang Wang, a postdoctoral associate in the Lyden laboratory. Dr. Jianlong Li, a scientific collaborator in the Lyden laboratory, is also a co-first author of the study.
The scientists suspect that the fatty liver condition benefits cancers in part by turning the liver into a lipid-based source of energy to fuel cancer growth.
"We see in liver cells not only an abnormal accumulation of fat but also a shift away from the normal processing of lipids so that the lipids that are being produced are more advantageous to the cancer," said co-senior author Dr. Robert Schwartz, associate professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology and a member of the Meyer Cancer Center at Weill Cornell Medicine and a hepatologist at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center.
That may not be the only benefit that cancers derive from this liver alteration. "There are also crucial molecules involved in immune cell function, but their production is altered in these fatty livers, hinting that this condition may also weaken anti-tumor immunity," said co-senior author Dr. Haiying Zhang, assistant professor of cell and developmental biology in pediatrics at Weill Cornell Medicine.
The researchers were able to mitigate these systemic effects of tumors on the livers by implementing strategies such as blocking tumor-EVP release, inhibiting the packaging of palmitic acid into tumor EVPs, suppressing TNF-α activity, or eliminating Kupffer cells in the experimental animal models. The researchers are further investigating the potential of implementing these strategies in human patients to block these remote effects of tumors on the liver and exploring the possibility of utilizing the detection of palmitic acid in tumor EVPs circulating in the blood as a potential warning sign of advanced cancer.
Reference: "Tumour extracellular vesicles and particles induce liver metabolic dysfunction" by Gang Wang, Jianlong Li, Linda Bojmar, Haiyan Chen, Zhong Li, Gabriel C. Tobias, Mengying Hu, Edwin A. Homan, Serena Lucotti, Fengbo Zhao, Valentina Posada, Peter R. Oxley, Michele Cioffi, Han Sang Kim, Huajuan Wang, Pernille Lauritzen, Nancy Boudreau, Zhanjun Shi, Christin E. Burd, Jonathan H. Zippin, James C. Lo, Geoffrey S. Pitt, Jonathan Hernandez, Constantinos P. Zambirinis, Michael A. Hollingsworth, Paul M. Grandgenett, Maneesh Jain, Surinder K. Batra, Dominick J. DiMaio, Jean L. Grem, Kelsey A. Klute, Tanya M. Trippett, Mikala Egeblad, Doru Paul, Jacqueline Bromberg, David Kelsen, Vinagolu K. Rajasekhar, John H. Healey, Irina R. Matei, William R. Jarnagin, Robert E. Schwartz, Haiying Zhang and David Lyden, 24 May 2023, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06114-4
News
Scientists Unlock a New Way to Hear the Brain’s Hidden Language
Scientists can finally hear the brain’s quietest messages—unlocking the hidden code behind how neurons think, decide, and remember. Scientists have created a new protein that can capture the incoming chemical signals received by brain [...]
Does being infected or vaccinated first influence COVID-19 immunity?
A new study analyzing the immune response to COVID-19 in a Catalan cohort of health workers sheds light on an important question: does it matter whether a person was first infected or first vaccinated? [...]
We May Never Know if AI Is Conscious, Says Cambridge Philosopher
As claims about conscious AI grow louder, a Cambridge philosopher argues that we lack the evidence to know whether machines can truly be conscious, let alone morally significant. A philosopher at the University of [...]
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]
What could the future of nanoscience look like?
Society has a lot to thank for nanoscience. From improved health monitoring to reducing the size of electronics, scientists’ ability to delve deeper and better understand chemistry at the nanoscale has opened up numerous [...]
Scientists Melt Cancer’s Hidden “Power Hubs” and Stop Tumor Growth
Researchers discovered that in a rare kidney cancer, RNA builds droplet-like hubs that act as growth control centers inside tumor cells. By engineering a molecular switch to dissolve these hubs, they were able to halt cancer [...]
Platelet-inspired nanoparticles could improve treatment of inflammatory diseases
Scientists have developed platelet-inspired nanoparticles that deliver anti-inflammatory drugs directly to brain-computer interface implants, doubling their effectiveness. Scientists have found a way to improve the performance of brain-computer interface (BCI) electrodes by delivering anti-inflammatory drugs directly [...]
After 150 years, a new chapter in cancer therapy is finally beginning
For decades, researchers have been looking for ways to destroy cancer cells in a targeted manner without further weakening the body. But for many patients whose immune system is severely impaired by chemotherapy or radiation, [...]
Older chemical libraries show promise for fighting resistant strains of COVID-19 virus
SARS‑CoV‑2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to mutate, with some newer strains becoming less responsive to current antiviral treatments like Paxlovid. Now, University of California San Diego scientists and an international team of [...]
Lower doses of immunotherapy for skin cancer give better results, study suggests
According to a new study, lower doses of approved immunotherapy for malignant melanoma can give better results against tumors, while reducing side effects. This is reported by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in the Journal of the National [...]
Researchers highlight five pathways through which microplastics can harm the brain
Microplastics could be fueling neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, with a new study highlighting five ways microplastics can trigger inflammation and damage in the brain. More than 57 million people live with dementia, [...]
Tiny Metal Nanodots Obliterate Cancer Cells While Largely Sparing Healthy Tissue
Scientists have developed tiny metal-oxide particles that push cancer cells past their stress limits while sparing healthy tissue. An international team led by RMIT University has developed tiny particles called nanodots, crafted from a metallic compound, [...]
Gold Nanoclusters Could Supercharge Quantum Computers
Researchers found that gold “super atoms” can behave like the atoms in top-tier quantum systems—only far easier to scale. These tiny clusters can be customized at the molecular level, offering a powerful, tunable foundation [...]
A single shot of HPV vaccine may be enough to fight cervical cancer, study finds
WASHINGTON -- A single HPV vaccination appears just as effective as two doses at preventing the viral infection that causes cervical cancer, researchers reported Wednesday. HPV, or human papillomavirus, is very common and spread [...]