Recent research reveals a breakthrough in lung repair, showing how delivering VEGFA via lipid nanoparticles can significantly repair damaged blood vessels, akin to plumbing repairs. This method, validated in animal models, offers promising insights into treating respiratory virus damages, enhancing oxygen delivery, and reducing lung inflammation and scarring.
In the human body, the lungs and their vasculature can be likened to a building with an intricate plumbing system. The lungs' blood vessels are the pipes essential for transporting blood and nutrients for oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide removal. Much like how pipes can get rusty or clogged, disrupting normal water flow, damage from respiratory viruses, like SARS-CoV-2 or influenza, can interfere with this "plumbing system."
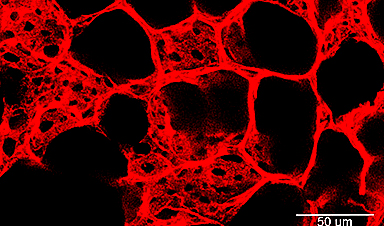
In a recent study, researchers looked at the critical role of vascular endothelial cells in lung repair. Their work, published in Science Translational Medicine, was led by Andrew Vaughan of the University of Pennsylvania's School of Veterinary Medicine and shows that, by using techniques that deliver vascular endothelial growth factor alpha (VEGFA) via lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), that they were able to greatly enhance modes of repair for these damaged blood vessels, much like how plumbers patch sections of broken pipes and add new ones.
Advanced Research Findings
"While our lab and others have previously shown that endothelial cells are among the unsung heroes in repairing the lungs after viral infections like the flu, this tells us more about the story and sheds light on the molecular mechanisms at play," says Vaughan, assistant professor of biomedical sciences at Penn Vet. "Here we've identified and isolated pathways involved in repairing this tissue, delivered mRNA to endothelial cells, and consequently observed enhanced recovery of the damaged tissue. These findings hint at a more efficient way to promote lung recovery after diseases like COVID-19."
They found VEGFA's involvement in this recovery, while building on work in which they used single cell RNA sequencing to identify transforming growth factor beta receptor 2 (TGFBR2) as a major signaling pathway. The researchers saw that when TGFBR2 was missing it stopped the activation of VEGFA. This lack of signal made the blood vessel cells less able to multiply and renew themselves, which is vital for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the tiny air sacs of the lungs.
"We'd known there was a link between these two pathways, but this motivated us to see if delivering VEGFA mRNA into endothelial cells could improve lung recovery after disease-related injury," says first author Gan Zhao, a postdoctoral researcher in the Vaughan Lab.
Innovative Delivery Methods
The Vaughan Lab then reached out to Michael Mitchell of the School of Engineering and Applied Science, whose lab specializes in LNPs, to see if delivery of this mRNA cargo would be feasible.
"LNPs have been great for vaccine delivery and have proven incredibly effective delivery vehicles for genetic information. But the challenge here was to get the LNPs into the bloodstream without them heading to the liver, which is where they tend to congregate as its porous structure lends favor to substances passing from the blood into hepatic cells for filtration," says Mitchell, an associate professor of bioengineering at Penn Engineering and a coauthor of the paper. "So, we had to devise a way to specifically target the endothelial cells in the lungs."
Lulu Xue, a postdoctoral researcher in the Mitchell Lab and a co-first author of the paper, explains that they engineered the LNP to have an affinity for lung endothelial cells, this is known as extra hepatic delivery, going beyond the liver.
"We've seen evidence in the literature suggesting it's doable, but the systems we'd seen are made up of positively charged lipids which were too toxic," Xue says. "This led me to developing an ionizable lipid that's not positively charged when it enters the bloodstream but gets charged when it gets to the endothelial cells, thereby releasing the mRNA."
Their LNPs proved effective in delivering VEGFA into endothelial cells and as a result, the researchers saw a marked improvement in vascular recovery in their animal models. Within the animal models, the researchers saw improved oxygen levels, and in some, the treatment helped them recover their weight better than the control group. These treated mice also had less lung inflammation, shown by lower levels of certain markers in their lung fluid, and their lungs showed less damage and scarring, with more healthy blood vessels.
"Although we went in hoping for this outcome, it was a real thrill to see how effective, safe, and efficiently this all panned out, so we're looking forward to testing this delivery platform for other cell types in the lung, and it will be important to evaluate whether TGFB signaling is important in other injury contexts including chronic conditions like emphysema and COPD," Vaughan says. "With this proof-of-concept being well validated, we're sure that we'll pave the way for new mRNA-based strategies for treating lung injury."
Reference: "TGF-βR2 signaling coordinates pulmonary vascular repair after viral injury in mice and human tissue" by Gan Zhao, Lulu Xue, Aaron I. Weiner, Ningqiang Gong, Stephanie Adams-Tzivelekidis, Joanna Wong, Maria E. Gentile, Ana N. Nottingham, Maria C. Basil, Susan M. Lin, Terren K. Niethamer, Joshua M. Diamond, Christian A. Bermudez, Edward Cantu, Xuexiang Han, Yaqi Cao, Mohamad-Gabriel Alameh, Drew Weissman, Edward E. Morrisey, Michael J. Mitchell and Andrew E. Vaughan, 31 January 2024, Science Translational Medicine.
DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adg6229
Andrew Vaughan is an assistant professor in the Department of Biomedical Sciences at the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine.
Michael Mitchell is an associate professor in the Department of Bioengineering in the School of Engineering and Applied Science and the director of the Lipid Nanoparticle Synthesis Core at the Penn Institute for RNA Innovation at the University of Pennsylvania.
Gan Zhao is a postdoctoral researcher in the Vaughn Lab at Penn Vet.
Lulu Xue is a postdoctoral researcher in the Mitchell Lab at Penn Engineering.
Other authors include Stephanie Adams-Tzivelekidis, Maria E. Gentile, Aaron I. Weiner, and Joanna Wong from Penn Vet; Ningqiang Gong and Xuexiang Han from Penn Engineering; and Mohamad-Gabriel Alameh, Maria C. Basil, Christian A. Bermudez, Edward Cantu, Yaqi Cao, Joshua M. Diamond, Susan M. Lin, Edward E. Morrisey, Terren K. Niethamer, Ana N. Nottingham, and Drew Weissman in the Perelman School of Medicine at Penn.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grants R01HL153539 and R01HL164350 and award DP2 TR002776, the Margaret Q. Landenberger Foundation, a Burroughs Wellcome Fund Career Award at the Scientific Interface; and the National Science Foundation (Award CBET-2145491).
News
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]