Neurological symptoms are apparently not a result of SARS-CoV-2 infection of the brain.
Scientists still are not sure how neurological symptoms arise in COVID-19. Is it because SARS-CoV-2 infects the brain? Or are these symptoms the result of inflammation in the rest of the body? A study by Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin has now produced evidence to support the latter theory. It was published today in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
Headaches, memory problems, and fatigue are just some of the neurological impacts that arise during coronavirus infection and can last well beyond the acute period. Even early on in the pandemic, researchers surmised that direct infection of the brain could be the cause.
"We took that as our hypothesis at the start, too. But so far, there has been no clear evidence that the coronavirus can persist in the brain, let alone proliferate," explains Dr. Helena Radbruch, head of the Chronic Neuroinflammation working group at the Department of Neuropathology at Charité. "For that, we would have needed to find evidence of intact virus particles in the brain, for example. Instead, the indications that the coronavirus could infect the brain come from indirect testing methods, so they aren't entirely conclusive."
According to a second hypothesis, the neurological symptoms would instead be a kind of side effect of the strong immune response the body deploys to defend against the virus. Past studies have produced indications that this might be the case. The current Charité study now bolsters this theory with detailed molecular biology and anatomical results from autopsies.
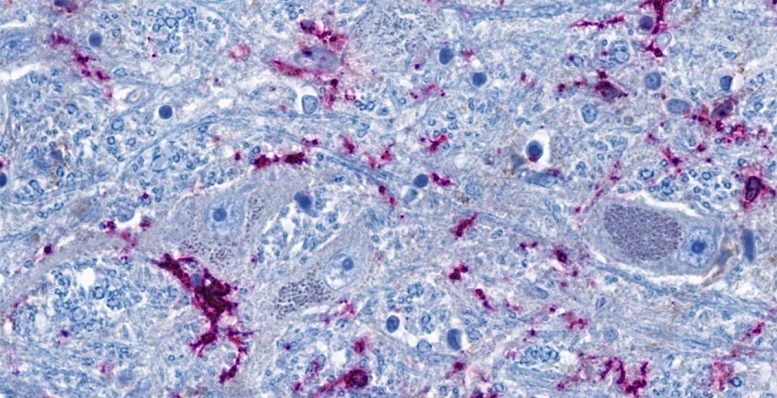
Cross-section of the brainstem: Neurons (blue-gray) are in close contact with immune cells (purple). The threadlike blue structures are extensions of the neurons, which can reach all the way into distant organs in the form of nerve fibers. According to the study, the immune cells and neurons in the brainstem can be activated directly via the nerve fibers as a result of inflammation in the lungs. Credit: © Charité | Jenny Meinhardt
No Signs of Direct Infection of the Brain
For the study, the team of researchers analyzed various areas of the brain in 21 people who died in hospital settings, typically in an ICU, due to severe coronavirus infection. For comparison, the researchers studied nine patients who died of other causes after treatment in intensive care. First, they looked to see whether the tissue showed any visible changes and hunted for any indication of coronavirus. Then they conducted a detailed analysis of genes and proteins to identify the specific processes that had taken place inside individual cells.
Like other teams of researchers before them, the Charité scientists found coronavirus genetic material in the brain in some cases. "But we didn't find neurons infected with SARS-CoV-2," Radbruch notes. "We assume that immune cells absorbed the virus in the body and then traveled to the brain. They're still carrying the virus, but it doesn't infect cells of the brain. So coronavirus has invaded other cells in the body, but not the brain itself."
Brain Reacts to Inflammation in the Body
Still, the researchers did note striking changes in molecular processes in some cells of the brain in those infected with COVID-19: For example, the cells ramped up the interferon signaling pathway, which is typically activated in the course of a viral infection.
"Some neurons evidently react to the inflammation in the rest of the body," says Prof. Christian Conrad, head of the Intelligent Imaging working group at the Berlin Institute of Health at Charité (BIH) and one of the principal investigators in the study, along with Radbruch. "This molecular reaction could be a good explanation for the neurological symptoms we see in COVID-19 patients. For example, neurotransmitters emitted by these cells in the brainstem could cause fatigue. That's because the brainstem is home to groups of cells that control drive, motivation, and mood."
The reactive nerve cells were found primarily in what are known as the nuclei of the vagus nerve. These are nerve cells located in the brainstem that extend all the way to organs such as the lungs, intestine, and heart. "In simplified terms, our interpretation of our data is that the vagus nerve 'senses' the inflammatory response in different organs of the body and reacts to it in the brainstem – without there being any actual infection of brain tissue," Radbruch explains. "Through this mechanism, the inflammation does spread from the body to the brain in a way, which can disrupt brain function."
Limited-Time Reaction
The neurons' reaction to the inflammation is temporary, as shown by a comparison of people who died during an acute coronavirus infection with those who died at least two weeks afterward. The molecular changes are most evident during the acute infection phase, but they do normalize again afterward – at least in the vast majority of cases.
"We think it's possible that if the inflammation becomes chronic, that could be what causes the neurological symptoms often observed in long COVID in some people," Conrad says. To follow up on this suspicion, the team of researchers is now planning to study the molecular signatures in the cerebral fluid of long COVID patients in greater detail.
Reference: "Proteomic and transcriptomic profiling of brainstem, cerebellum and olfactory tissues in early- and late-phase COVID-19" by Josefine Radke, Jenny Meinhardt, Tom Aschman, Robert Lorenz Chua, Vadim Farztdinov, Sören Lukassen, Foo Wei Ten, Ekaterina Friebel, Naveed Ishaque, Jonas Franz, Valerie Helena Huhle, Ronja Mothes, Kristin Peters, Carolina Thomas, Shirin Schneeberger, Elisa Schumann, Leona Kawelke, Julia Jünger, Viktor Horst, Simon Streit, Regina von Manitius, Péter Körtvélyessy, Stefan Vielhaber, Dirk Reinhold, Anja E. Hauser, Anja Osterloh, Philipp Enghard, Jana Ihlow, Sefer Elezkurtaj, David Horst, Florian Kurth, Marcel A. Müller, Nils C. Gassen, Julia Melchert, Katharina Jechow, Bernd Timmermann, Camila Fernandez-Zapata, Chotima Böttcher, Werner Stenzel, Elke Krüger, Markus Landthaler, Emanuel Wyler, Victor Corman, Christine Stadelmann, Markus Ralser, Roland Eils, Frank L. Heppner, Michael Mülleder, Christian Conrad and Helena Radbruch, 16 February 2024, Nature Neuroscience.
DOI: 10.1038/s41593-024-01573-y
News
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]