Research indicates a significant reduction in long COVID risk, largely due to vaccination and the virus's evolution.
The study analyzes data from over 441,000 veterans, showing lower rates of long COVID among vaccinated individuals compared to their unvaccinated counterparts across different COVID-19 variants.
Decreased Long COVID Risk and the Role of Vaccination
The risk of developing long COVID has decreased significantly over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to an analysis of data led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Researchers attributed about 70% of the risk reduction to vaccination against COVID-19 and 30% to changes over time, including the SARS-CoV-2 virus's evolving characteristics and improved detection and management of COVID-19.
The research is published July 17 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
"The research on declining rates of long COVID marks the rare occasion when I have good news to report regarding this virus," said the study's senior author, Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a Washington University clinical epidemiologist and global leader in COVID-19 research. "The findings also show the positive effects of getting vaccinated."
The risk of long COVID has declined over the course of the pandemic, although it remains a persistent threat. Researchers from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis identified vaccination as a primary factor in reducing the risk of long COVID. Credit: Sara
Impact of Long COVID Across Organ Systems
Long COVID encompasses the lingering and debilitating effects on health experienced by about 10% of people who have been infected with COVID-19. To date, the World Health Organization has documented more than 775 million cases of COVID-19.
In more than 30 high-profile studies, Al-Aly has detailed the virus's indiscriminate, long-term health impacts across nearly all organ systems affecting the heart, brain, kidneys and gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Although his latest findings sound more reassuring than previous studies, Al-Aly tempered the good news. "Long COVID is not over," said the nephrologist, who treats patients at Washington University-affiliated John J. Cochran Veterans Hospital in St. Louis. "We cannot let our guard down. This includes getting annual COVID vaccinations, because they are the key to suppressing long COVID risk. If we abandon vaccinations, the risk is likely to increase."
Analyzing Long COVID Trends and Variants
Since the pandemic's beginning, Al-Aly has dedicated himself to analyzing long COVID with the aim of helping the public make informed health choices; supporting scientists in generating research-backed recommendations on prevention and treatment; and enabling politicians to make educated decisions regarding funding and public policies. Al-Aly's latest study builds on this body of work by examining the virus's variants and overall evolution.
To do this, Al-Aly and his team analyzed millions of de-identified medical records in a database maintained by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the nation's largest integrated health-care system. The study included 441,583 veterans with SARS-CoV-2 infections and more than 4.7 million uninfected veterans, from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2022.
Patients included people of diverse ages, races and sexes; statistical modeling ensured parity in representation.
The researchers divided the veterans into five groups: unvaccinated COVID-19 sufferers who acquired the original strain in 2020; the delta variant in 2021; and the omicron variant in 2022. The other two groups included vaccinated people who had the delta variant, and vaccinated people with omicron. No vaccines existed while the original strain circulated.
Since the pandemic's beginning, Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has dedicated himself to analyzing long COVID with the aim of helping the public make informed health choices and educating scientists and policymakers on prevention and treatment. Al-Aly's latest study in The New England Journal of Medicine builds on his research by examining the virus's variants and overall evolution. Credit: Matt Miller
Vaccination Efficacy and Continuing Challenges
The team estimated rates of long COVID one-year postinfection for each of the five groups.
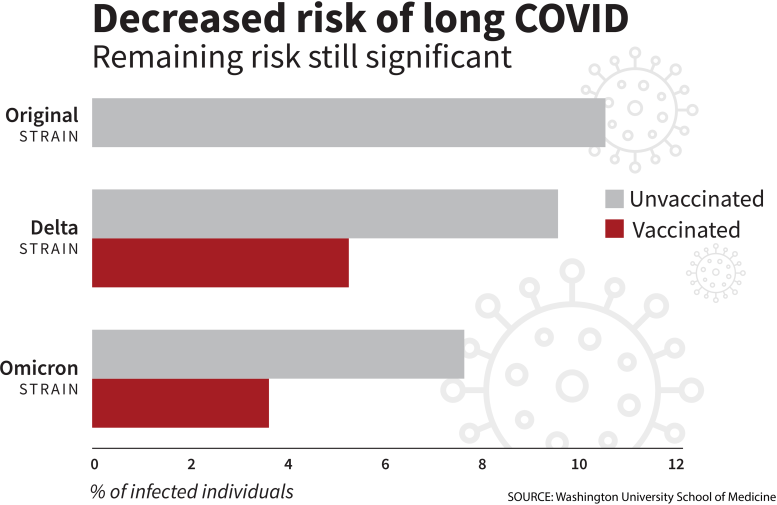
Unsurprisingly, the rate of long COVID was the highest among those with the original strain, Al-Aly said, with 10.4% of those who had infections that developed into long COVID.
That declined to 9.5% among those in the unvaccinated groups during the delta era and 7.7% during omicron.
Among the vaccinated, the rate of long COVID during delta was 5.3% and 3.5% during omicron.
"You can see a clear and significant difference in risk during the delta and omicron eras between the vaccinated and unvaccinated," said Al-Aly, who is also director of the Clinical Epidemiology Center at the VA St. Louis Health Care System and head of the research and development service. "So, if people think COVID is no big deal and decide to forgo vaccinations, they're essentially doubling their risk of developing long COVID."
Al-Aly also emphasized that even with the overall decline, the lowest rate — 3.5% — remains a substantial risk. "That's three to four vaccinated individuals out of 100 getting long COVID," he said. "Multiplied by the large numbers of people who continue to get infected and reinfected, it's a lot of people. This remaining risk is not trivial. It will continue to add an already staggering health problem facing people across the world."
Evolution of the Virus and Its Diverse Impacts
Since the pandemic's beginning, Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has dedicated himself to analyzing long COVID with the aim of helping the public make informed health choices and educating scientists and policymakers on prevention and treatment. Al-Aly's latest study in The New England Journal of Medicine builds on his research by examining the virus's variants and overall evolution.
Another notable finding offers clues to the virus's evolution, Al-Aly added. While analyzing the risk among all people infected with COVID-19 during the omicron era of 2022, the likelihood of heart, brain, kidney and lung problems declined. In contrast, diseases and illnesses associated with metabolic function and the GI system increased.
"People tend to think of SARS-CoV-2 as a homogeneous virus," Al-Aly said. "But each variant has its own fingerprint. The original virus hit the respiratory system hard. Omicron targeted metabolic and GI issues. It's important because while the risk of long COVID is quantitatively lower, a person can be at a higher risk of developing an illness based on the part of the body that the COVID variant targets.
"It's really good news that the risk has declined," he said. "But we know millions of people already have long COVID, and millions more will continue to get long COVID. We need to double down on our efforts to understand it so we can prevent suffering and treat affected individuals."
Reference: "Postacute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the Pre-Delta, Delta, and Omicron Eras" by Yan Xie, Taeyoung Choi and Ziyad Al-Aly, 16 July 2024, New England Journal of Medicine.
DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2403211
This research was funded by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs.
News
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]