| Tools that detect cancer in its early stages can increase patient survival and quality of life. However, cancer screening approaches often call for expensive equipment and trips to the clinic, which may not be feasible in rural or developing areas with little medical infrastructure. | |
| The emerging field of point-of-care diagnostics is therefore working on cheaper, faster, and easier-to-use tests. An international pair of engineering labs are championing this approach and have developed a tool that changes the colour of mouse urine when colon cancer, also known as bowel cancer, is present. | |
| The findings are published in Nature Nanotechnology (“Renal clearable catalytic gold nanoclusters for in vivo disease monitoring”). |
| The early stage technology, developed by teams led by Imperial’s Professor Molly Stevens and MIT’s Professor Sangeeta Bhatia, works by injecting nanosensors into mice, which are cut up by enzymes released by tumours known as proteases. | |
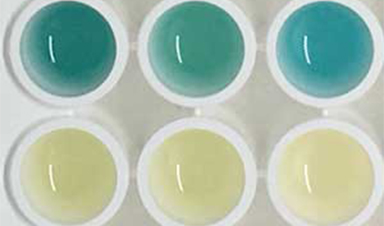
| When the nanosensors are broken up by proteases, they pass through the kidney, and can be seen with the naked eye after a urine test that produces a blue colour change. | |
| The researchers applied this technology to mice with colon cancer, and found that urine from tumour-bearing mice becomes bright blue, relative to test samples taken from healthy mice. | |
| Professor Stevens, of Imperial’s Departments of Materials and Bioengineering, said: “By taking advantage of this chemical reaction that produces a colour change, this test can be administered without the need for expensive and hard-to-use lab instruments. | |
| “The simple readout could potentially be captured by a smartphone picture and transmitted to remote caregivers to connect patients to treatment.” |
Image Credit: Imperial College London
News This Week
AI matches doctors in mapping lung tumors for radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, precision can save lives. Oncologists must carefully map the size and location of a tumor before delivering high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. But this process, called [...]
Scientists Finally “See” Key Protein That Controls Inflammation
Researchers used advanced microscopy to uncover important protein structures. For the first time, two important protein structures in the human body are being visualized, thanks in part to cutting-edge technology at the University of [...]
AI tool detects 9 types of dementia from a single brain scan
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool that helps clinicians identify brain activity patterns linked to nine types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, using a single, widely available scan—a transformative [...]
Is plastic packaging putting more than just food on your plate?
New research reveals that common food packaging and utensils can shed microscopic plastics into our food, prompting urgent calls for stricter testing and updated regulations to protect public health. Beyond microplastics: The analysis intentionally [...]
Aging Spreads Through the Bloodstream
Summary: New research reveals that aging isn’t just a local cellular process—it can spread throughout the body via the bloodstream. A redox-sensitive protein called ReHMGB1, secreted by senescent cells, was found to trigger aging features [...]
AI and nanomedicine find rare biomarkers for prostrate cancer and atherosclerosis
Imagine a stadium packed with 75,000 fans, all wearing green and white jerseys—except one person in a solid green shirt. Finding that person would be tough. That's how hard it is for scientists to [...]
Are Pesticides Breeding the Next Pandemic? Experts Warn of Fungal Superbugs
Fungicides used in agriculture have been linked to an increase in resistance to antifungal drugs in both humans and animals. Fungal infections are on the rise, and two UC Davis infectious disease experts, Dr. George Thompson [...]
Scientists Crack the 500-Million-Year-Old Code That Controls Your Immune System
A collaborative team from Penn Medicine and Penn Engineering has uncovered the mathematical principles behind a 500-million-year-old protein network that determines whether foreign materials are recognized as friend or foe. How does your body [...]
Team discovers how tiny parts of cells stay organized, new insights for blocking cancer growth
A team of international researchers led by scientists at City of Hope provides the most thorough account yet of an elusive target for cancer treatment. Published in Science Advances, the study suggests a complex signaling [...]
Nanomaterials in Ophthalmology: A Review
Eye diseases are becoming more common. In 2020, over 250 million people had mild vision problems, and 295 million experienced moderate to severe ocular conditions. In response, researchers are turning to nanotechnology and nanomaterials—tools that are transforming [...]
Natural Plant Extract Removes up to 90% of Microplastics From Water
Researchers found that natural polymers derived from okra and fenugreek are highly effective at removing microplastics from water. The same sticky substances that make okra slimy and give fenugreek its gel-like texture could help [...]
Instant coffee may damage your eyes, genetic study finds
A new genetic study shows that just one extra cup of instant coffee a day could significantly increase your risk of developing dry AMD, shedding fresh light on how our daily beverage choices may [...]
Nanoneedle patch offers painless alternative to traditional cancer biopsies
A patch containing tens of millions of microscopic nanoneedles could soon replace traditional biopsies, scientists have found. The patch offers a painless and less invasive alternative for millions of patients worldwide who undergo biopsies [...]
Small antibodies provide broad protection against SARS coronaviruses
Scientists have discovered a unique class of small antibodies that are strongly protective against a wide range of SARS coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-1 and numerous early and recent SARS-CoV-2 variants. The unique antibodies target an [...]
Controlling This One Molecule Could Halt Alzheimer’s in Its Tracks
New research identifies the immune molecule STING as a driver of brain damage in Alzheimer’s. A new approach to Alzheimer’s disease has led to an exciting discovery that could help stop the devastating cognitive decline [...]
Cyborg tadpoles are helping us learn how brain development starts
How does our brain, which is capable of generating complex thoughts, actions and even self-reflection, grow out of essentially nothing? An experiment in tadpoles, in which an electronic implant was incorporated into a precursor [...]