Researchers at UC San Diego have utilized advanced imaging techniques to explore the metabolic processes behind Alzheimer's disease, leading to potential new strategies for treatment.
Alzheimer's disease, the most common type of dementia, significantly impairs memory, thinking, and behavior, affecting over 50 million people globally each year. Projections suggest that this number will triple by 2050.
Using their own state-of-the-art imaging technologies, scientists at the University of California San Diego have now revealed how the metabolism of lipids, a class of molecule that includes fats, oils, and many hormones, is changed in Alzheimer's disease. They also revealed a new strategy to target this metabolic system with new and existing drugs. The findings are published in Cell Metabolism.
"Lipids have been associated with Alzheimer's for as long as we've known about the disease," said senior and co-corresponding author Xu Chen, Ph.D., an assistant professor in the Department of Neurosciences at UC San Diego School of Medicine, referring to the original 1907 report by Alois Alzheimer that described the unusual presence of fat deposits in the brain of the first person to be diagnosed with the disease. "So much of the emphasis since then has been placed on tau and other proteins that the research community has, until the last decade or so, largely overlooked this important aspect of the disease."
Innovative Imaging Techniques
"Driven by a keen interest in lipid droplet functions in aging and disease, we initiated this fruitful collaboration to harness cutting-edge SRS technology for studying lipid metabolism in tauopathy mouse brains." Said Yajuan Li, M.D., Ph.D., a postdoctoral researcher in the Shu Chien-Gene Lay Department of Bioengineering at UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering. SRS imaging is an approach that analyzes the way molecules in a sample interact with laser light.
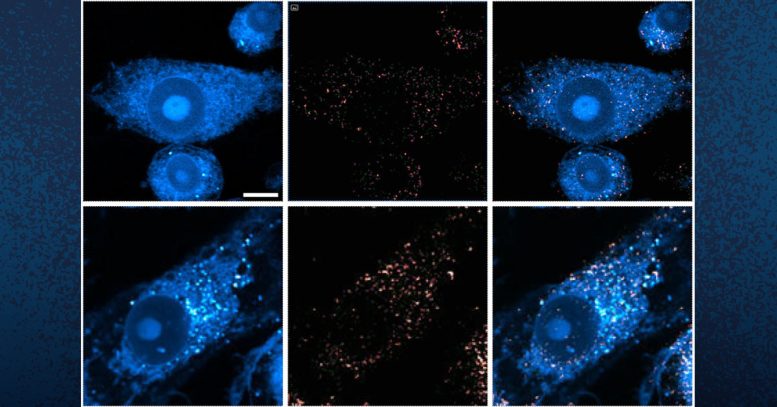
These images show microglia containing lipid droplets (white spots). Researchers at UC San Diego have revealed that in brains with Alzheimer's and related diseases, neurons offload excess lipid droplets to microglia, which triggers further inflammation. Credit: UC San Diego Health Sciences
In the brain, lipids come in the form of tiny droplets that control a variety of processes, such as energy storage and cellular responses to stress. These processes are tightly regulated in typical brains, but in Alzheimer's or similar diseases, lipid droplet metabolism can malfunction. While scientists understand that there is a relationship between Alzheimer's and lipid metabolism, exactly how they influence one another has remained a mystery.
To answer this question, the team looked directly at lipid droplets in the brains of mice with excess tau protein. They used a state-of-the-art SRS imaging platform developed in Lingyan Shi's lab at the Jacobs School of Engineering. The platform makes it possible to take microscopic images of lipid droplets within cells without the use of chemical dyes, which can alter the delicate molecules and compromise the results.
Mechanisms and Implications
"Intriguingly, the inert lipid droplets observed in tauopathy brains exhibit similar behavior to those found in aging brains", said co-corresponding author Lingyan Shi, Ph.D., assistant professor of bioengineering at the Jacobs School. "We are now focusing on understanding the underlying mechanisms by combining SRS imaging with other utilizing multidisciplinary techniques. Our approach is biologically neutral, so we're able to observe what's happening in the brain at the molecular level with as little interference as possible."
Shi and her team, including Li, pioneered the new approach, which uses a specially modified version of water, called heavy water, as a metabolic probe.
"Instead of using a typical chemical dye to stain lipids, we use heavy water that is naturally participating in the metabolic activities we're interested in," added Shi. "This gives us a much clearer picture of how lipids are formed spatiotemporally, which would not be possible with other approaches. Our current focus is on comprehending the underlying mechanisms of these dynamic changes of lipid metabolism in the context of aging and diseases."
The researchers discovered that in brains with tauopathy, neurons accumulate excess lipids as a result of stress or damage. This influx forces neurons to offload the excess to immune cells in the brain, called microglia. These microglia then mount an inflammatory response that causes further stress to neurons, triggering a repeating and worsening cycle.
In addition to characterizing this process, they were also able to identify a critical enzyme, called adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) that orchestrates the cycle. According to the researchers, breaking this cycle could unlock new treatment options for Alzheimer's disease. Chen is particularly optimistic about the possibility of repurposing existing drugs that modify lipid metabolism.
"We don't think this is an incidental phenomenon," said Chen. "The evidence suggests that lipid metabolism is a driving mechanism for Alzheimer's disease. There are many drugs that target lipid metabolism in other body systems, such as in the liver, so we might be able to change this system quite dramatically using tools we already have."
Reference: "Microglial lipid droplet accumulation in tauopathy brain is regulated by neuronal AMPK" by Yajuan Li, Daniel Munoz-Mayorga, Yuhang Nie, Ningxin Kang, Yuren Tao, Jessica Lagerwall, Carla Pernaci, Genevieve Curtin, Nicole G. Coufal, Jerome Mertens, Lingyan Shi and Xu Chen, 23 April 2024, Cell Metabolism.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.03.014
This work was funded, in part, by the National Institutes of Health (grants R01AG074273, R01AG078185, 1R01GM149976-01, R01NS111039 R21NS125395) and by the startup fund from UC San Diego Department of Neurosciences and Jacob School of Engineering.
News
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]